State of the Industry Report: Best Practices & Industry Benchmarks for Optimizing ASC Operations

Online
Just keep scrolling down!
Click here to download your copy.
Video
Watch the authors break down 5 trends and 13 benchmarks.
eBook
Audiobook
Available for $0.99 on 30+ platforms, including Audible, Nook, and Libby. Email HST a PDF of your order confirmation within 7 days to claim your rebate.
What’s Inside the Report
We are in an era where data-driven decision-making is the only option, where the fine line between efficiency and efficacy becomes the key differentiator in patient outcomes and operational success. The report includes best practices, key process steps, key performance indicators, and benchmarking data for every step of the patient journey and every recurring administrative duty.
Introduction & Trends
Patient Journey: Pre-Day of Service
Patient Journey: Day of Service
Patient Journey: Post Day of Service
Regularly Recurring Operations: Daily/Weekly
Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly
Regularly Recurring Operations: Annual
Closing Message

Introduction
The surgery center industry continues to play a pivotal role in healthcare. ASCs deliver high-quality, cost-effective, patient-centered care in a reliable, safe environment – an environment proven to be preferred by doctors, patients, nurses, and payers.
As we move further into 2024, we continue to live in an era where precision operations, driven by data, is no longer just an advantage. It is a necessity. Leveraging data in every aspect of operations and focusing on meticulous and strategic decision-making is now essential for long-term success.
HST first introduced our State of the Industry Report in 2023, and its success underscored just how valuable data is to our readers. Building on that success, we are thrilled to present the 2024 edition, now even more comprehensive:
- 130+ KPIs
- 50 chapters
- 35+ charts
- 12 year-over-year comparisons
- 5 emerging trends
We hope you find this helpful, and please feel free to reach out if you have any questions.
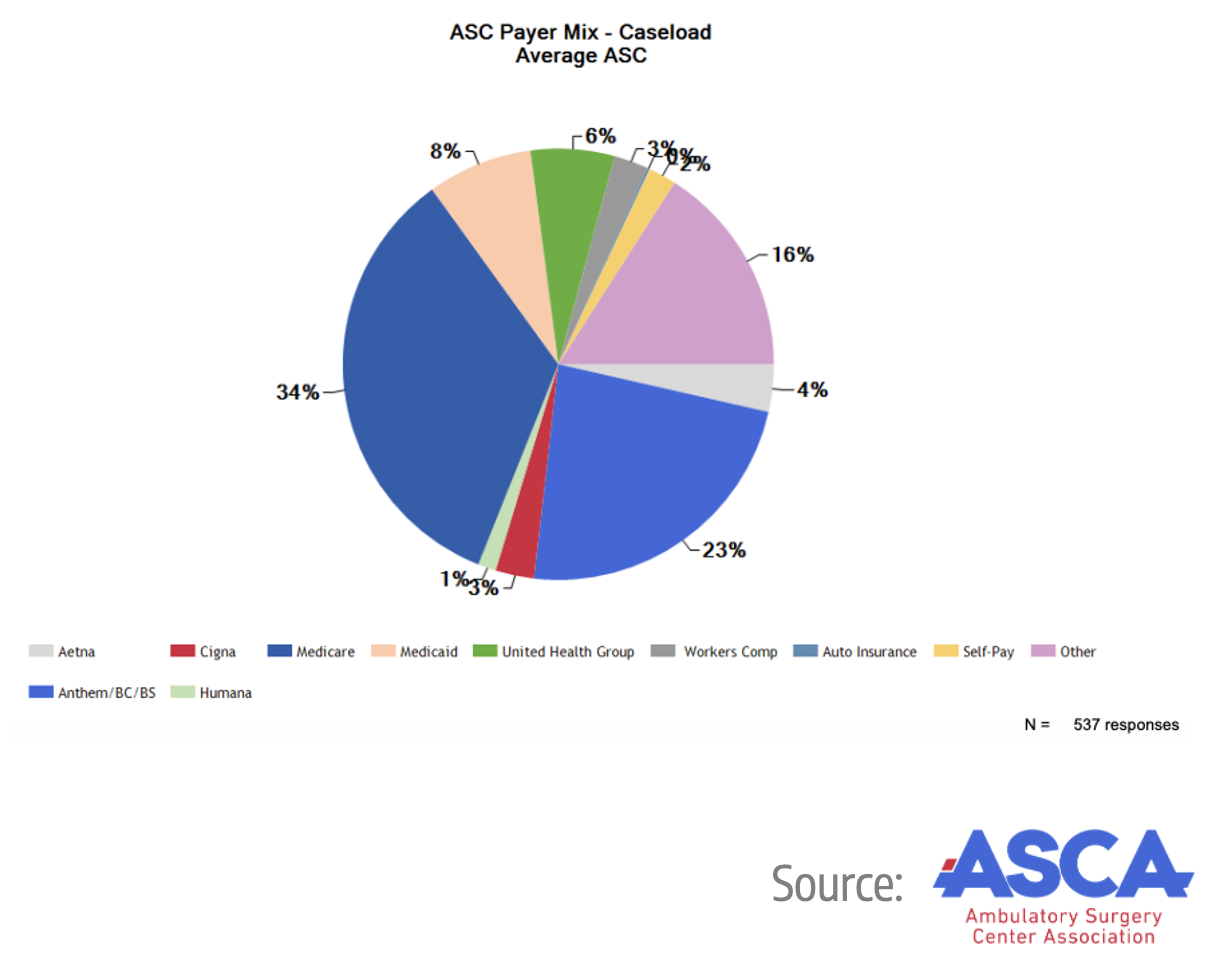
The insights presented in this report are drawn from an extensive dataset of 590 surgery centers across 47 states, representing nearly 3 million unique patient visits. These surgery centers are HST clients who have granted permission for their data to be used in this analysis, offering a comprehensive look into the trends and dynamics shaping the industry today. Below you’ll find a breakdown of ownership, OR count, and number of cases.

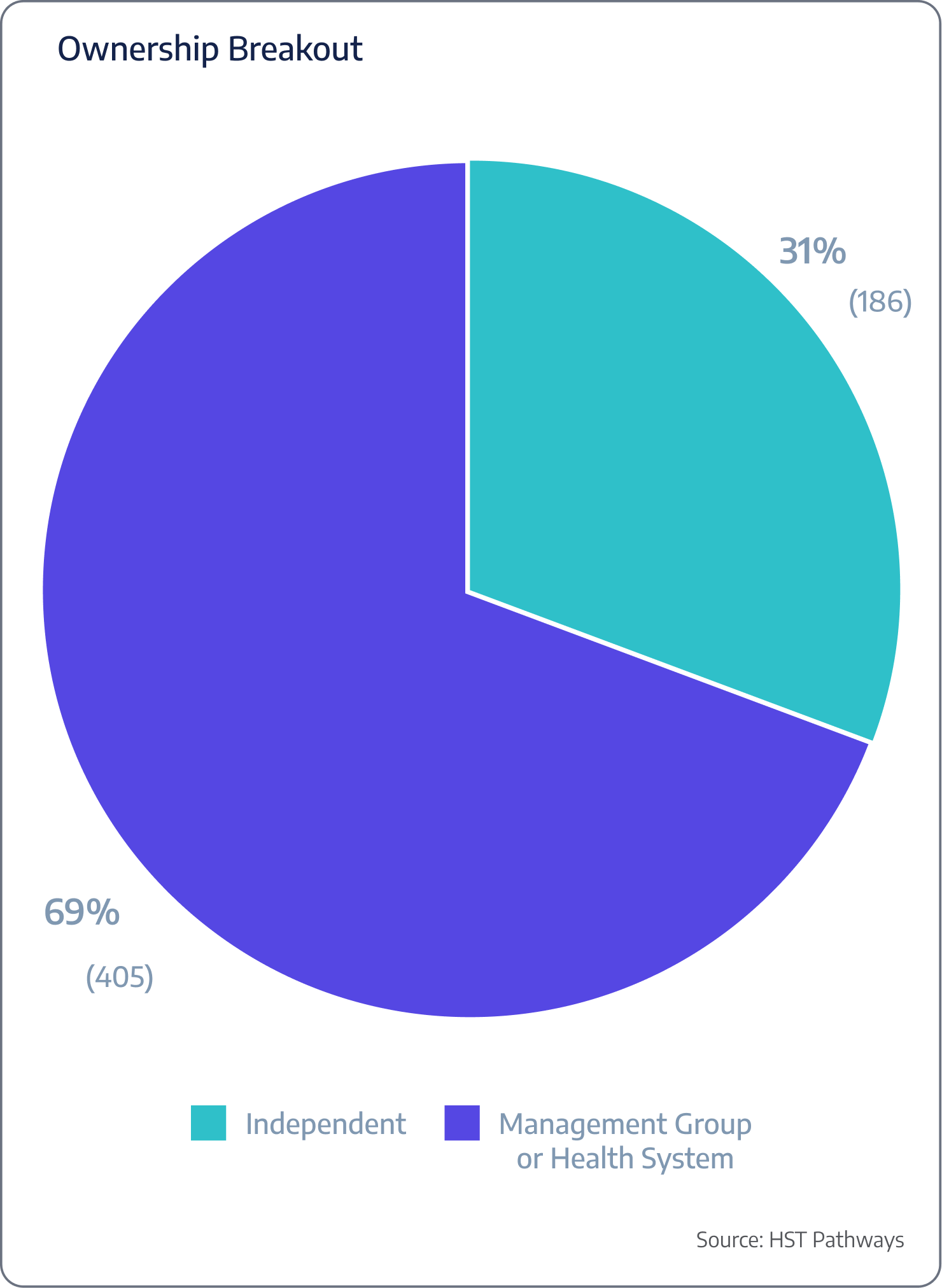
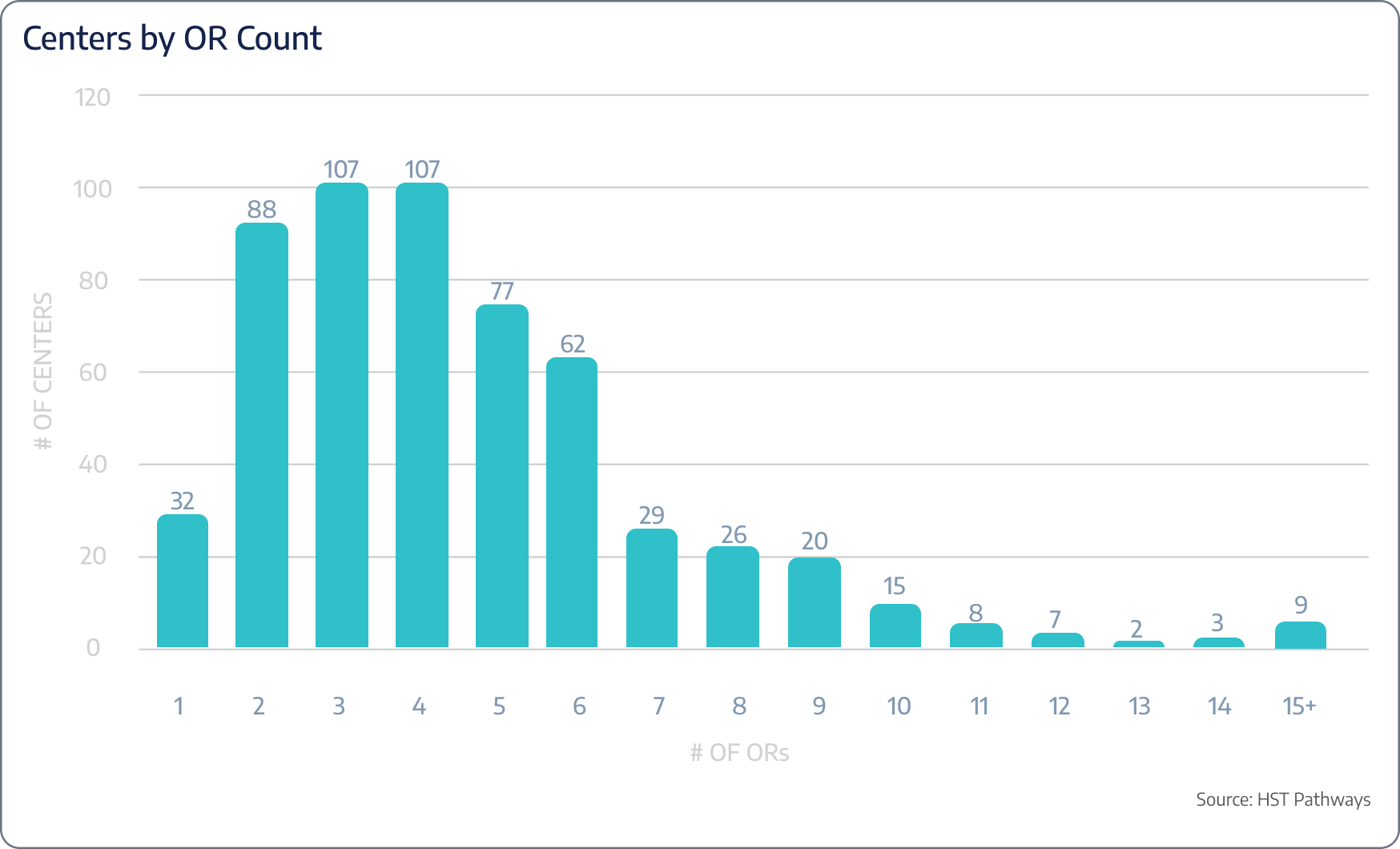
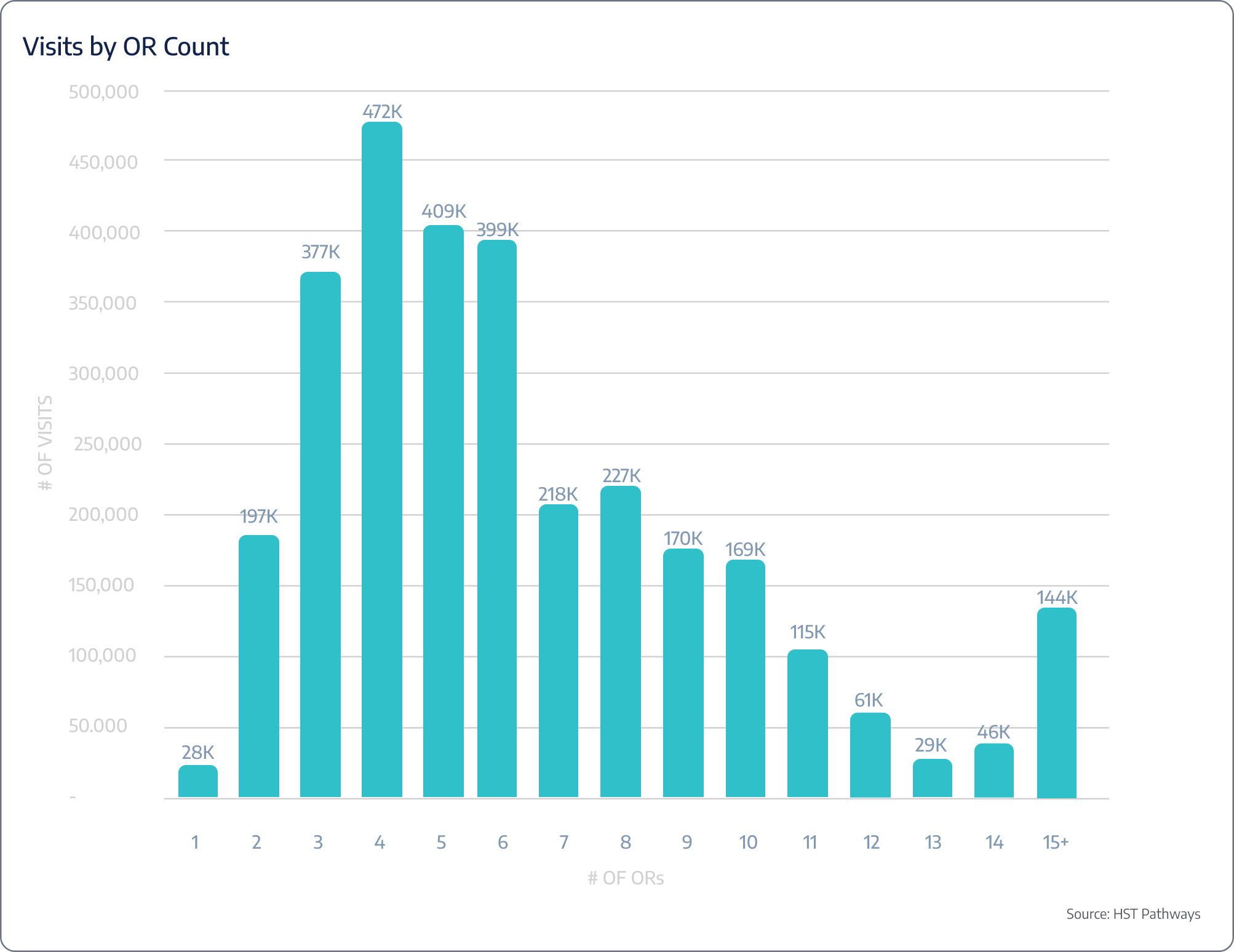
Emerging Trends to Know
Insight #1 – Cardiology: A Specialty on the Rise
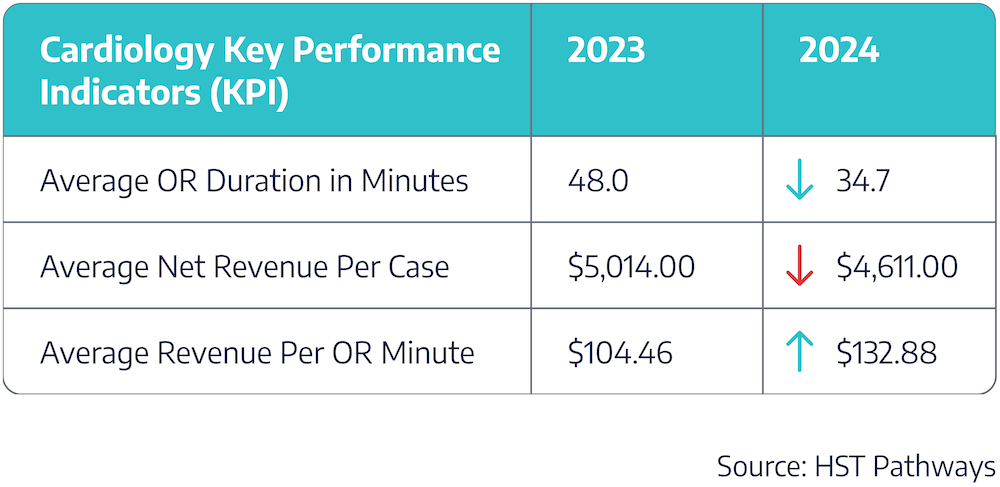
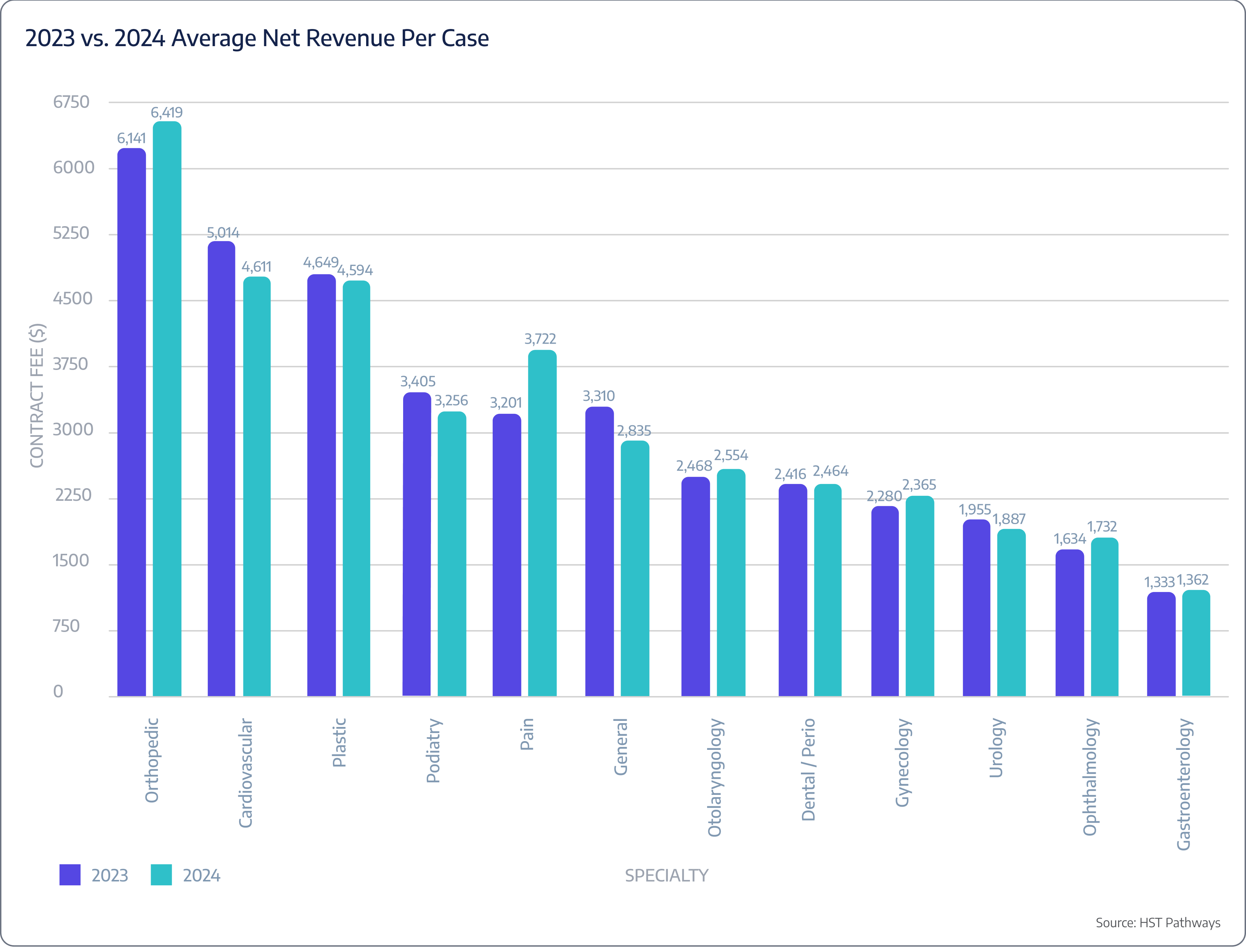
The cardiology trends in surgery centers between 2023 and 2024 reveal key shifts. Average OR duration dropped 28% from 48.0 to 34.7 minutes, indicating improved efficiency and faster procedures. However, this efficiency did not result in higher revenue per case, as the average net revenue per case declined 8% from $5,014 to $4,611. Notably, average revenue per OR minute surged from $104.46 to $132.88, demonstrating that despite shorter procedures and lower total revenue per case, the efficiency gains are translating into higher revenue generated per minute in the OR.
These changes matter because they highlight the balance between operational efficiency and financial performance. Influences such as payer reimbursement policies, shifts in case volume, and technological advancements may be impacting both procedure times and revenue outcomes.
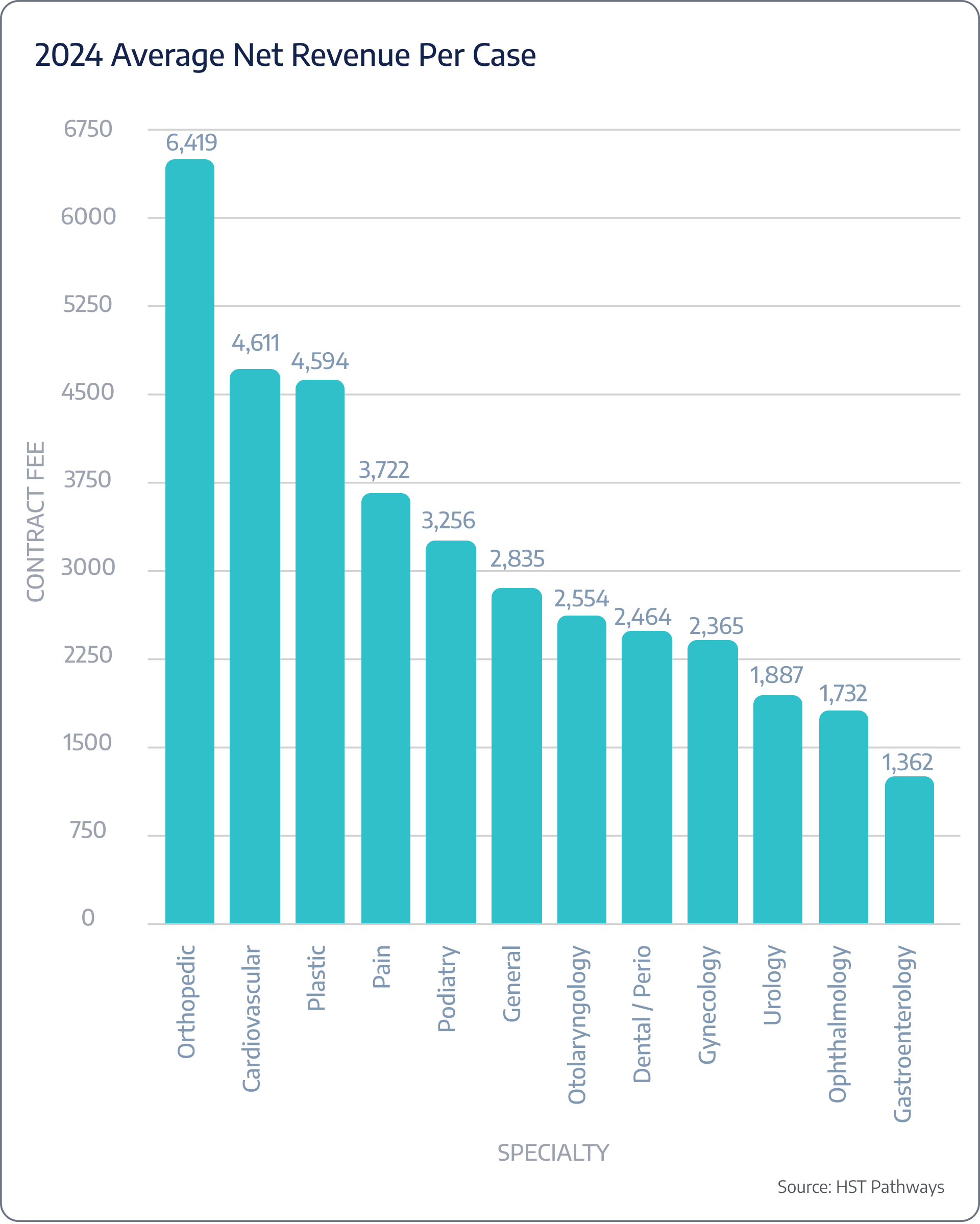
Insight #2 – Orthopedics Achieves 4.5% Growth in Net Revenue Per Case
Orthopedics continues to generate the highest net revenue per case in surgery centers, with an increase from $6,141 in 2023 to $6,419 in 2024. This growth reflects strong demand for orthopedic procedures and potentially higher reimbursement rates or a greater mix of complex cases. The consistent rise in revenue underscores orthopedics as a key specialty for surgery centers, contributing significantly to overall financial performance and profitability while highlighting the value of investing in orthopedic services.

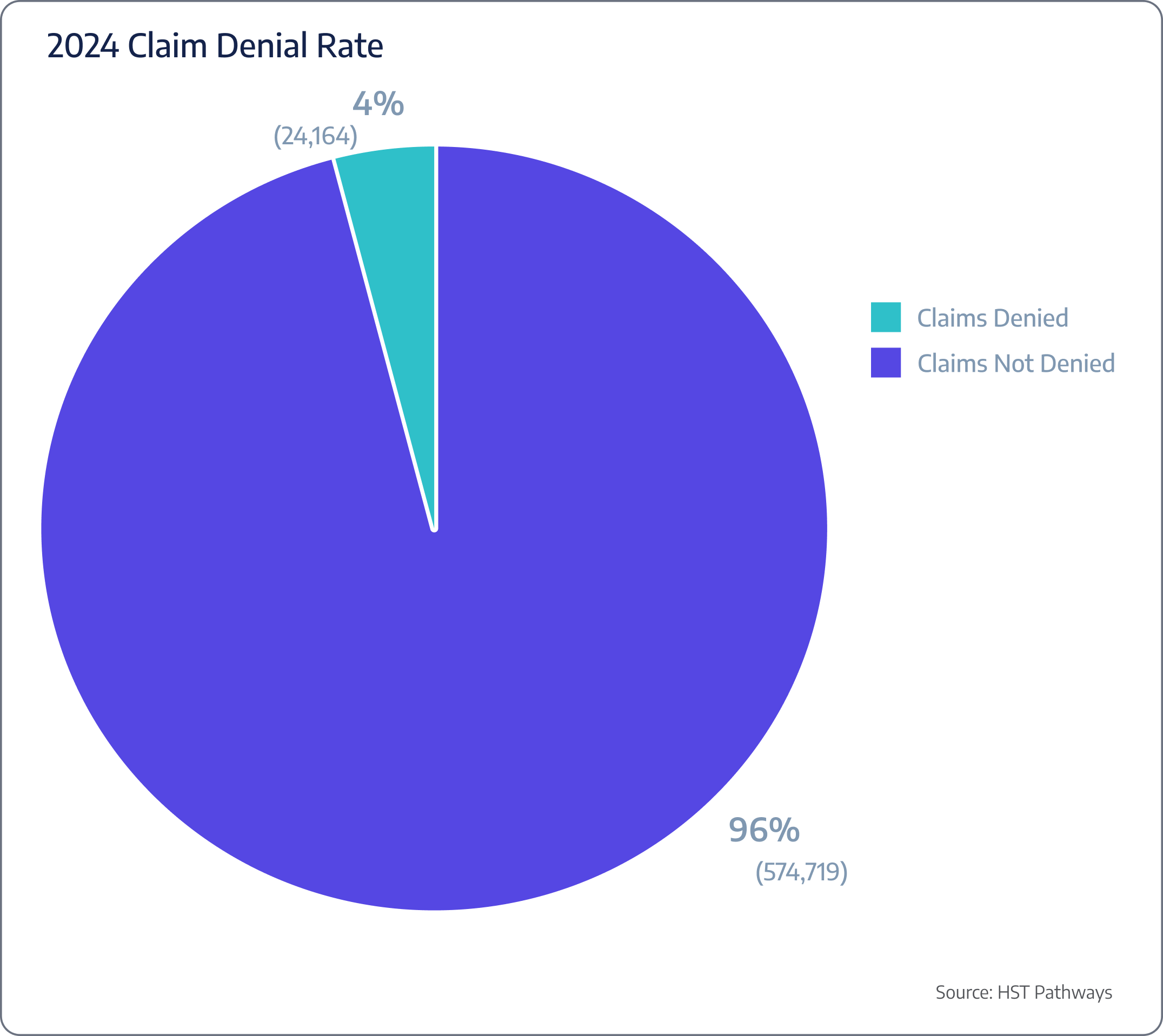
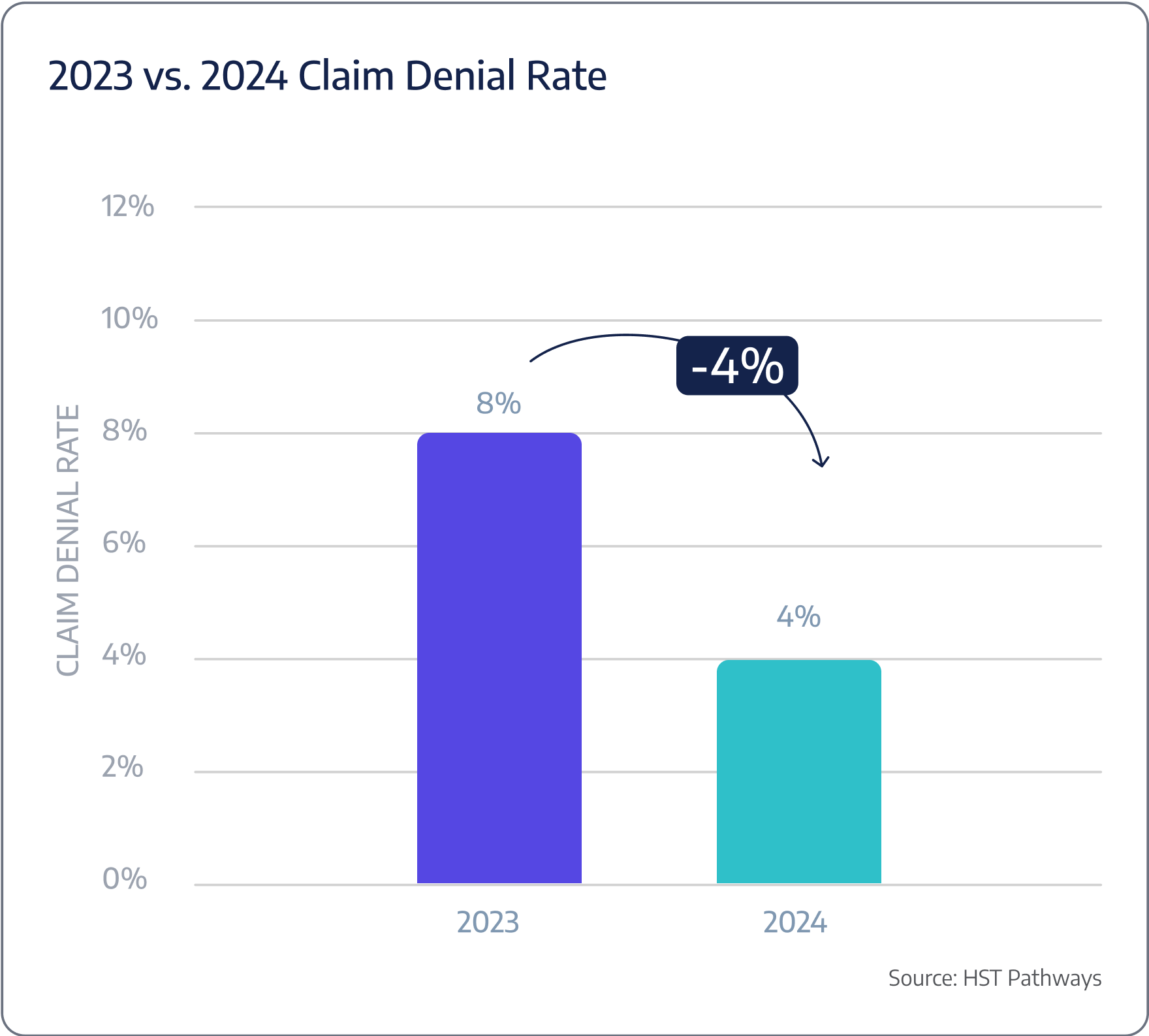
Insight #3 – Claim Denial Rates Notably Improved
Between 2023 and 2024, surgery centers saw a significant improvement in claim denial rates, dropping from 8% to just 4%. This trend indicates more effective revenue cycle management, possibly due to better documentation and improved coding practices, perhaps due to AI. Reducing denial rates by half allows surgery centers to capture more revenue and reduce the administrative burden of resubmitting claims, ultimately improving financial stability and operational efficiency. This progress points to a more streamlined and successful claims process.

Insight #4 – ASCs with Two ORs Saw the Highest YoY Growth
From 2023 to 2024, surgery centers with 2 operating rooms (ORs) saw the most significant year-over-year growth, increasing by 22%. This surge may indicate that smaller ASCs are becoming more efficient or are better positioned to adapt to market demands. In contrast, larger ASCs with 15+ ORs experienced an 8% decline, potentially due to operational complexities or challenges in scaling efficiently. These trends suggest a shifting dynamic in ASC performance, with smaller centers thriving while larger ones face headwinds.

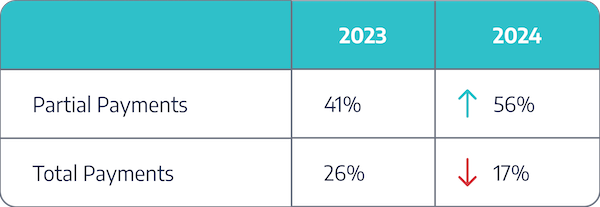
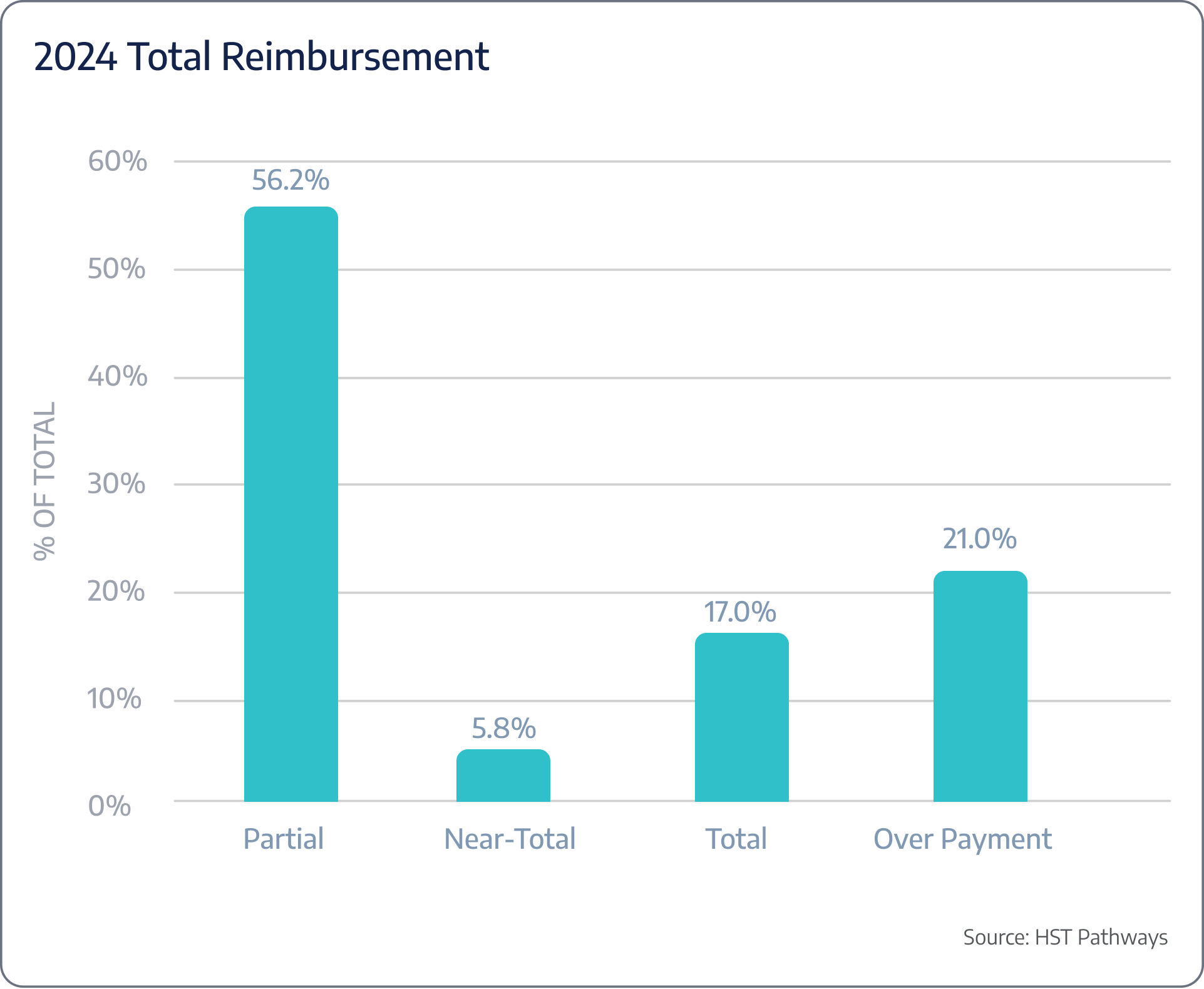
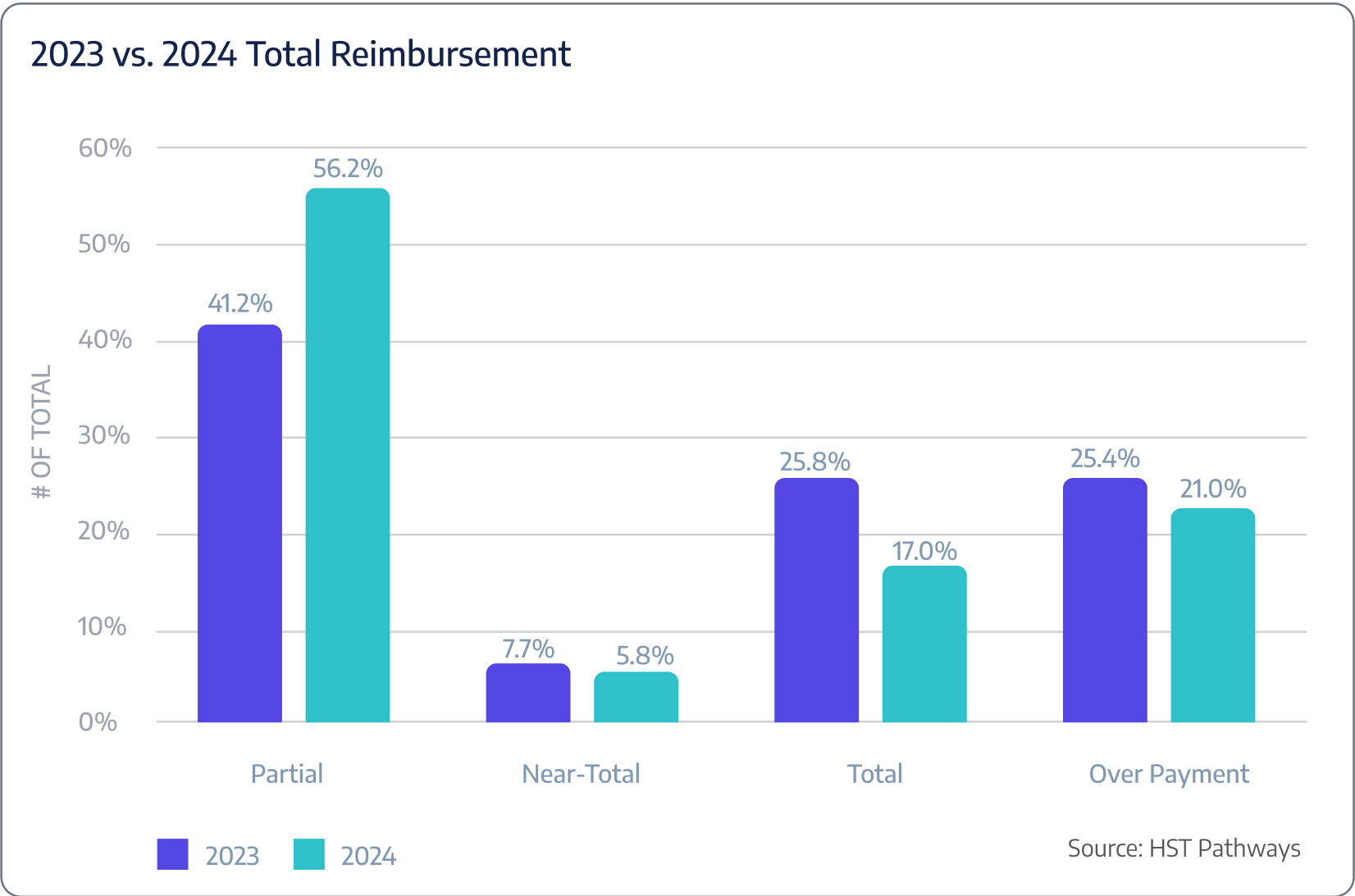
Insight #5 – Partial Payments Increased While Total Payments Decreased
Between 2023 and 2024, surgery centers experienced a significant shift in payment patterns. Partial payments increased from 41.2% to 56.2%, indicating that more patients are paying in installments and payers are reimbursing incomplete amounts. Meanwhile, total payments decreased from 25.8% to 17.0%, suggesting fewer patients are settling their bills in full.
This trend highlights a growing challenge for ASCs in collecting patient responsibility upfront, emphasizing the need for improved payment plans, financial assistance options, and strategies to boost collections. Collecting payments before the date of service (pre-DOS) is critical, with some ASCs going as far as implementing policies where surgeries are not performed unless the patient has paid in full beforehand. These strategies not only improve cash flow but also reduce the risk of outstanding balances post-procedure, providing a more secure financial framework for ASCs.
The graph below combines payments from both payers and patients.

Pre-Day of Service

01
Patient Begins to Research Surgery Center
02
Doctor’s Office Communicates with ASC to Schedule the Case
03
Doctor’s Office Verifies Insurance Eligibility and Prior Authorization
04
Manage Case Until Date of Service
05
Review Case for Profitability and Implants
06
Send Pre-Assessment Form to Patient
07
Generate & Send Patient Estimate to Patient Prior to Date-of-Service
08
Communicate Appointment Reminders & Pre-Op Instructions via Text
09
Pull Supplies from Supply Room the Day Before


Patient Journey: Pre-Day of Service
1. Patient Begins to Research Surgery Center
Best Practices
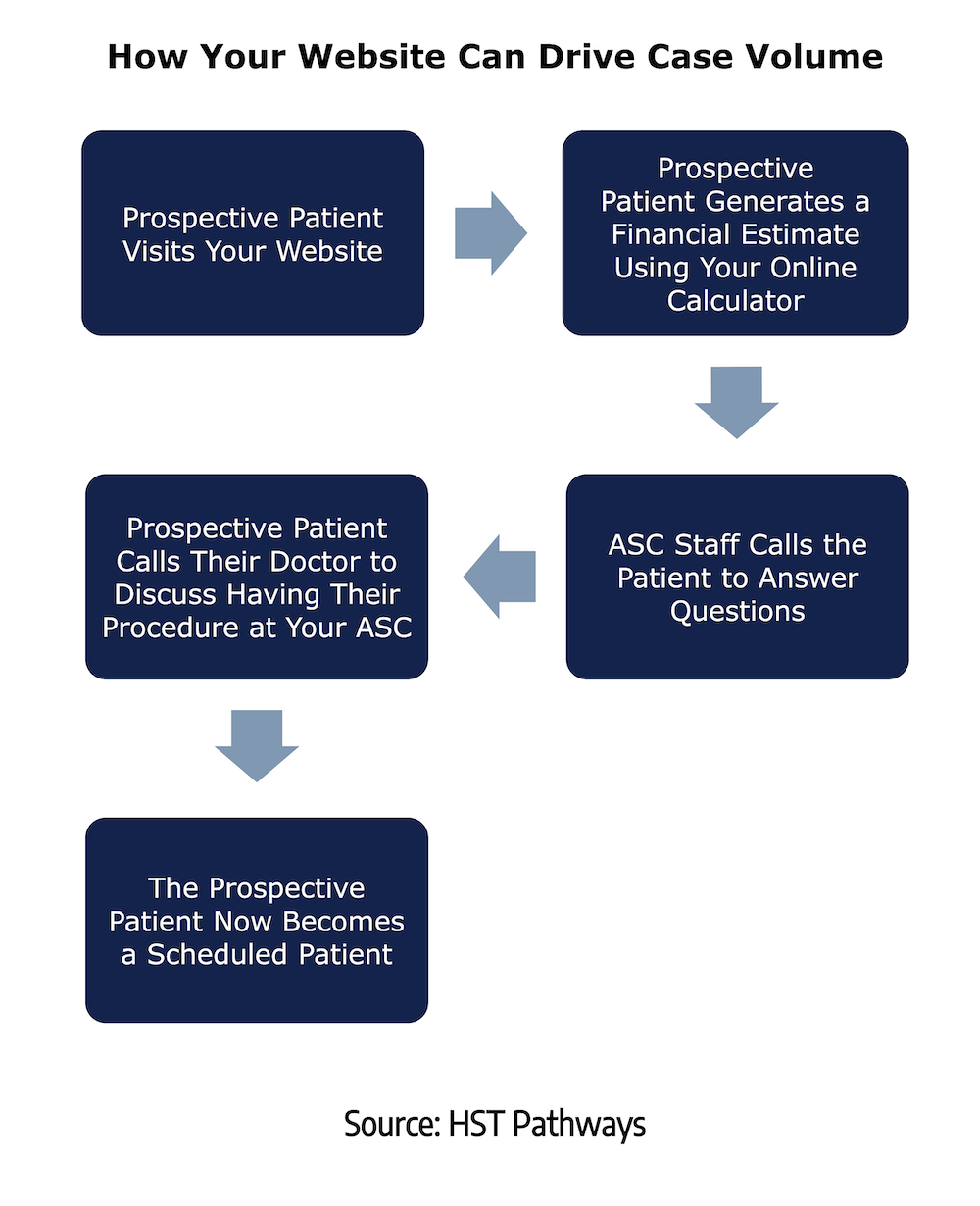
When a patient learns they will need surgery, a million questions start racing through their mind. To get answers to those questions, they will begin researching – both online and offline – about the surgery center and what they can expect. To put their mind at ease and start their experience with you off on the right foot, they need to be able to find answers to all their questions on your website.
A website that is built correctly will cover the spectrum of the most common patient questions: How much will my procedure cost? What is the parking situation? Will my family be able to stay? How can I fill out the necessary paperwork? And so on. Your website should also allow patients to generate a financial estimate to see exactly what they will owe without proactively contacting you or, even worse, waiting for you to call them.
Covering these topics on your website will build patient trust, reduce redundant patient phone calls, and improve the overall patient experience.
Key Process Steps
Research and find a trustworthy, experienced third-party consultant or agency to guide you through the process.
Together, perform a comprehensive audit of your existing website to identify your shortcomings (design, copy, imagery, etc.) and what changes you can make to improve the patient experience.
During the process, make sure to focus on a patient-centric design that caters to your patients and their family’s experience.
Identify opportunities for interaction: price transparency calculators, informational videos on what to expect, driving and parking directions, pre-assessment forms, and more.
Optimize your website for performance, keeping in mind the mobile experience, as most patients will visit your website on their phones.
Test out your new website & launch.
Key Performance Indicators
Monthly website visitors
Website traffic referral sources
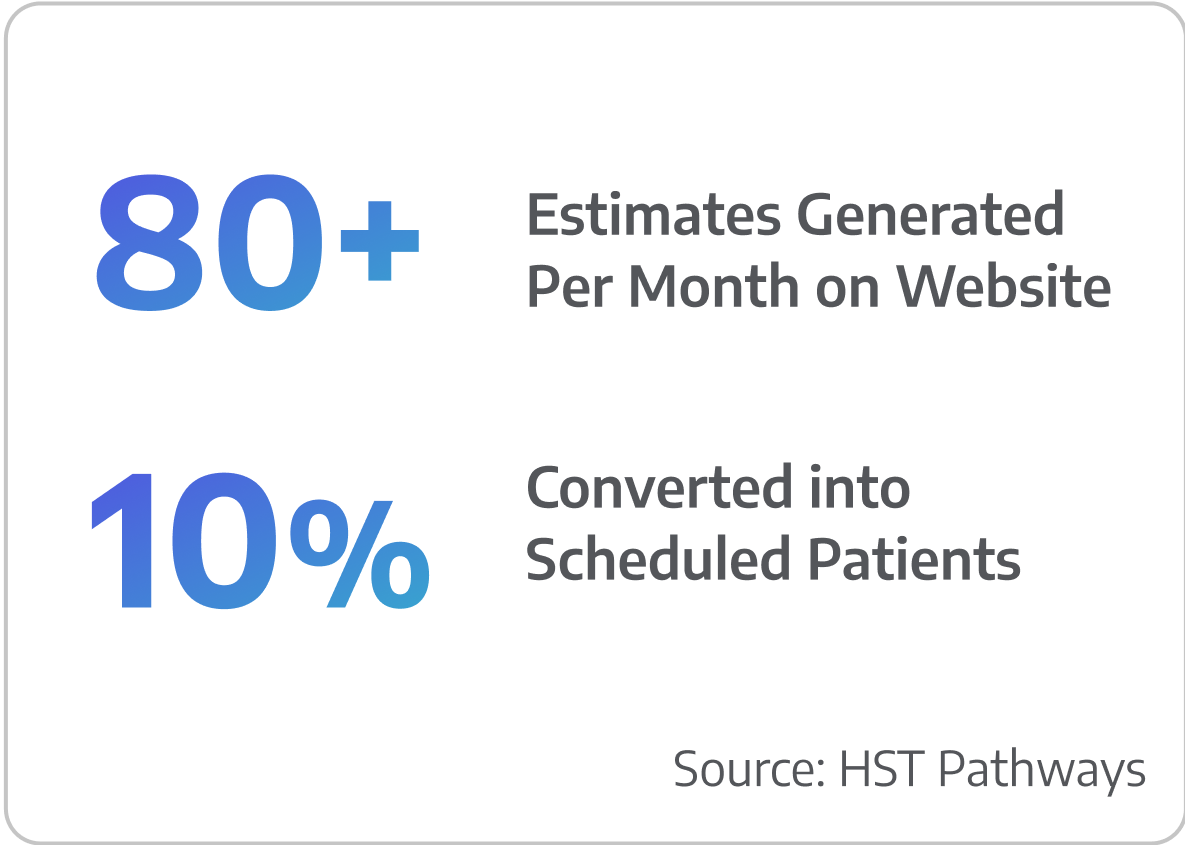
Monthly page views of your price transparency calculator
% of patients who scheduled surgery after generating a financial estimate
Benchmarking Data
Here’s how an online calculator directly translated into increased case volume and revenue for a four OR, multi-specialty facility in Greenville, SC.


Patient Journey: Pre-Day of Service
2. Doctor’s Office Communicates with ASC to Schedule the Case
Best Practices
The more harmonious and seamless communication is between the doctor’s office and the surgery center, the easier it will be to drive case volume effectively. As a best practice, you do not want to communicate with a doctor’s office via phone or fax. These antiquated workflows consume precious staff time, typically end with phone tag, and cause countless hurdles.
Alternatively, your surgery center should use technology that allows you to broadcast your OR availability to all your physician offices. Providing your partners with 24/7 access to your OR availability will simplify the process for them to electronically submit a request for a specific operating room on a particular date and time. Your team can then review the request and either confirm or provide a suggestion.
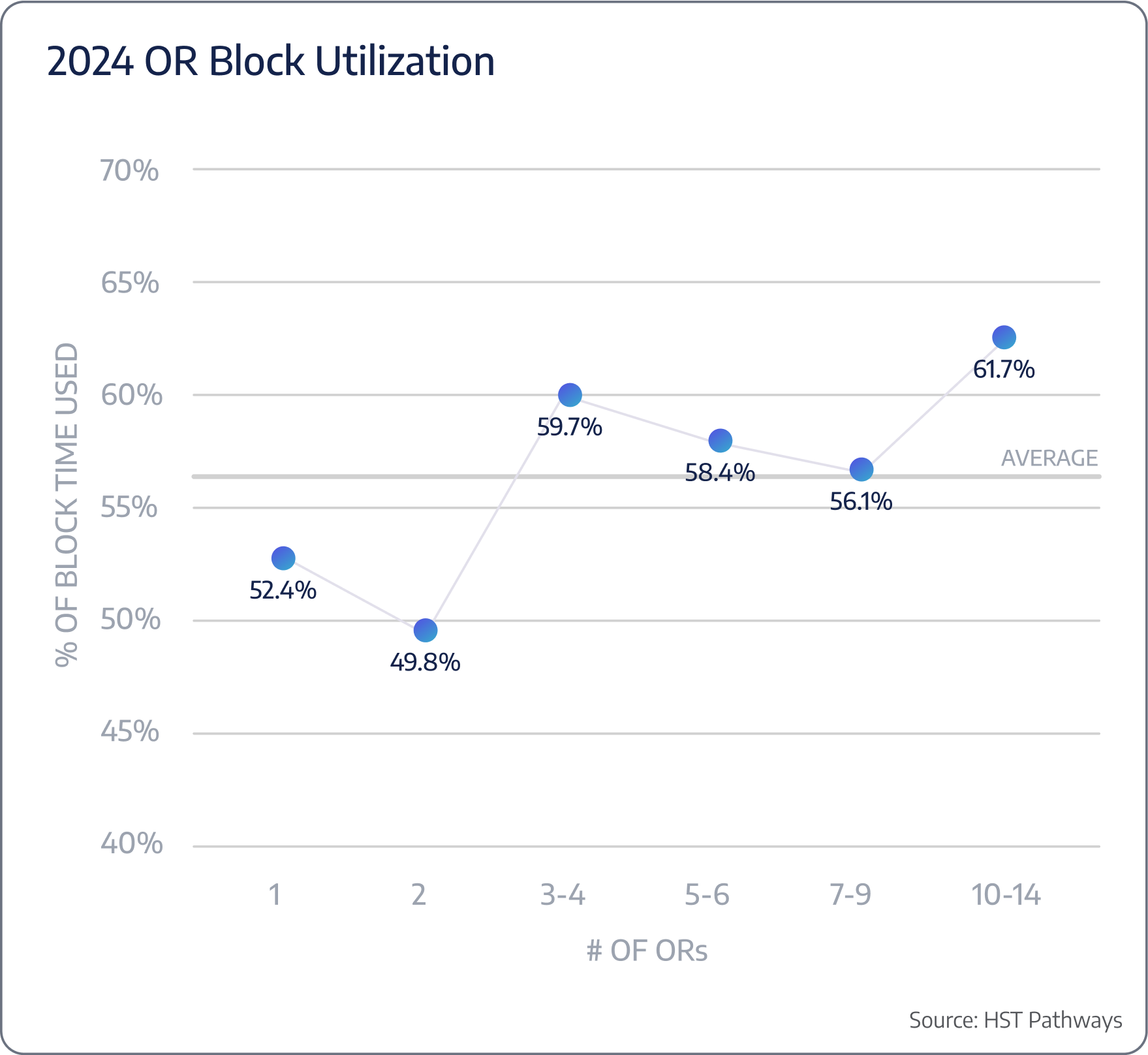
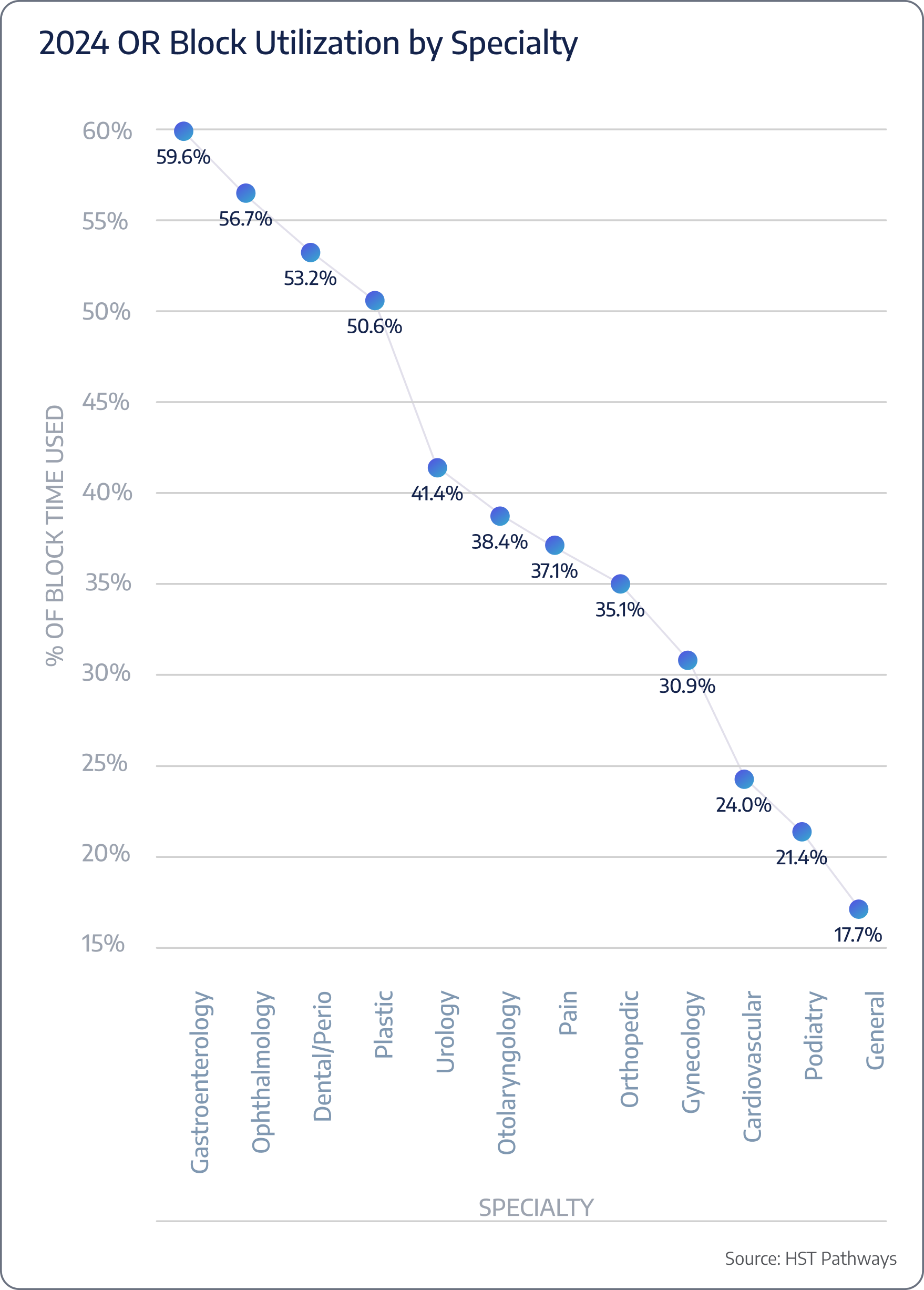
To improve OR usage, specifically block time usage, ASCs should remind physicians and their schedulers to release unused block times through automated emails, require unused block times to be released at least 72 hours in advance, and publicly recognize those who efficiently use their allocated block times, striving for 70% usage.
Key Process Steps
The doctor’s office submits a request online for a specific date & time.
The surgery center receives an alert that a request has been made.
The surgery center reviews the request and confirms or suggests a change if necessary.
Key Performance Indicators
Time spent scheduling per case
OR utilization per physician
OR downtime
Benchmarking Data
On average, 44% of scheduled OR time is unused.


Patient Journey: Pre-Day of Service
3. Doctor’s Office Verifies Insurance Eligibility and Prior Authorization
Best Practices
Verifying insurance eligibility and obtaining prior authorization are critical steps in ensuring seamless patient care and preventing potential financial issues.
The doctor’s office should verify insurance eligibility first to confirm whether the patient’s insurance is active and covers the proposed procedure. Even after the doctor’s office completes this crucial step, your surgery center needs to re-run verification at least twice – the first time should be immediately after accepting the case, and the second time should be the morning of the procedure. You should also get into the routine of re-running verification on the first of the month for the current month’s cases to ensure coverage has not lapsed. Integrated payer technology must be used to verify coverage so that team members do not spend unnecessary hours on the phone with payers.
Insurance companies often require prior authorization for certain medical procedures. Obtaining prior authorization prevents denials and delays in reimbursement and ensures that the insurance company has approved coverage before the patient undergoes treatment. Your surgery center must verify any prior authorization obtained by the doctor’s office so you can mitigate the risk of performing a procedure that you will not be reimbursed for.
Key Process Steps
The doctor’s office verifies insurance eligibility.
The doctor’s office obtains the necessary prior authorization (if applicable).
The doctor’s office communicates insurance verification & prior authorization to the surgery center via software integration.
The surgery center re-runs insurance eligibility upon receipt and contacts the payer to obtain their own prior authorization.
The surgery center re-runs insurance eligibility the morning of the procedure to ensure the patient’s insurance has not lapsed.
Key Performance Indicators
Time spent per verification
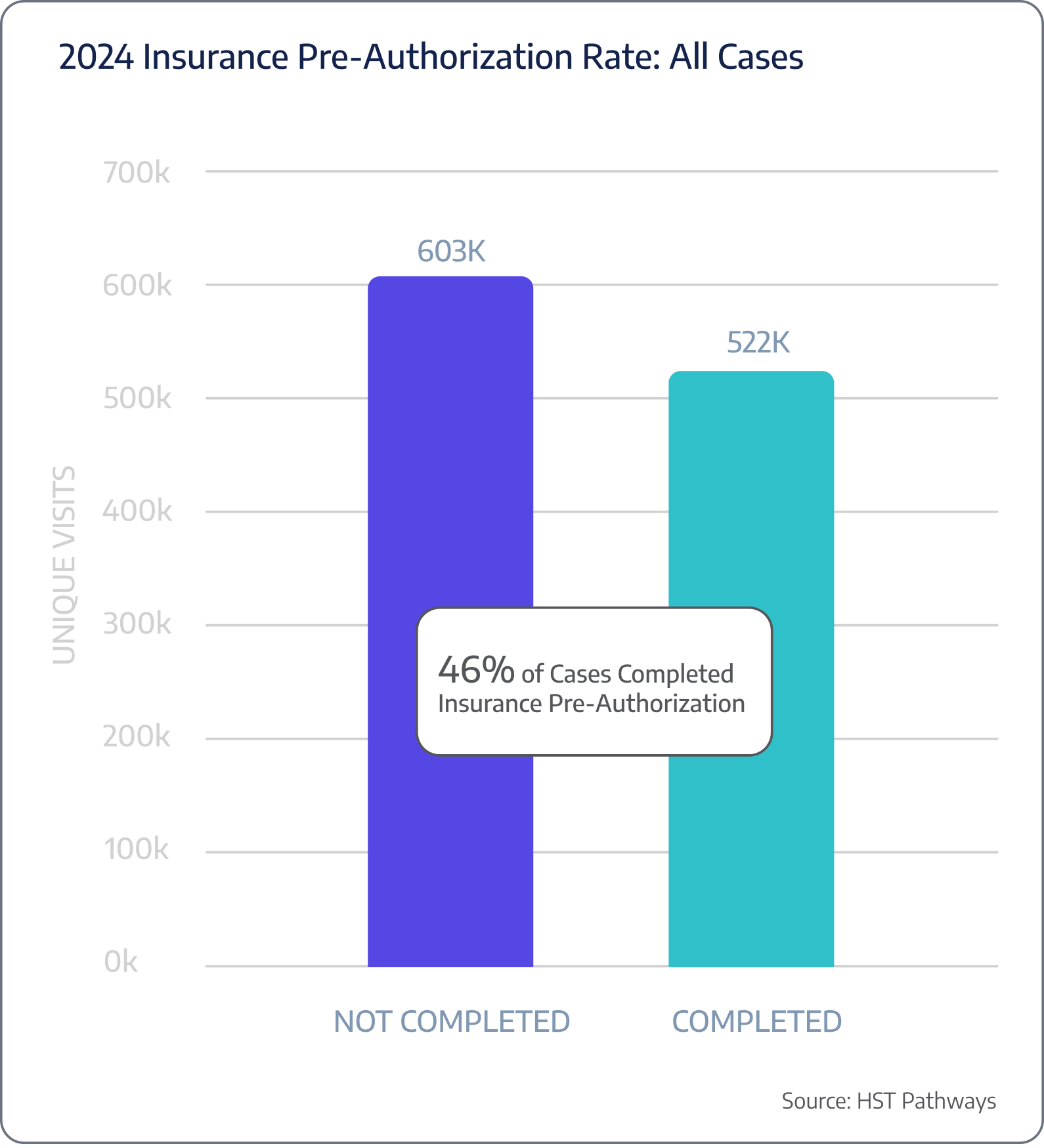
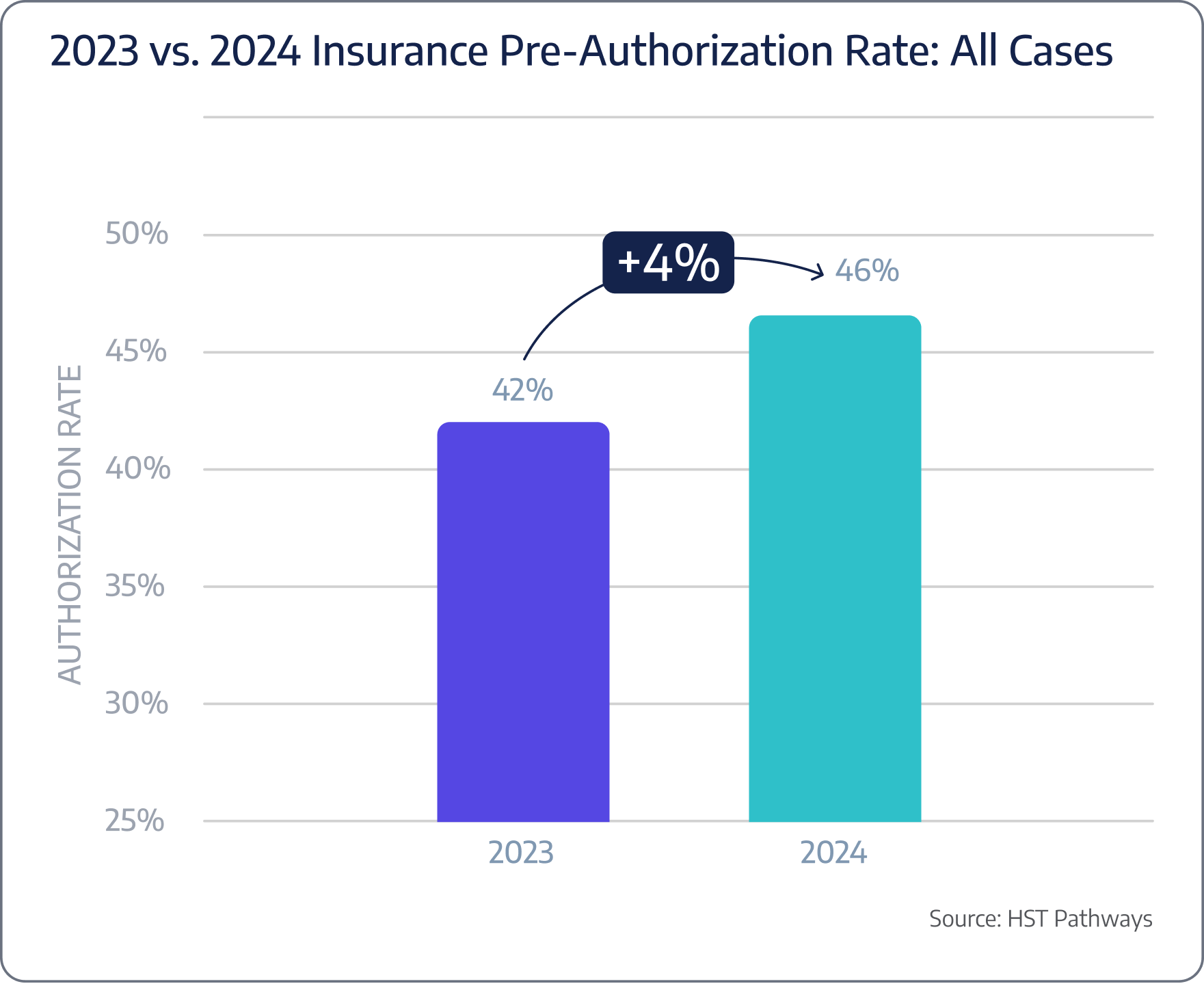
Pre-authorization rate
# of procedures that required pre-authorization but it was not obtained
Benchmarking Data
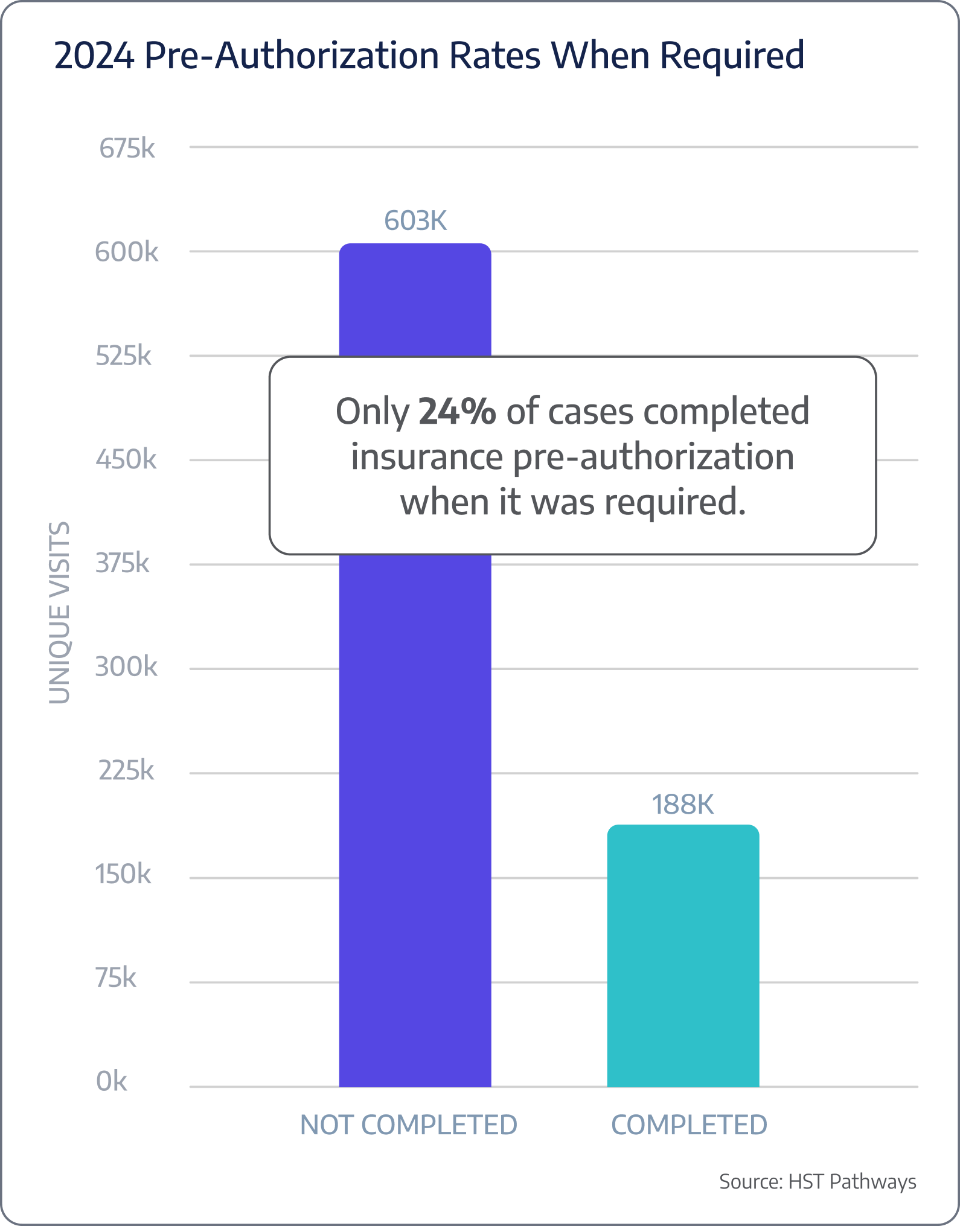
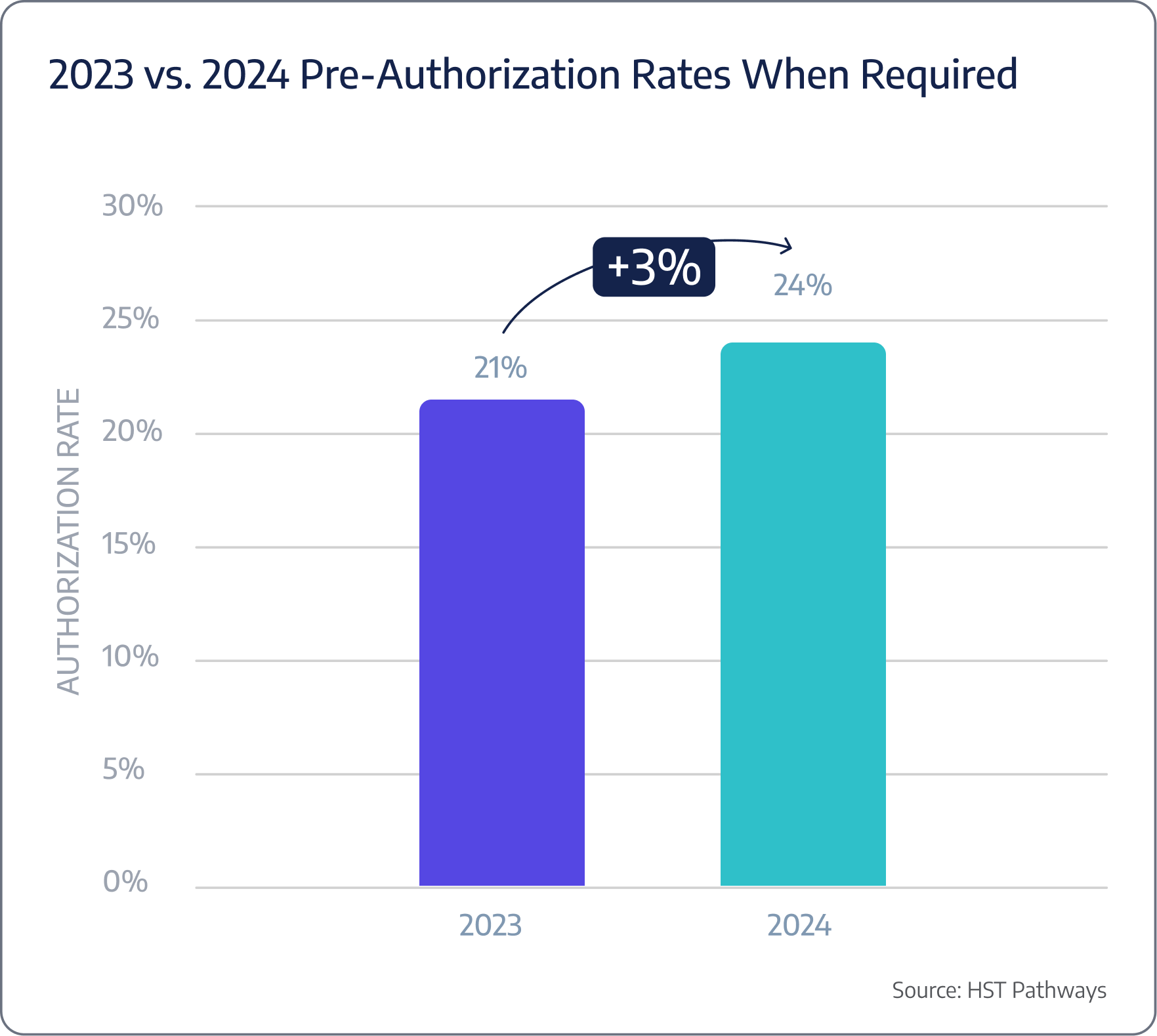
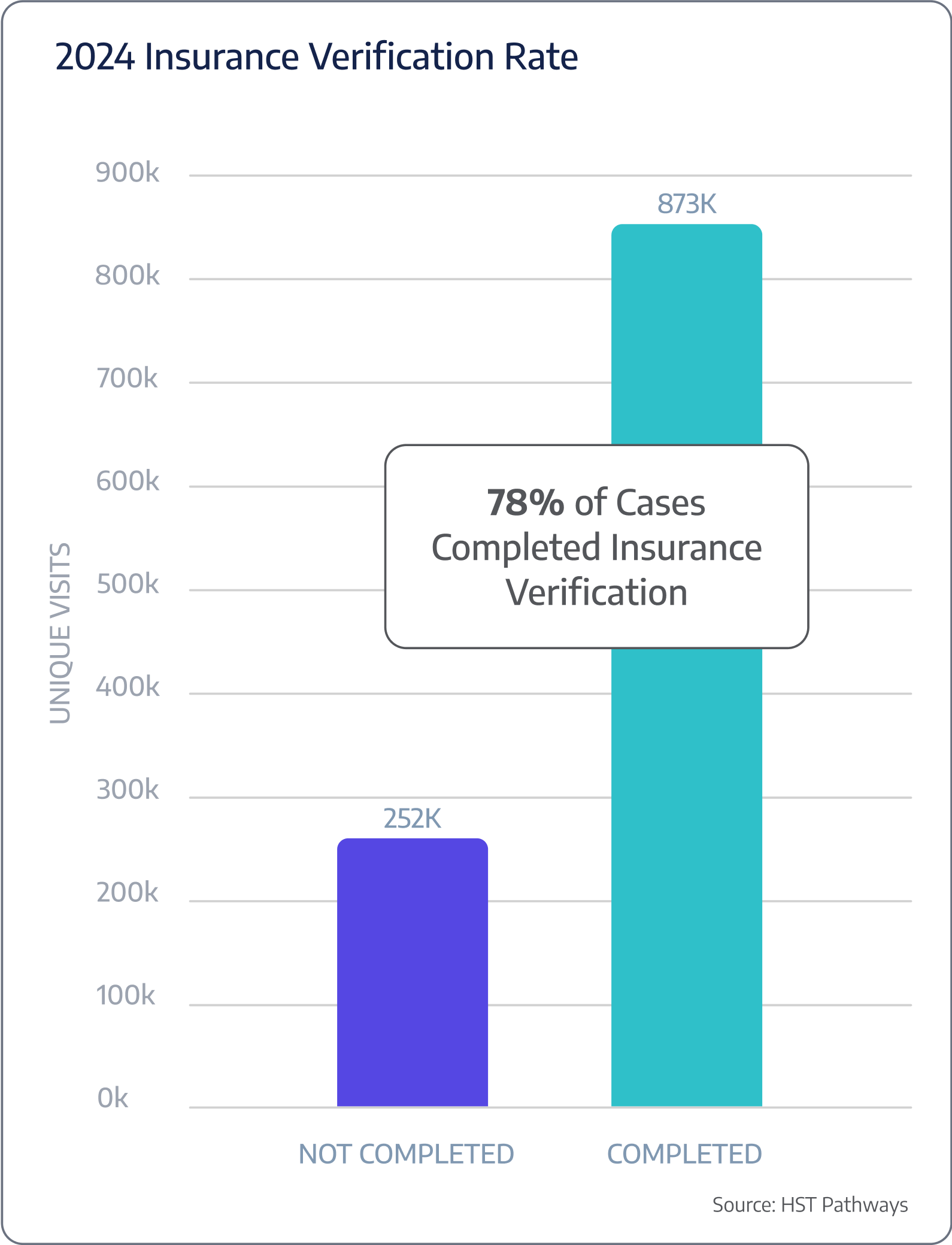
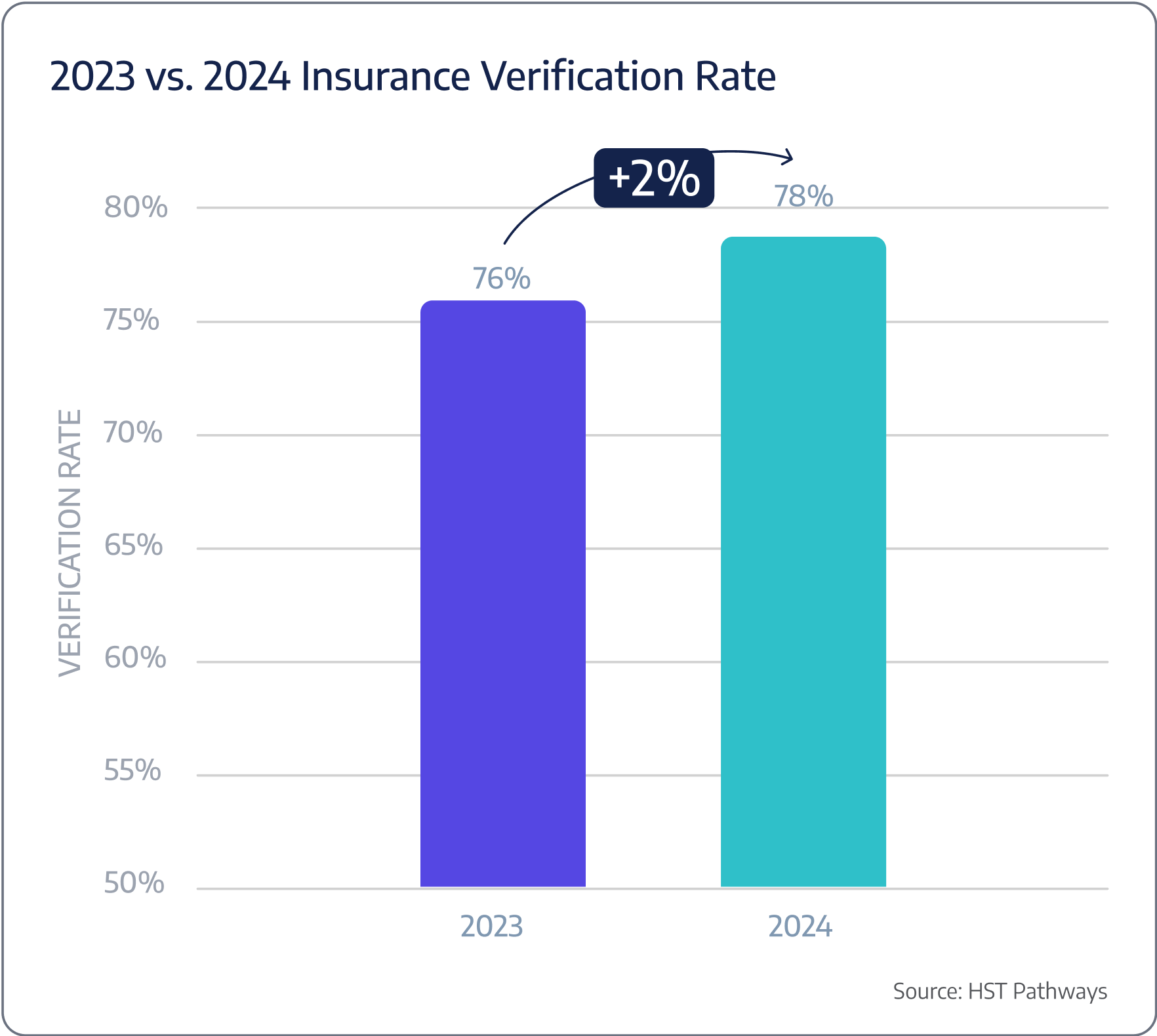


Patient Journey: Pre-Day of Service
4. Manage Case Until Date of Service
Best Practices
After a case is scheduled, it’s important to maintain contact with the patient, physician, and vendors to ensure the case stays on track. In the rare instance the case needs to be canceled or rescheduled, you can reach that conclusion with as much lead time as possible.
The key to seamlessly managing a case is centralized management. Using technology, you can oversee each surgical case from start to finish in one location accessible by the entire care team. Your front office staff, surgeon, anesthesia group, supply coordinator, and other vendors should all have access to this centralized location so they can provide updates, discuss any special requirements, share patient considerations, and ultimately prevent last-minute cancellations and potential delays.
Proactive and effective patient communication will also help ensure the cancellation or rescheduling is not initiated from the patient’s side.
Key Process Steps
Create case in centralized case management location
Provide access to the case to the entire care team (internal staff and external vendors)
Share pertinent updates leading up to the date of service
Key Performance Indicators
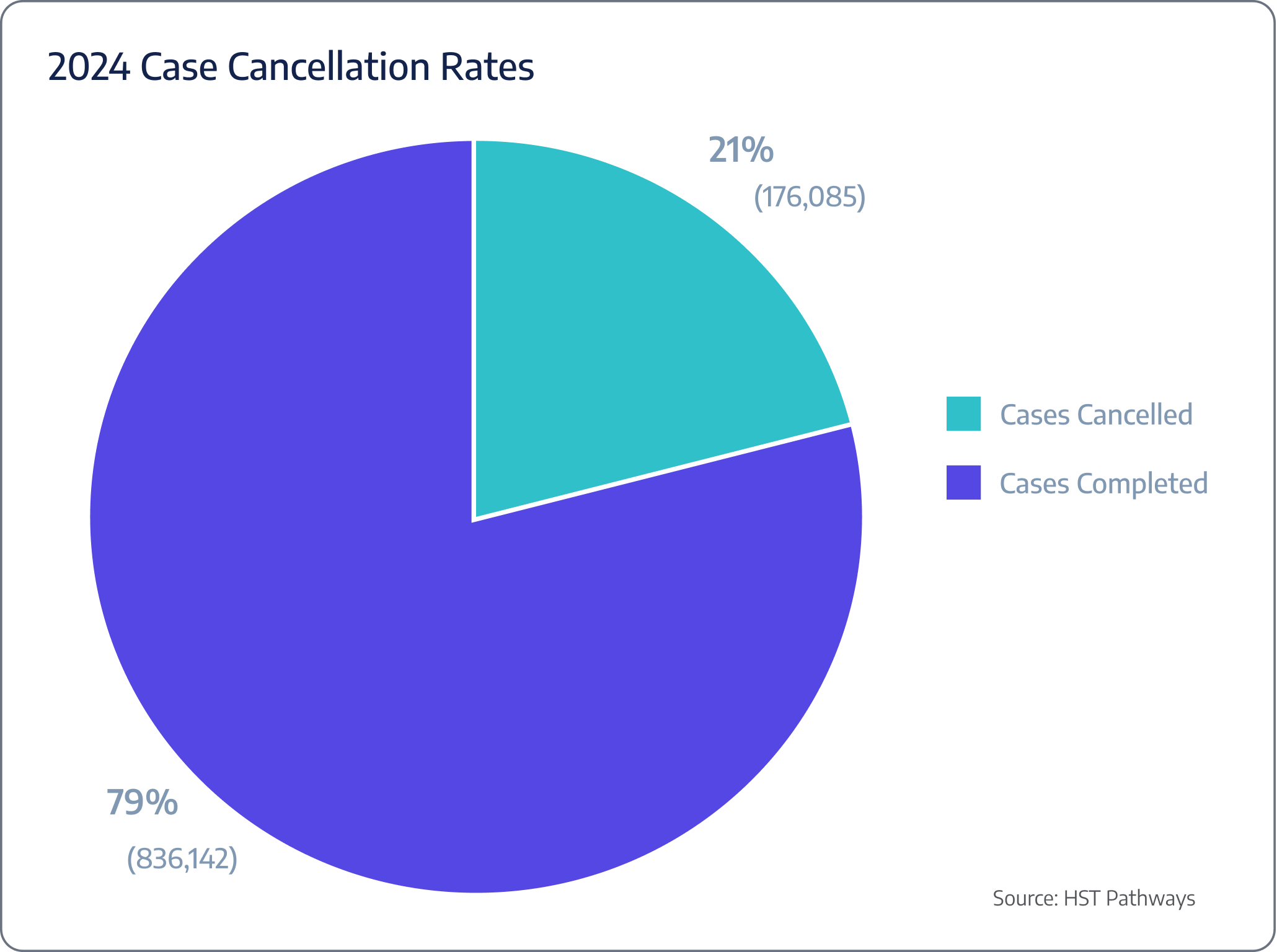
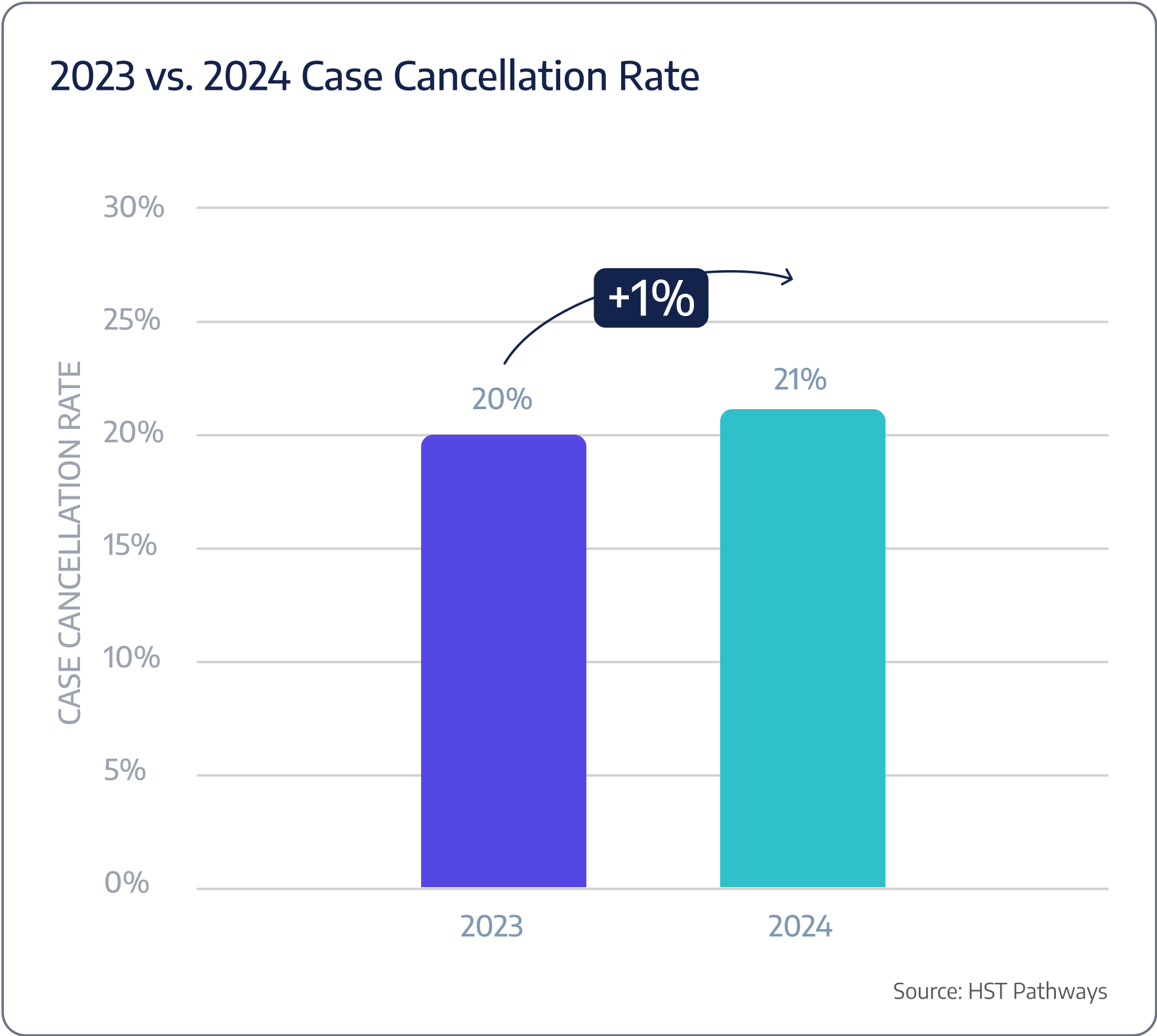
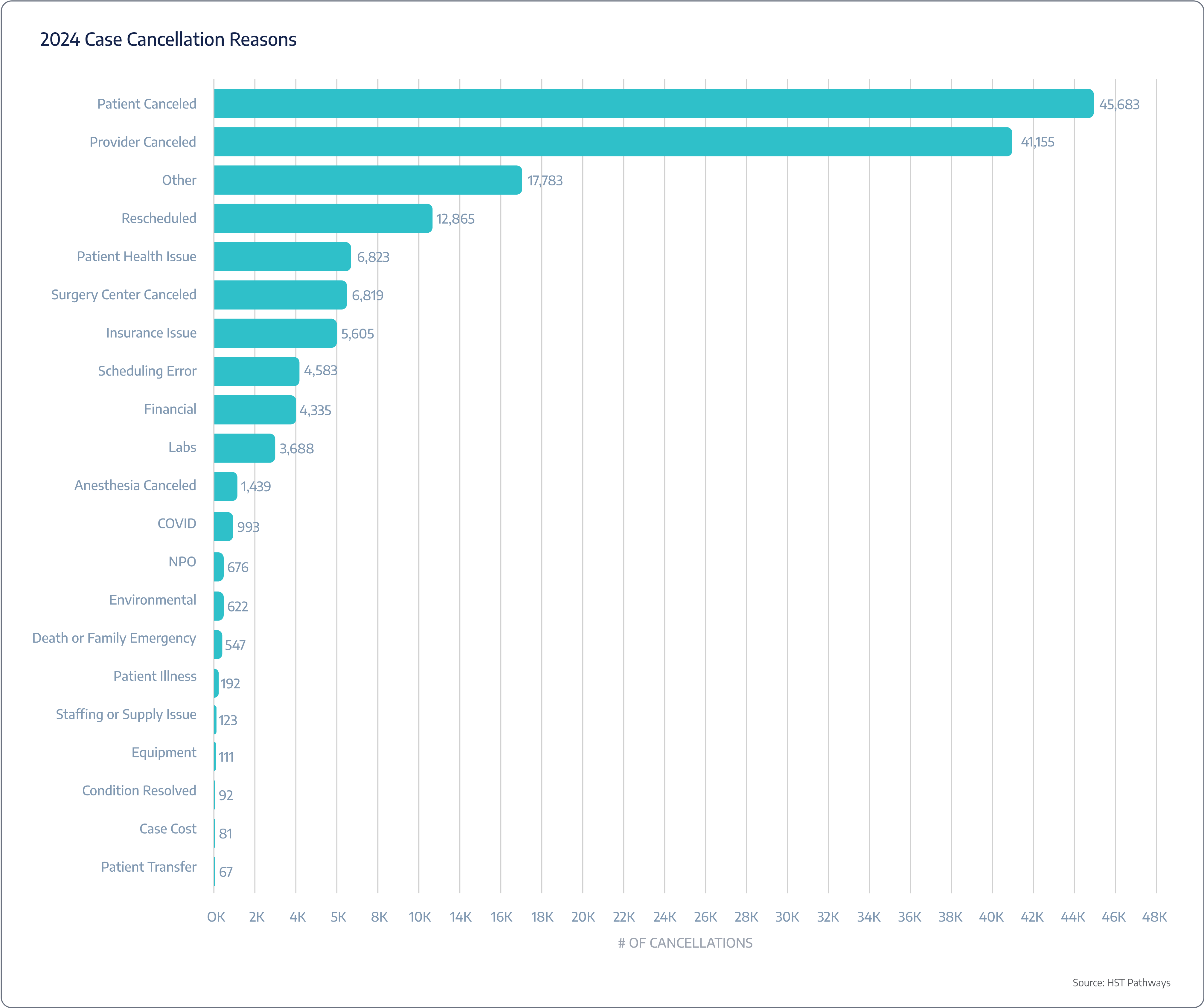
Case cancellation
Case reschedules
No shows
Cancellation reasons
Benchmarking Data
ASCs are experiencing, on average, a 21% case cancellation rate.


Patient Journey: Pre-Day of Service
5. Review Case for Profitability & Implants
Best Practices
Before proceeding with any case, surgery center administrators must understand how much the center will profit (or lose) from the procedure. Surgeries are complex events – payer contracts are complicated, overhead needs to be accounted for, and costs vary significantly by procedure, especially when implants are involved. Analyzing case profitability well in advance of the date of service ensures that the center can continue to provide high-quality services without compromising financial health and that no one is blindsided after it’s too late.
While staff experience and custom spreadsheets are how most surgery centers identify potentially unprofitable cases, leading surgery centers use advanced software, such as HST, to automate the profit estimation process. By identifying your costs per OR minute, flat supply costs, and what percentage of revenue you expect, your predetermined auto-flagging settings (e.g., when an implant is needed) will highlight potential concerns and provide you with the data you need to accept, deny, or modify confidently.
Key Process Steps
Confirm seamless integration between your billing, scheduling, and profitability software.
Identify a range of surgical cases for review, including both common and rare procedures.
Collate all pertinent data related to the case, including procedural costs, staffing hours, equipment usage, and overhead.
Factor in insurance reimbursements, patient payments, and any other revenue streams associated with the case.
Determine net profit/loss by subtracting the total costs from the revenue to ascertain the profitability of each case.
Host discussions with physicians and other stakeholders to interpret the data and determine thresholds, scenarios, and edge cases that everyone is comfortable accepting.
If applicable and case profitability is too low, contact your implant vendor to evaluate potential modifications to improve profitability.
Monitor and adjust over time.
Key Performance Indicators
Expected profit margin
Expected profit margin by procedure
Expected profit margin by physician
Implant cost per procedure


Patient Journey: Pre-Day of Service
6. Send Pre-Assessment Form to Patient
Best Practices
Pre-assessment forms provide a comprehensive overview of a patient’s medical history, current medications, allergies, and other relevant health information. They are pivotal in surgical planning, risk mitigation, and patient engagement.
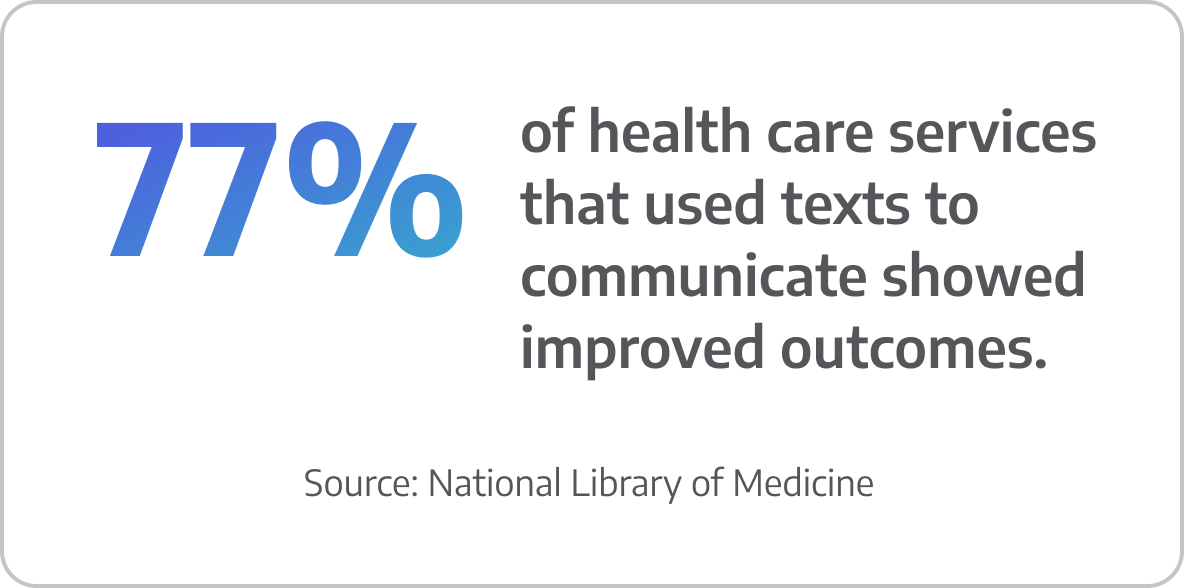
The most efficient way to collect this information is by communicating with patients in a way they prefer: texting. By texting patients a secure link to complete the pre-assessment form, they can do so privately and on their own time. This will enhance the accuracy of information, reduce paperwork, and improve the overall patient experience.
It is recommended that your forms have a user-friendly design, provide patients with clear guidelines and help features, are available in multiple languages, and are accessible to patients with eyesight limitations.
Key Process Steps
Choose a secure platform that integrates with your EHR.
Design a comprehensive pre-assessment form that captures all necessary patient details and has a patient-centric design.
Send the electronic pre-assessment form link to the patient, either via email or text (text is recommended).
Set up reminders to encourage timely form submissions.
As forms are submitted, have medical staff review them for completeness and accuracy.
If there are discrepancies or additional clarifications are needed, reach out to the patient directly.
Ensure that the submitted data automatically populates the patient’s electronic health record.


Patient Journey: Pre-Day of Service
7. Generate & Send Patient Estimate Prior to Date-of-Service
Best Practices
The financial aspect of surgery often causes just as much anxiety for patients and their families as the procedure itself. Trying to navigate the complexities of how much insurance will cover, what will need to be paid out of pocket by when, and hoping surprise bills don’t show up weeks or months later is extremely daunting for the average consumer.
Providing patients with an accurate financial estimate before their date of service (ideally 1-2 weeks out) allows them to plan better and prepare, ultimately enabling you to build trust, collect upfront, reduce last-minute cancellations, and improve patient satisfaction scores.
Using proven technology, you can generate accurate patient estimates in minutes, send the estimate to the patient via text or email, and allow them to submit payment. The estimate should be easy to read, devoid of medical jargon, and include a payer versus patient responsibility breakout.
Key Process Steps
Populate your estimation software with all patient information, including demographics, procedure type, primary and secondary insurance details, and any related services that might impact cost.
Through a clearinghouse integration, validate the patient’s insurance information.
Leverage your estimation software to generate a financial estimate that is clear, concise, and easy to understand.
Based on the patient’s preferences, send the financial estimate to the patient via text or email well before the date of service.
Confirm the estimate was delivered and opened through your estimation software.
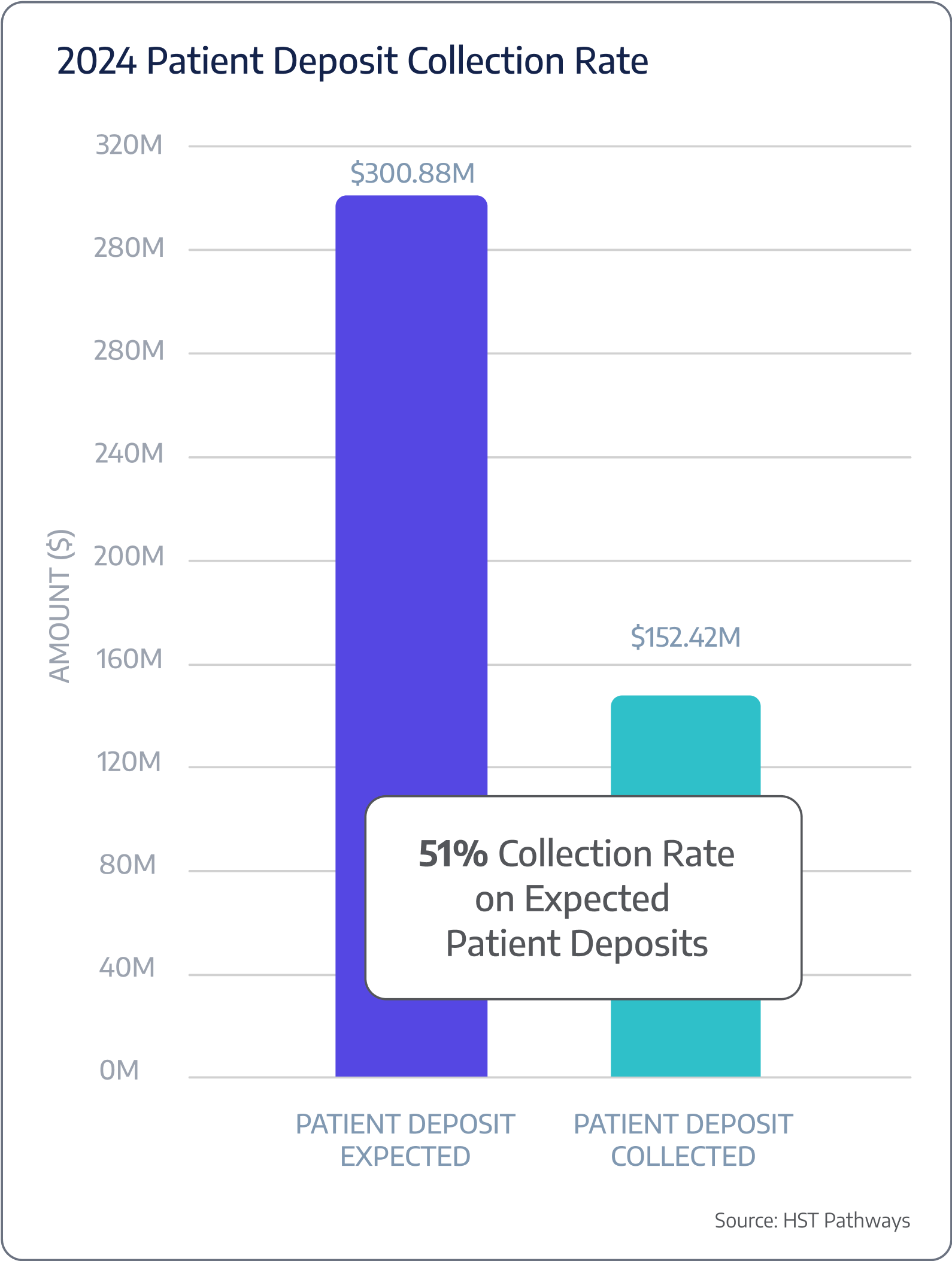
Key Performance Indicators
Accuracy rate of estimate
Upfront collection rate
Pay in full vs. payment plan
Benchmarking Data
A typical ASC is only collecting 51% of expected patient deposits at time of service.
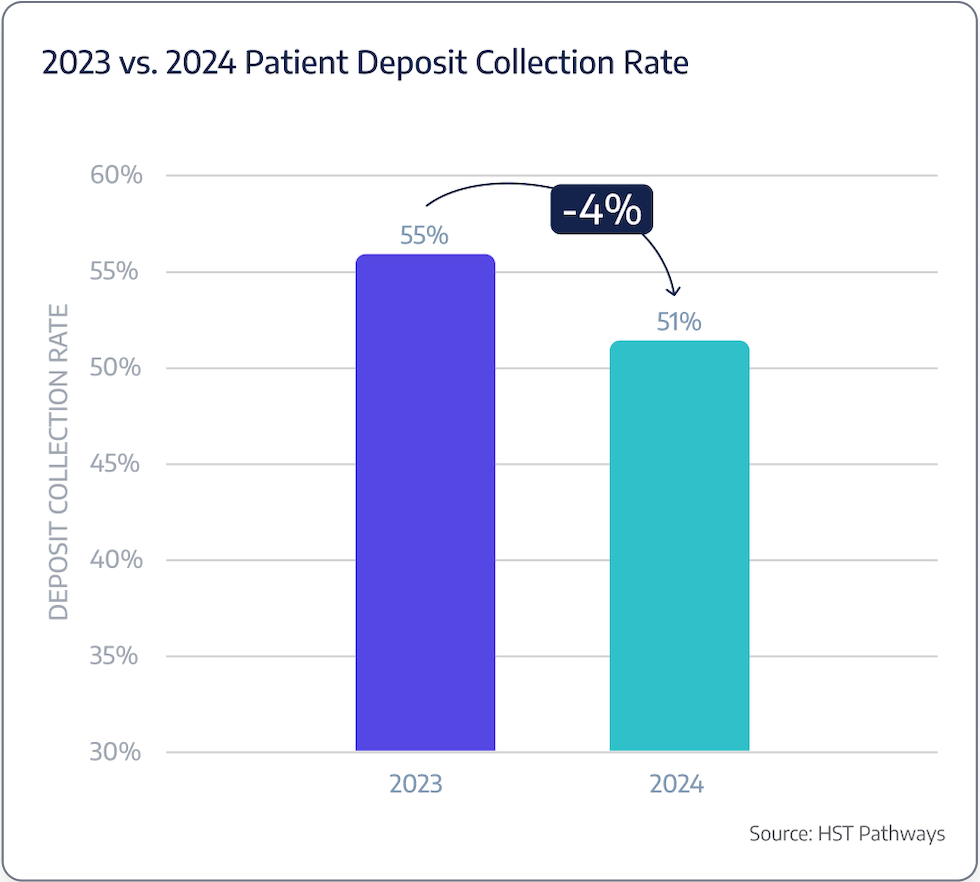


Patient Journey: Pre-Day of Service
8. Communicate Appointment Reminders & Pre-Op Instructions via Text
Best Practices
Sending patient appointment reminders and pre-operative instructions via text message is a modern and efficient way to ensure effective communication and patient preparedness. To have timely and effective dialogue with your patients, you must communicate with them how they prefer instead of forcing them to communicate with you in ways that don’t fit into their everyday lives.
Using text messages to send appointment reminders and pre-op instructions will reduce appointment no-shows and cancellations, increase patient compliance with pre-operative instructions, and enhance overall patient satisfaction. The most successful texts are timely, clear, concise, personalized, and allow for two-way communication. Plus, using readily available technology, you can build and automate your texting cadence so that it’s automatically set up for every new scheduled patient.
Key Process Steps
Confirm your EHR has accurate and up-to-date patient phone numbers and integrate your EHR with a secure text messaging platform that complies with health information privacy laws.
Draft your standardized text messages for appointment reminders and pre-op instructions that include the date, time, location, and all necessary information. Personalize the message with the patient’s name, type of procedure, and the physician’s name.
Set the text messaging platform to automatically send text messages at a specific time frame before the procedure (e.g., two weeks before, one week before, one day before)
Enable a two-way communication feature and allow patients to confirm their appointment directly through the text message.
Build in any keyword triggers and alerts directly into your software to alert the scheduler of any potential changes (e.g., if patient response contains “reschedule,” alert the scheduler immediately).


Patient Journey: Pre-Day of Service
9. Pull Supplies from Supply Room the Day Before
Best Practices
Ensuring that the necessary supplies are pulled from the supply room the day before a patient’s surgery is crucial for efficient surgical operations and patient safety. This will help to guarantee there are minimal to no surprises on the day of surgery.
As a standard practice, you should train all staff members to be able to pull supplies. This will help make sure there is accountability and consistency in the process. You can also develop standardized procedures for pulling supplies based on the surgical procedure. To maintain the highest levels of quality control, staff should regularly audit the supplies pulled to ensure they match the requirements and are within their expiration dates.
Key Process Steps
Using your practice management system, view the physician preference cards and the intra-op supply list to see what is needed.
Retrieve the supplies from the supply room based on the checklist.
Ensure that all items are in good condition and not expired.
Document the supplies pulled and their quantities for accurate inventory management.
Key Performance Indicators
# of instances when you are out of stock
# expired/unusable items

Day of Service

01
Check in with the Front Desk & Meet with the Registration Team
02
Collect Outstanding Balance from Patients
03
Prepare the Operating Room, Equipment, and Supplies
04
Patient & Care Team Enter Pre-Op
05
Patient & Care Team Enter OR
06
Share Patient Updates with Family/Friends
07
Patient is Moved to Recovery Area
08
Patient is Discharged


Patient Journey: Day of Service
1. Check in with the Front Desk & Meet with the Registration Team
Best Practices
Patients arriving for surgery with their loved ones are undoubtedly nervous and filled with questions. The check-in process is likely their first time stepping foot in your facility and interacting with your staff in person, so it’s critical that this first touchpoint is smooth and sets the right tone. Your front office team should greet patients with a friendly and empathetic demeanor. Having a designated area for check-ins will maintain patient privacy and prevent sensitive information from being overheard. Lastly, you’ll want to communicate the next steps, timing, and expectations to the patient and their family/ride home.
Leading surgery centers are also exploring patient kiosks to assist with patient check-ins. For the patients, it offers faster check-ins and shorter wait times; for your staff, it provides automated workflows and accurate data and reporting. Your front office team will always be there to answer additional questions, but this process will allow for automation and improved patient flow.
When your team is ready to bring the patient back, avoid standing in the doorway and calling out the patient’s name. Instead, the receptionist can note the patient’s name and location in the waiting area, and when the nurse comes to get the patient, they can approach them directly, introduce themselves, and personally escort them. This small change creates a more personalized and positive experience for both the patient and the staff, setting the tone for exceptional care.
Key Process Steps
Greet the patient as they arrive and provide a warm welcome to the surgery center.
Check the patient’s identification, such as a driver’s license or ID card, to confirm their identity.
Confirm the patient’s insurance details and coverage, ensuring accuracy for billing purposes.
Key Performance Indicators
Time it takes to check-in
Wait time after check-in


Patient Journey: Day of Service
2. Collect Outstanding Balance from Patients
Best Practices
The art of collecting outstanding balances from patients on the day of their surgery is entirely contingent on how you have communicated with them up to this point and the level of price transparency you have shared.
Patients should never hear how much they owe for the first time on the morning of their procedure. This will only add to their anxiety and make them feel overwhelmed and blindsided. In a previous chapter, we discussed the best practices for generating and sending an estimate as early as possible (ideally weeks before their surgery). Your day-of-collection success is strongly influenced by how that step was handled.
Regardless, on the day of, you will need to have a financial discussion with the patient, clearly laying out an itemized breakdown of any co-pays, deductibles, or out-of-pocket expenses for them. You should be prepared to accept payment via credit card and provide a receipt. Your staff should then update the patients’ records to include payment transactions, dates, amounts, payment methods, and payment plan agreements.
Key Process Steps
Have a designated, private area where you can discuss the patient’s financial responsibility without other patients overhearing.
Clearly communicate the estimated patient responsibility, including co-pays, deductibles, and any additional charges. Share payment options, such as credit card, check, or cash.
If applicable, set up and document payment plans according to the patient’s needs and financial situation.
Walk the patient through financial consent forms, patient rights and responsibilities, privacy practices, and any other required paperwork per your center’s policies.
Accept patient payment and update the patients’ records.
If a balance remains, share with the patient when and how you will be following up on unpaid balances so there are no surprises post-procedure.
Clearly communicate with the patient any additional bills they may be receiving from third parties (e.g., Anesthesia group).
Key Performance Indicators
Day of collection rate


Patient Journey: Day of Service
3. Prepare the Operating Room, Equipment, and Supplies
Best Practices
Efficiently preparing the operating room, equipment, and supplies is critical to ensuring successful surgical procedures within a surgery center. Proper preparation not only promotes patient safety but also contributes to the overall effectiveness of the surgical team.
Properly preparing the operating room, equipment, and supplies is a multifaceted process that demands attention to detail, collaboration, and adherence to established protocols. Proper preparation not only promotes patient safety but also contributes to the overall effectiveness of the surgical team and better surgical outcomes.
Standardized checklists, collaborative planning, and proper inventory management are crucial to making this part of the workflow seamless.
Key Process Steps
Review the schedule for the day, looking at types of procedures, their estimated durations, and any special requirements.
Make sure that the room is adequately prepared, including adjusting the operating table, arranging necessary equipment, and positioning monitors and lights.
Conduct a thorough check of all equipment and instruments required for the procedure, confirming that they are clean, functional, and readily available in the operating room.
Verify that all necessary supplies are available and ensure that surgical instruments are properly sterilized according to established protocols.
Once all checks are complete, the surgical team can begin the procedure.
Make sure to update the patient’s chart as you go.
Key Performance Indicators
OR turnaround time
Benchmarking Data
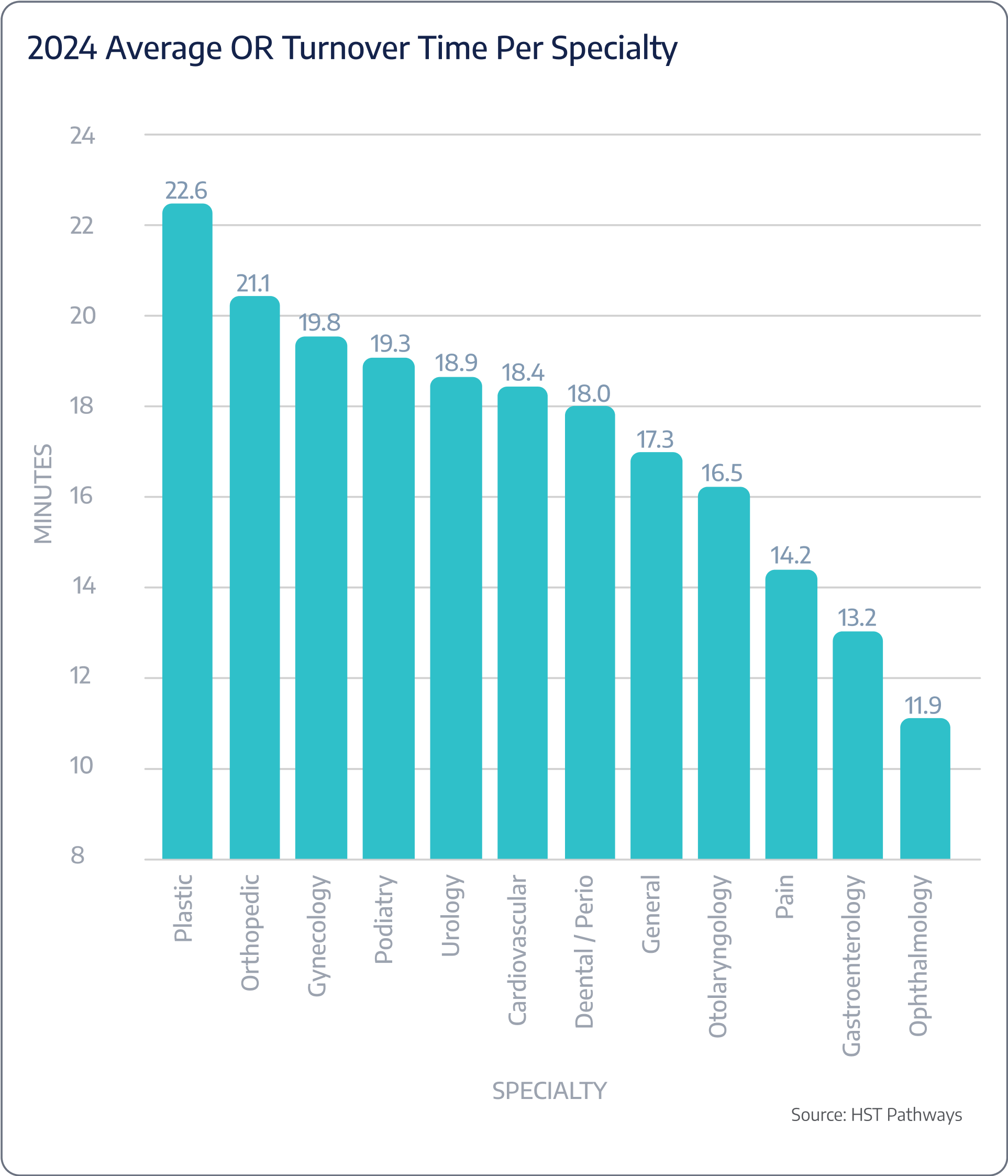


Patient Journey: Day of Service
4. Patient & Care Team Enter Pre-Op
Best Practices
The seamless entry of patient and the care team into the pre-operative (pre-op) area is crucial to ensuring the safety, comfort, and efficiency of surgical procedures. This phase sets the tone for the entire surgical experience, contributes to positive surgical outcomes, and enhances the overall patient experience.
The pre-op team should provide patients with clear and concise information about what to expect during the procedure. This includes explaining the process, addressing any concerns, and outlining the roles of different team members. At this time, it’s also critical that you verify that the patient’s consent forms are properly completed and signed and review the patient’s medical history, allergies, and any pre-operative medications one final time.
Key Process Steps
Greet the patient warmly upon arrival in the pre-op area.
Use a standardized protocol to verify the patient’s identity using two unique identifiers, such as full name and date of birth.
Conduct a comprehensive pre-op assessment, including reviewing the patient’s medical history, allergies, vital signs, and current medications.
Ensure that the patient’s consent forms are signed and accurate and that appropriate transportation arrangements have been made for their journey home.
Confirm with the patients who their designated contact person is and that they have the patient’s consent to share updates and discuss the extent of information that can be shared.
Inform the family or friends of the anticipated timing for the next update. This could be based on the estimated duration of the surgery or other relevant milestones.
Complete any necessary pre-operative in-house lab tests and medications that were ordered. Administer prophylactic antibiotics any start IV.
The anesthesiologist meets with the patient to discuss anesthesia options, address concerns, and gather information about the patient’s anesthesia history.
Once the patient is fully prepared and all necessary assessments are complete, have the anesthesiologist or OR circulator accompany the patient to the operating room.
Key Performance Indicators
Pre-op waiting time
Cancellation rate in pre-op on day of surgery
# of IV attempts


Patient Journey: Day of Service
5. Patient & Care Team Enter OR
Best Practices
The entry of patients and the care team into the operating room is pivotal in the surgical process, requiring precision, communication, and adherence to strict protocols. Surgery center leaders and staff must establish a seamless and organized approach, prioritizing patient safety, sterility, and effective communication.
When entering the OR, all care team members must adhere to the highest level of sterility within the operating room and enforce rigorous protocols to prevent contamination and reduce the risk of surgical site infections. For a successful surgical outcome, the surgical lead should ensure everyone knows the surgical plan, patient history, and any specific considerations. The OR nurse and surgeon must confirm that all necessary surgical instruments, equipment, and supplies are available and properly arranged within the OR. As a required practice, you’ll always want to verify that the patient’s consent forms are accurate, complete, and signed and that you’ve completed the surgical safety checklist and the Time Out checklist per center protocol.
Key Process Steps
Perform thorough sterile hand hygiene using an approved antiseptic solution before entering the OR.
Care team members should put on their surgical attire and PPE according to established protocols.
Transfer the patient from the pre-op area to the OR bed, ensuring proper body alignment and comfort.
Use at least two unique patient identifiers to verify the patient’s identity before entering the OR. This step is crucial for preventing errors.
Gather the care team for a brief huddle to ensure that everyone is on the same page regarding the surgical plan and patient information.
Conduct a final verification of the patient’s identity, surgical site, and any critical details with the entire care team present.
Coordinate with the anesthesia provider to begin the induction process. Ensure that the patient is comfortable and adequately monitored.
The surgical team is now ready to assume control.
Make sure to update the patient’s chart and document supply usage as you go.
Key Performance Indicators
Start time expected vs. actual
Surgery duration expected vs. actual
Benchmarking Data
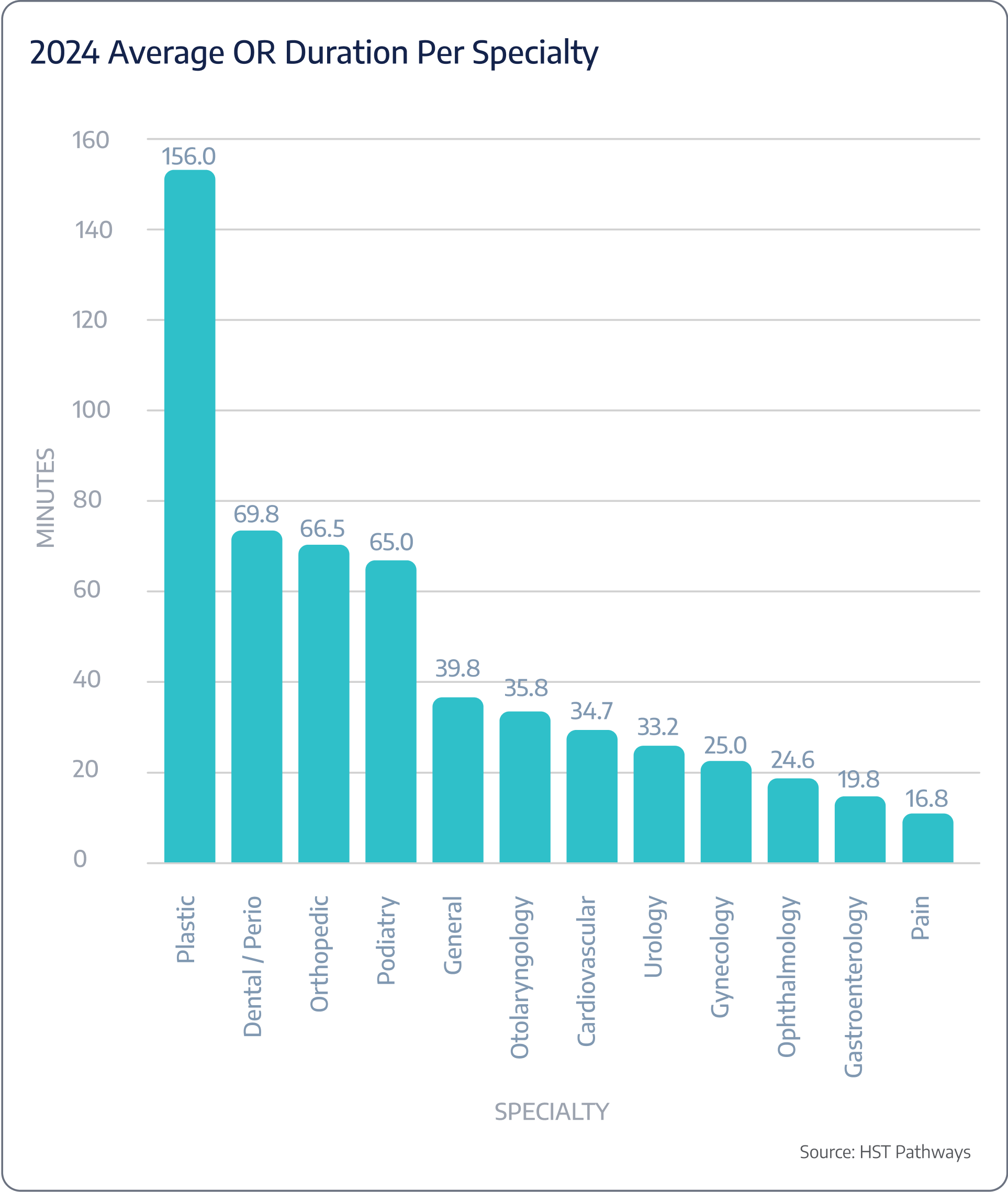
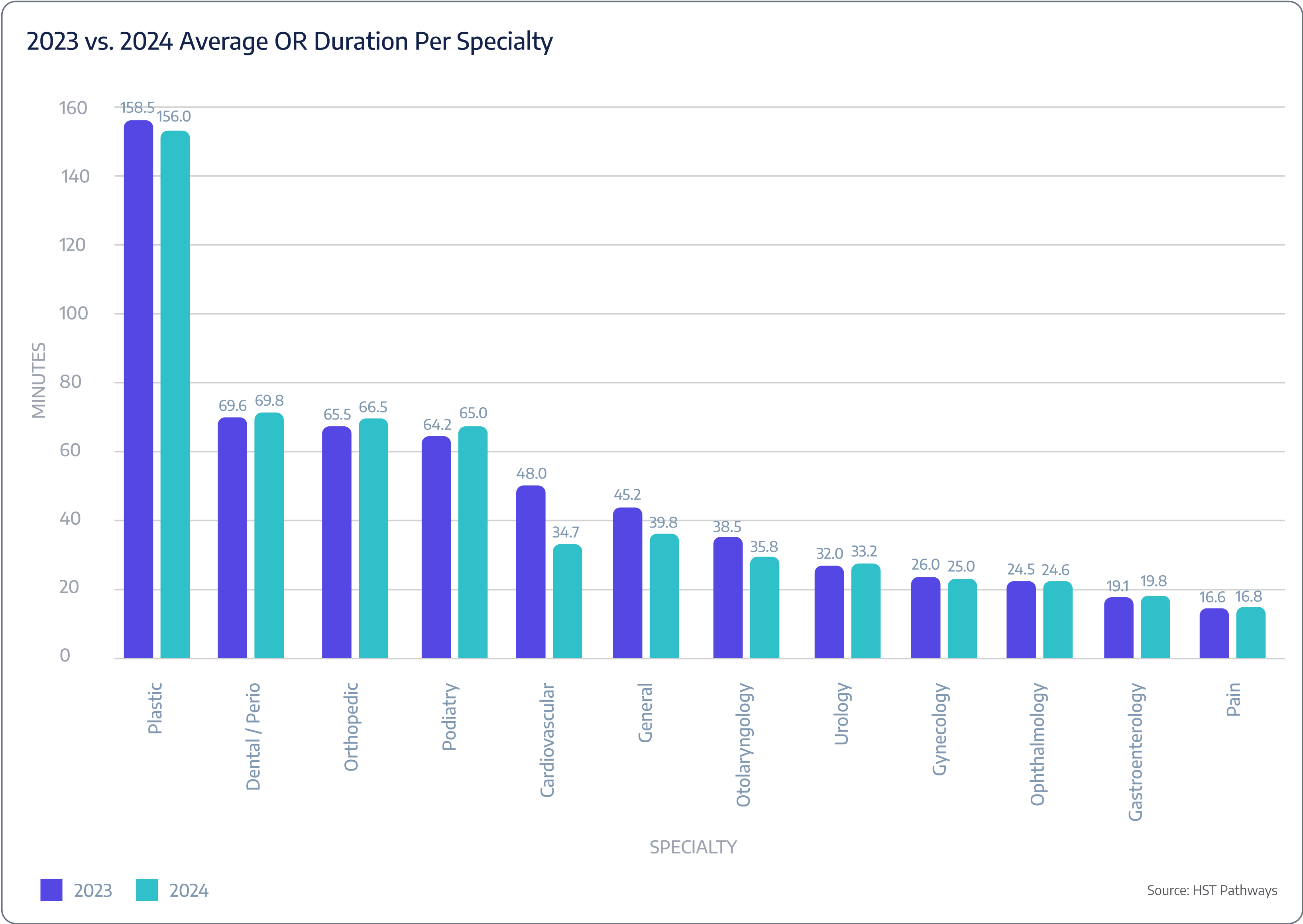
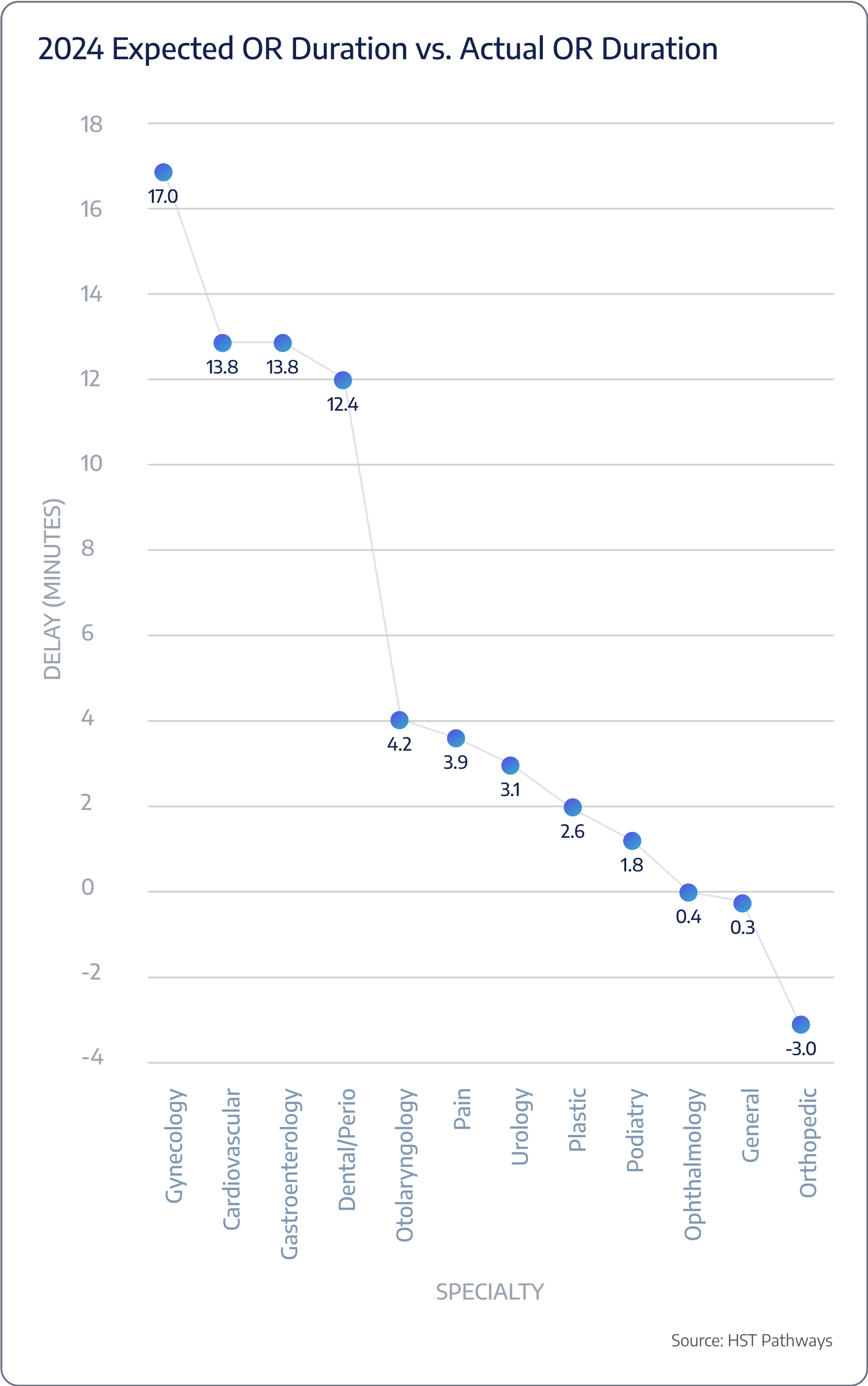
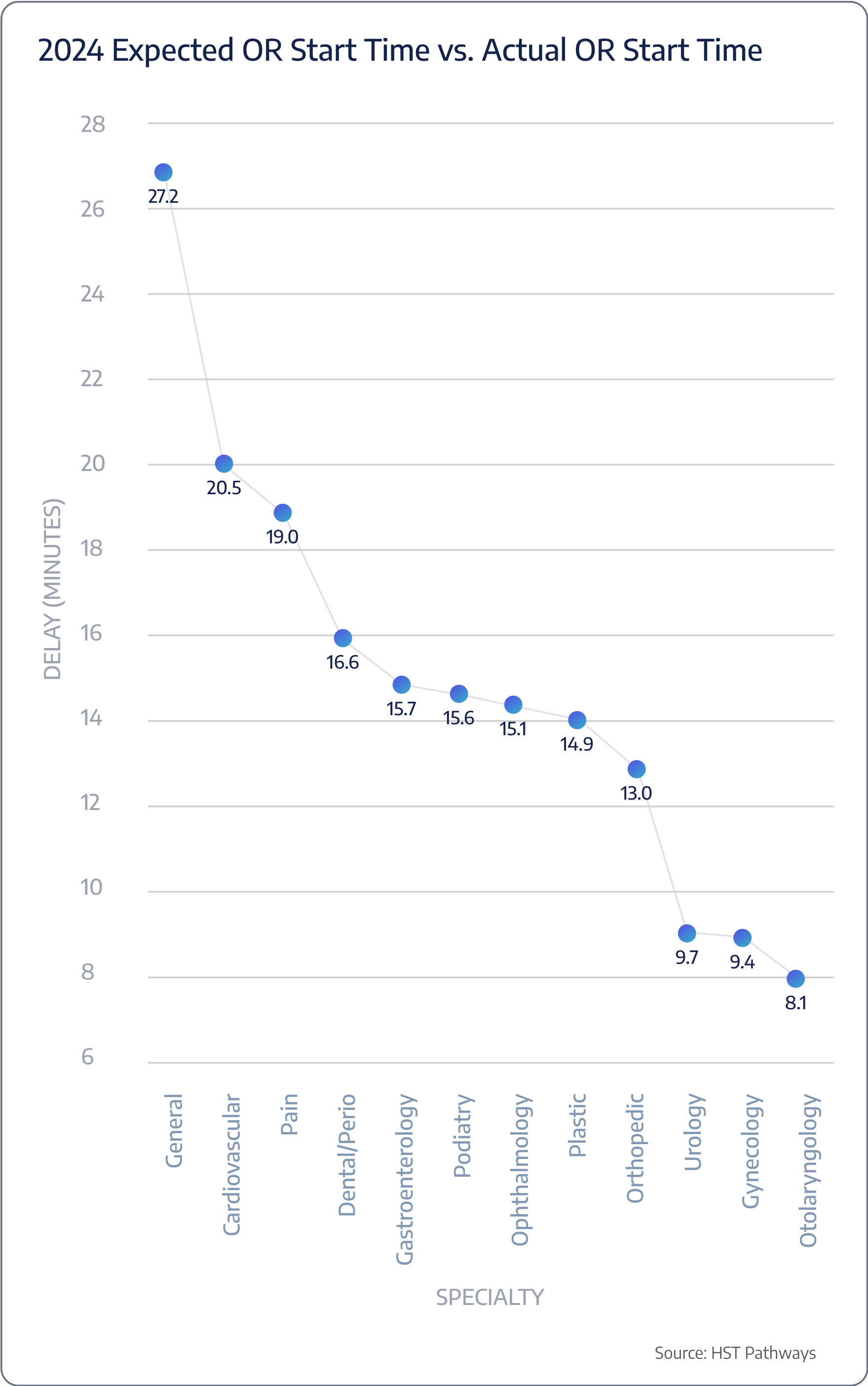


Patient Journey: Day of Service
6. Share Patient Updates with Family/Friends
Best Practices
Keeping family and friends informed about a patient’s status during surgery is critical to patient-centered care. Effective, timely, and proactive communication comforts loved ones, fostering trust and transparency. If you do not set clear expectations with patients’ loved ones on when they can expect an update and how the updates will be shared, your front office staff will be inundated with family members approaching the desk or calling the front desk, ultimately distracting your team from providing care and working on other tasks.
To make sharing updates seamless, offer multiple communication channels, such as text messages or surgery boards in the waiting room, where real-time status updates can be displayed. These surgery boards provide a visual and immediate way for family members to stay informed without needing to inquire constantly. Train staff to communicate updates with empathy, sensitivity, and professionalism. Use clear, jargon-free language that non-medical individuals can easily understand. Lastly, develop a consistent format for sharing updates, including information such as the patient’s condition, progress, and any relevant milestones.
Key Process Steps
Collect accurate contact information from family or friends, including phone numbers, email addresses, and any preferred communication methods.
Prepare updates that include relevant information, such as the surgery’s progress, any unexpected findings, and the patient’s overall condition. Use neutral and accurate language.
If there are any changes in the patient’s condition or unexpected developments, communicate these changes promptly and honestly.
As the surgery nears completion, provide a final update and inform the family or friends of the impending reunion with the patient once they are in the recovery area.
Key Performance Indicators
Time spent updating family/friends


Patient Journey: Day of Service
7. Patient is Moved to Recovery Area
Best Practices
The safe and efficient transfer of patients from the operating room to the recovery area requires careful coordination, monitoring, and attention to the patient’s well-being.
The care team must continuously monitor the patient’s overall condition during the transfer and initial recovery phase. You’ll want to foster clear and effective communication between the surgical team, anesthesia providers, nursing staff, and the patient, double-checking that everyone knows the patient’s status and any pertinent details.
Prioritizing the patient’s comfort, dignity, and emotional well-being and promptly addressing any pain, discomfort, or concerns will improve patient satisfaction and overall experience. Lastly, keep family and friends informed about the patient’s transfer to the recovery area. Accurate and reassuring updates will provide relief from their stress and worry.
Key Process Steps
Before transferring the patient, the anesthesiologist will conduct a thorough post-operative assessment to ensure they are stable and ready for the next phase of recovery.
The post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) will be notified the patient is headed their way.
Provide a concise handoff to the nursing staff in the recovery area, including details about the surgery, patient condition, medications administered, and any specific requirements.
If the patient is in pain, administer appropriate pain relief medications based on the patient’s needs and the surgeon’s orders.
Once in the recovery area, the nursing staff will initiate recovery protocols, including monitoring the patient’s vital signs, addressing any immediate needs, and ensuring a smooth wake-up from anesthesia.
If allowed and requested, facilitate a controlled reconnection between the patient and their family or friends in accordance with the recovery area’s policies.
Make sure to update the patient’s chart and document supply usage as you go.
Key Performance Indicators
Post-op recovery time
Benchmarking Data
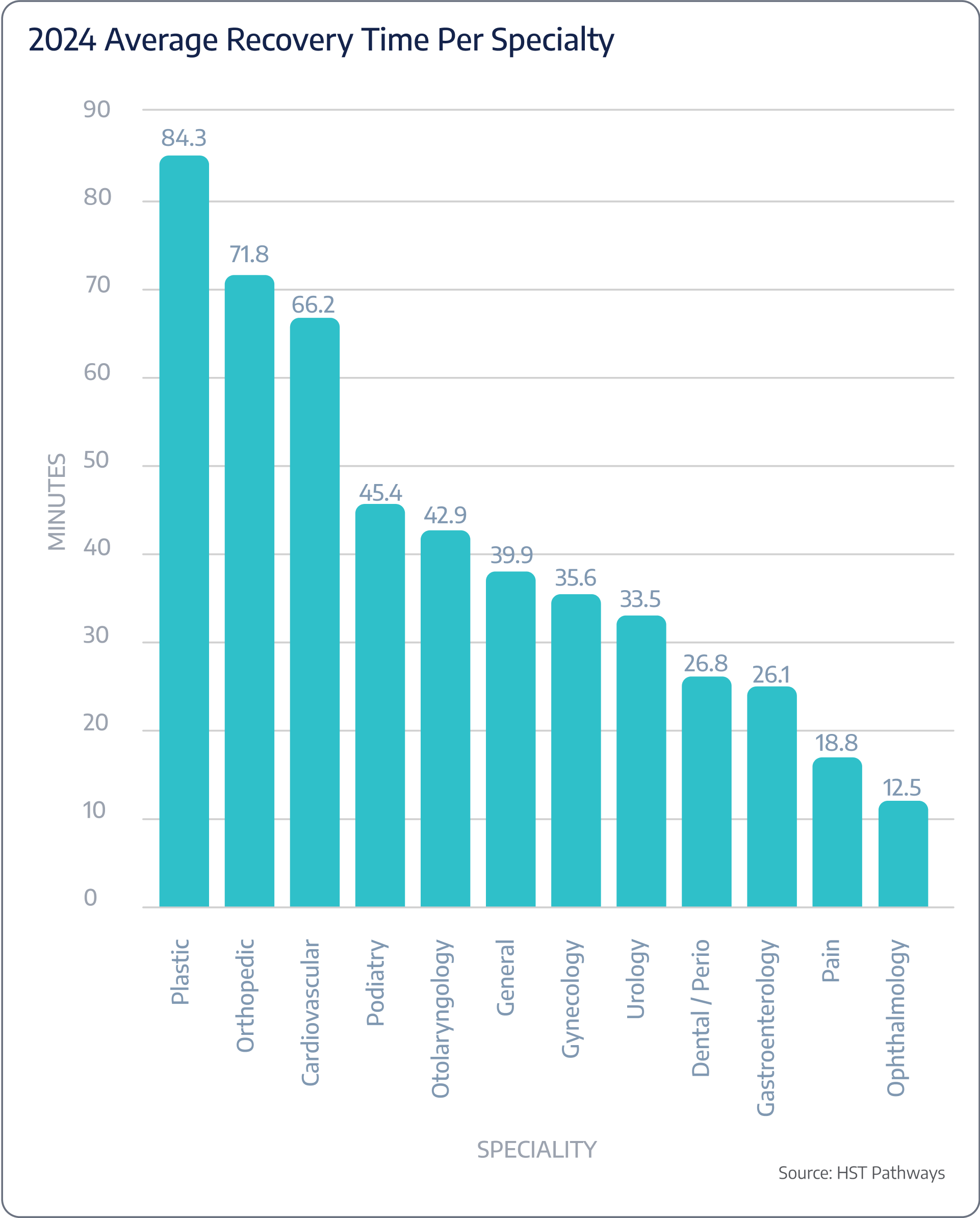
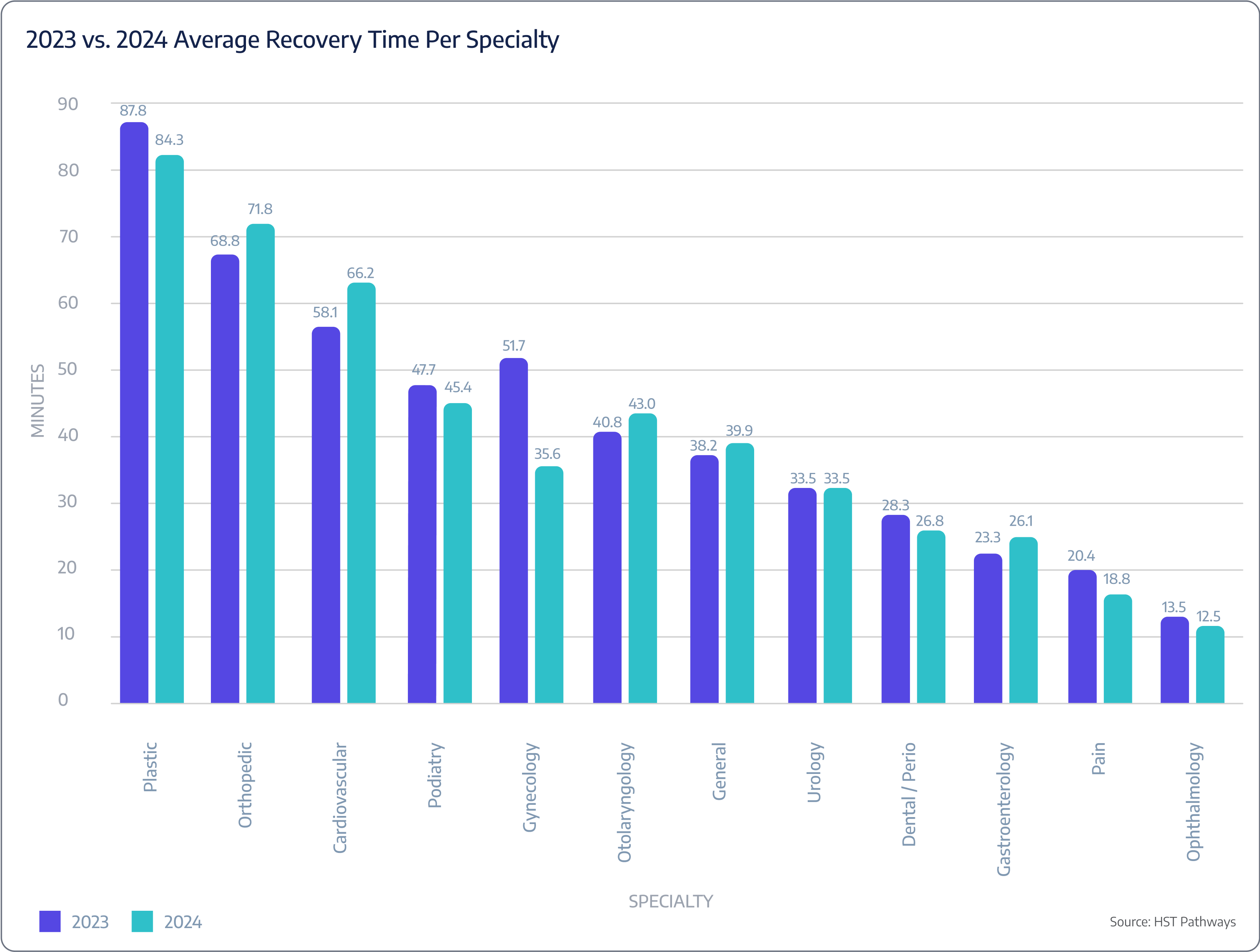


Patient Journey: Day of Service
8. Patient is Discharged
Best Practices
The moment the patient and their loved ones are waiting for – it’s time to go home! While this is the final step in the patient’s journey at your facility, it’s equally as important as the previous steps, and it’s critical that the discharge process is seamless and thorough.
Clear communication is the key to success. Straightforward guidance on medication management, wound care, activity restrictions, and potential complications helps prevent avoidable errors and adverse events during recovery. When done correctly, proper discharge instructions lead to optimal recovery and empower patients to take appropriate actions if they notice any signs of trouble.
It is recommended that you provide verbal and written instructions in your patient’s native language and that you use clear, jargon-free language that non-medical individuals can easily understand.
Key Process Steps
Conduct a final assessment of the patient’s condition to ensure that they are medically stable and fit for discharge.
Review the patient’s prescribed medications and provide clear instructions for taking them, including dosage, frequency, and potential side effects.
If applicable, provide detailed wound care instructions, including how to keep the surgical site clean, change dressings, and identify signs of infection.
Clearly communicate any activity restrictions or limitations, offer guidance on personal hygiene, and provide dietary recommendations based on the patient’s surgical procedure and any post-operative dietary restrictions.
Discuss pain management strategies, including prescribed pain medications and any over-the-counter options.
Provide the patient with written discharge instructions that summarize all discussed points.
Confirm that the patient and their family understand the instructions and have a clean, safe environment for recovery, access to proper food, and access to anything needed for a successful recovery.
Key Performance Indicators
Discharge time

Post-Day of Service

01
Check-in With Patient
02
Review Chart for Completion and Close
03
Send Patient Satisfaction Survey
04
Perform Coding & Charge Entry
05
Perform Claim Management


Patient Journey: Post-Day of Service
1. Check-in With Patient
Best Practices
Checking a patient’s health the day after surgery is vital in providing comprehensive post-operative care. Prompt and proactive follow-up will demonstrate dedication to your patient’s well-being and foster patient trust, satisfaction, and successful outcomes.
Your patient engagement software, such as HST, should present you with a clear, straightforward list of which patients need to receive a phone call and which already have. Implementing a process like this will streamline follow-up and make it clear to all care team members the status of each patient. It is also recommended that post-phone call, you communicate any additional post-operative instructions via text to your patients, allowing them to respond via text and have two-way communication. You will then want to maintain detailed and accurate records of follow-up interactions, including the patient’s condition, any symptoms, and advice given.
Key Process Steps
Choose an appropriate communication method, such as a phone call, text message, or both, based on the patient’s preferences.
Initiate the follow-up call or communication with the patient, introducing yourself and explaining the purpose of the call.
Ask about the patient’s general well-being, comfort level, pain level, and any concerns they may have.
Confirm that the patient is following prescribed medication regimens and all relevant discharge instructions.
Thank the patient for their time, express the surgery center’s commitment to their well-being, and provide contact information for further questions or concerns.
Remind the patient to complete the patient satisfaction survey.
Accurately document the follow-up conversation, noting the patient’s responses, any recommendations provided, and any actions taken.
Key Performance Indicators
Time spent on follow-up


Patient Journey: Post-Day of Service
2. Review Chart for Completion and Close
Best Practices
Closing the patient’s chart the day after surgery is a crucial task to make sure all necessary documentation, including surgical notes, post-operative instructions, and billing information, is complete and accurate. This not only aids in providing coordinated and comprehensive post-operative care but also ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and helps minimize legal risks.
Using an EHR to streamline reviewing and completing the patient’s chart is a game-changer. Electronic charting helps guarantee that all necessary information is easily accessible and updated in real time and that charts are closed in a timely manner. It also allows doctors to review and sign from wherever they are (no more stalking them in the hallways trying to get them to sign off on a paper chart!) and can provide visual indicators of completed charts to stay organized.
Key Process Steps
Ensure that all post-surgery documentation, including surgical notes, post-operative instructions, and billing information, is completed and included in the patient’s chart immediately after the surgery. Don’t forget to link operative reports and lab results.
Review the patient’s chart using a standardized checklist to make sure all necessary documentation and information is complete and accurate.
Address any discrepancies or missing information identified during the review process. This may involve contacting the surgical team or other relevant staff members to obtain the necessary information.
Conduct a final review of the patient’s chart to ensure that all necessary documentation is complete and accurate before officially closing the chart.
Officially close the patient’s chart in the EHR system and maintain a record of all patient charts for future reference and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Key Performance Indicators
Post-DOS chart completion rates
Benchmarking Data
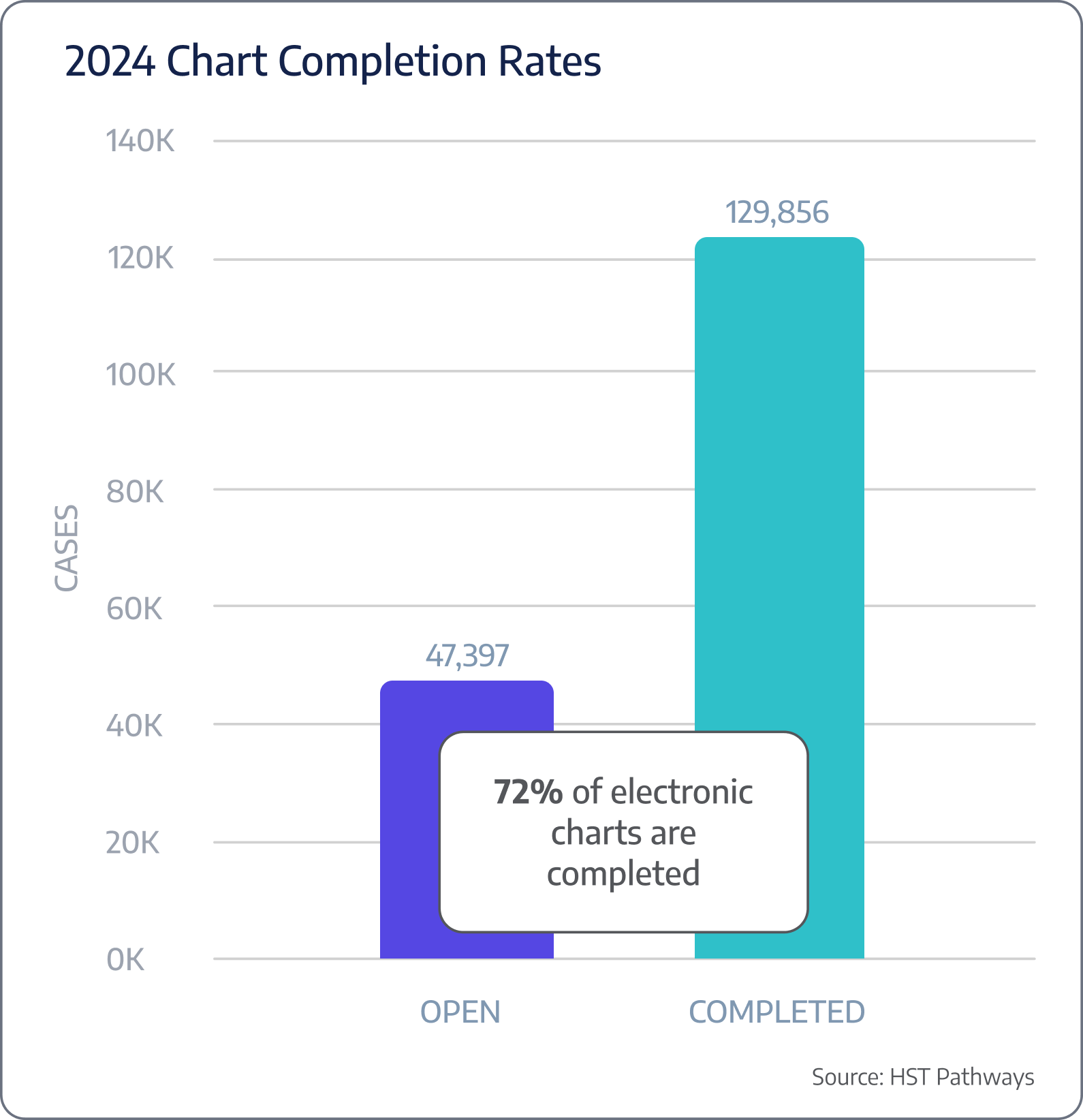


Patient Journey: Post-Day of Service
3. Send Patient Satisfaction Survey
Best Practices
Patient satisfaction surveys are essential for surgery centers to assess the quality of care provided, identify areas for improvement, and ultimately enhance the overall patient experience.
The timing of when you distribute the survey is crucial. You want to send the survey while the experience is fresh in your patient’s mind, but you don’t want to send it too soon as the patient may still be experiencing side effects of the anesthesia or potentially in discomfort. Typically, 48 hours post-surgery is the perfect time to distribute. Distribution methods also play a huge role. Using email and text to send a survey link, versus collecting feedback over the phone or via mail, will keep costs down and increase response rates. Other ideas for success would be ensuring anonymity, keeping the survey concise and easy to read, and personalizing with the patient’s name.
Lastly, it is recommended that you build alerts and triggers into your collection software, such as HST, to notify the administration immediately if there are any words within the open-ended questions that may warrant immediate attention (e.g., infection, hospital, or pain).
Note: Once OAS CAHPS becomes required in 2025, you will need to ensure you are properly distributing, aggregating, and reporting results. Given that the OAS CAHPS survey consists of 31 questions, many ASCs may opt for the minimum necessary to meet the survey requirements. However, for the remaining patients, ASCs can offer a more concise and personalized patient survey. This approach allows ASCs to strike a balance between compliance and meaningful patient responses.
Key Process Steps
Develop a comprehensive survey that covers all aspects of the patient’s experience or leverage OAS CAHPS for guidance.
Determine the most appropriate mode(s) of survey distribution based on the patient’s preferences (text or email will warrant the highest and quickest response rates).
Set up your software so that it automatically sends the survey 48 hours post-surgery.
Analyze the survey results to identify trends, patterns, and areas of concern that need to be addressed.
Develop and implement an action plan to address the identified areas of concern and make necessary improvements.
Key Performance Indicators
Frequency of feedback that requires immediate follow-up
Distribution Breakdown (paper, text, email)
This chapter covers survey distribution. For more detailed information on reviewing your survey results, please jump to the “Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly” section.


Patient Journey: Post-Day of Service
4. Perform Coding & Charge Entry
Best Practices
Accurate and timely coding and charge entry are fundamental to any facility’s financial health and operational efficiency. The process involves assigning appropriate codes for procedures and entering the corresponding charges into the billing system. This is crucial for reimbursement and compliance with regulatory requirements and maintaining a transparent and efficient billing process.
Utilizing EHR and practice management systems, ideally integrated with a clearinghouse, will help to streamline the process significantly. Human error is inevitable, but using software, such as HST, and employing well-trained coders who are well-versed in the latest coding standards and guidelines will help reduce denials and avoidable mistakes. When a denial occurs, it’s important to take meticulous notes and review to avoid the same errors in the future.
Key Process Steps
Ensure that detailed documentation of the surgical procedure, including surgical notes and operative reports, is completed and included in the patient’s chart immediately after the surgery.
Assign the appropriate codes for the procedures performed based on the detailed documentation provided. This should be done by a certified coder who is well-versed in the latest coding standards and guidelines.
Enter the corresponding charges for the procedures performed into the billing system. This should be done based on the assigned codes and the surgery center’s fee schedule.
Conduct a thorough review of the codes and charges entered to identify and correct any errors or discrepancies.
Submit the coded and audited charges to the payer for reimbursement. This may involve electronic submission via a clearinghouse or direct submission to the payer.
Key Performance Indicators
Time spent to make each entry
Charge lag (time between DOS and date charges are entered)
Denial rates due to coding errors
Benchmarking Data
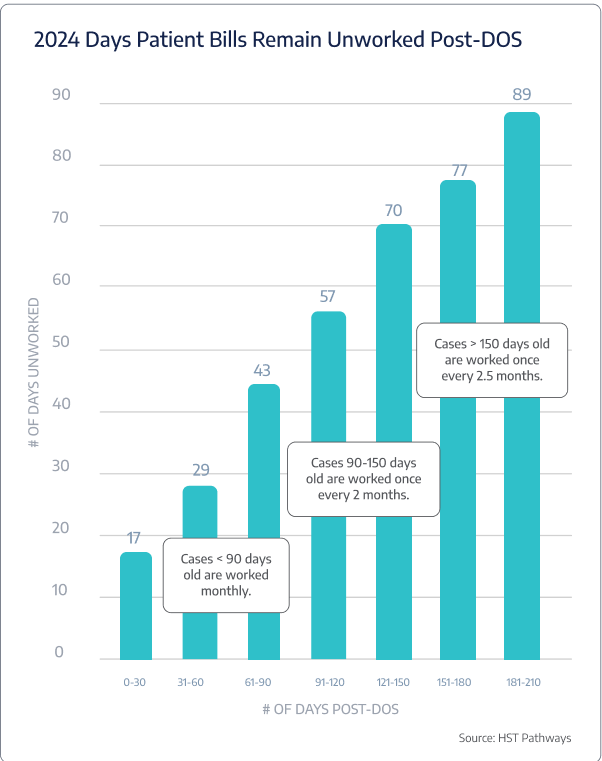
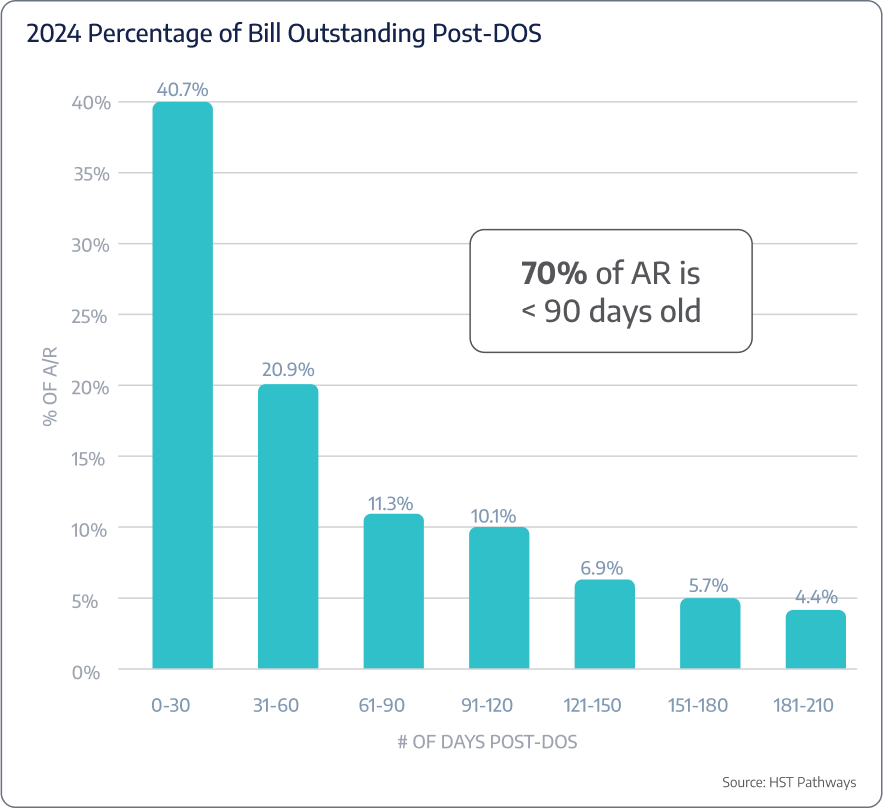
On average, ASCs are taking 4.4 days to bill post-DOS.
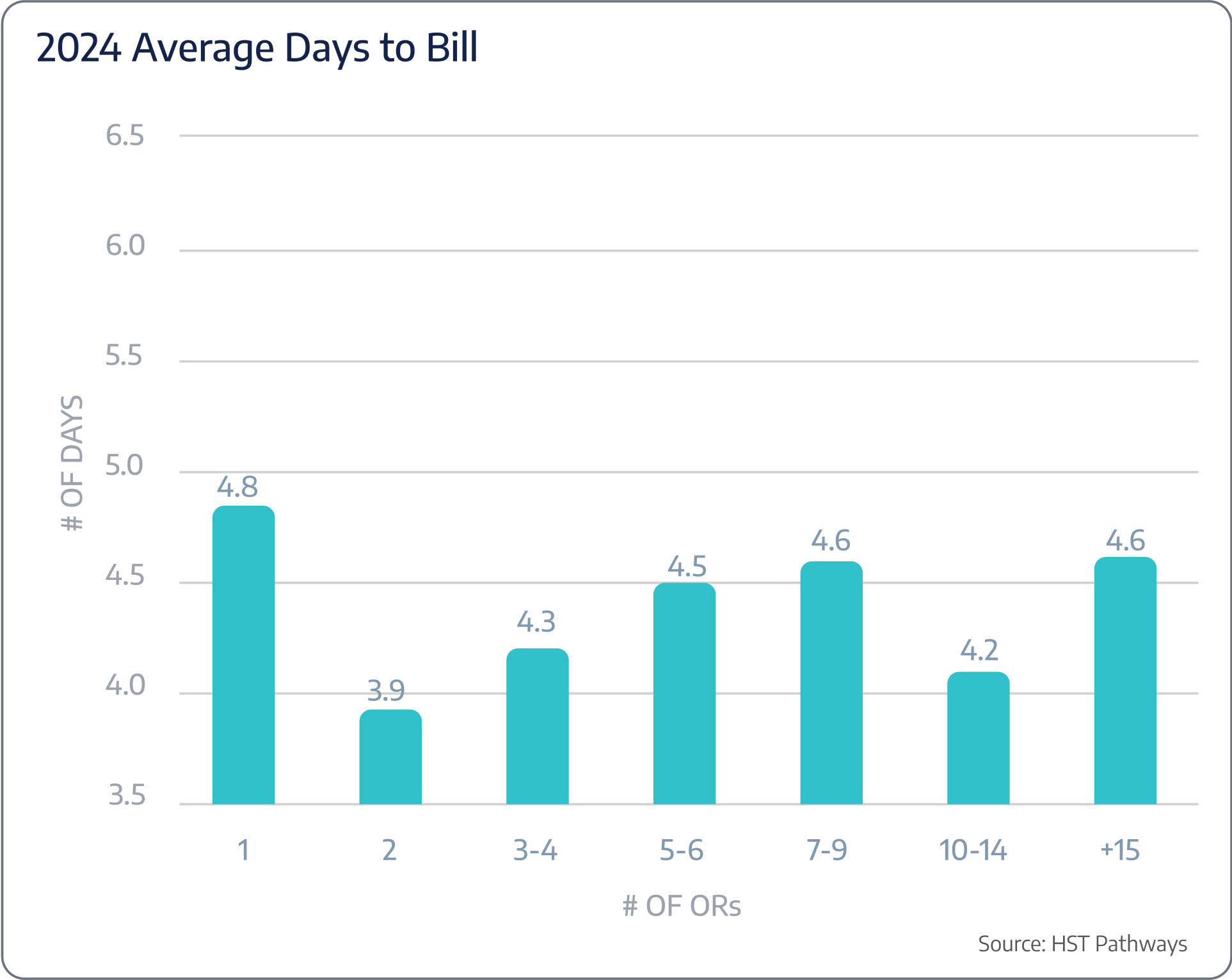
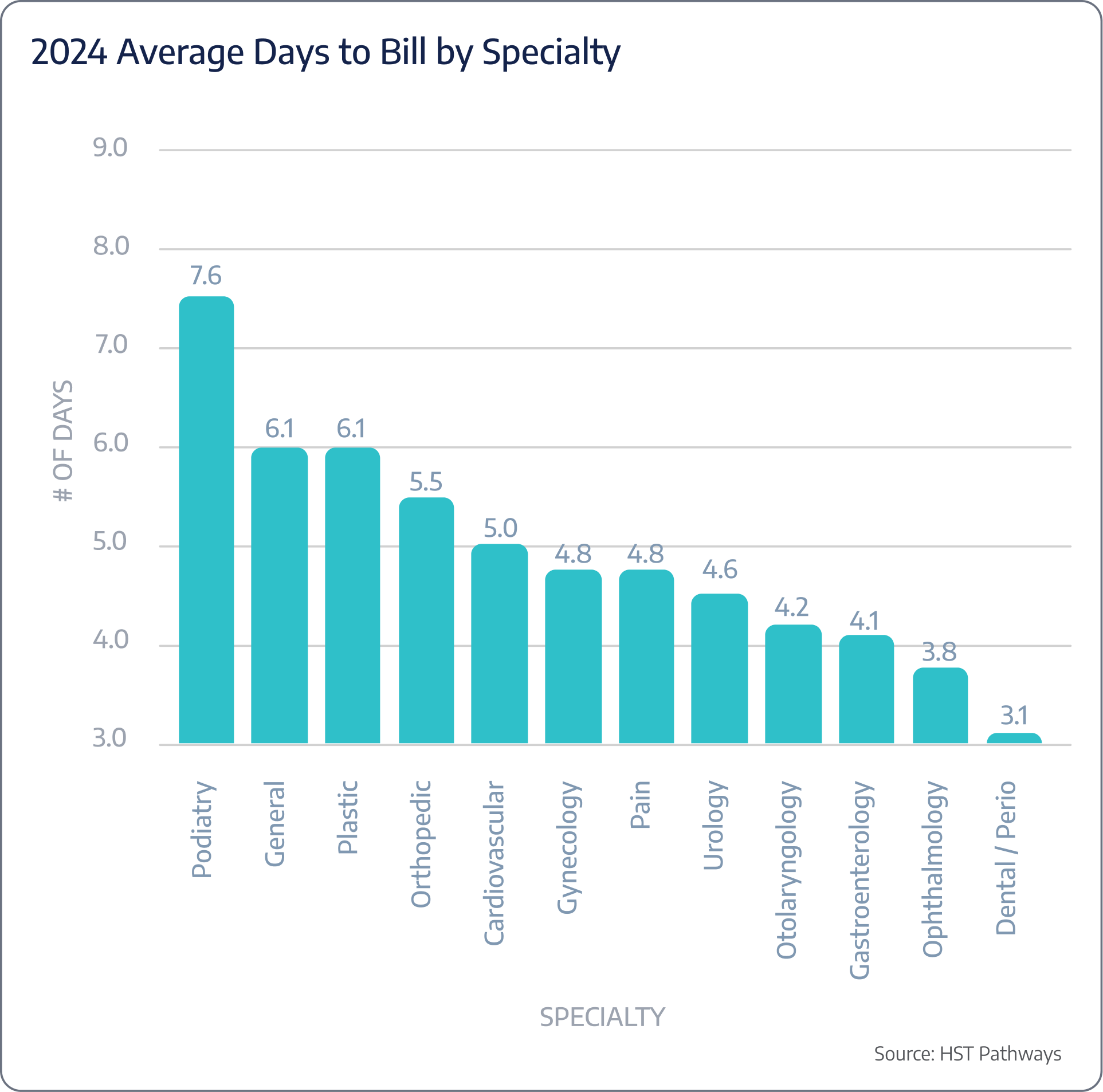
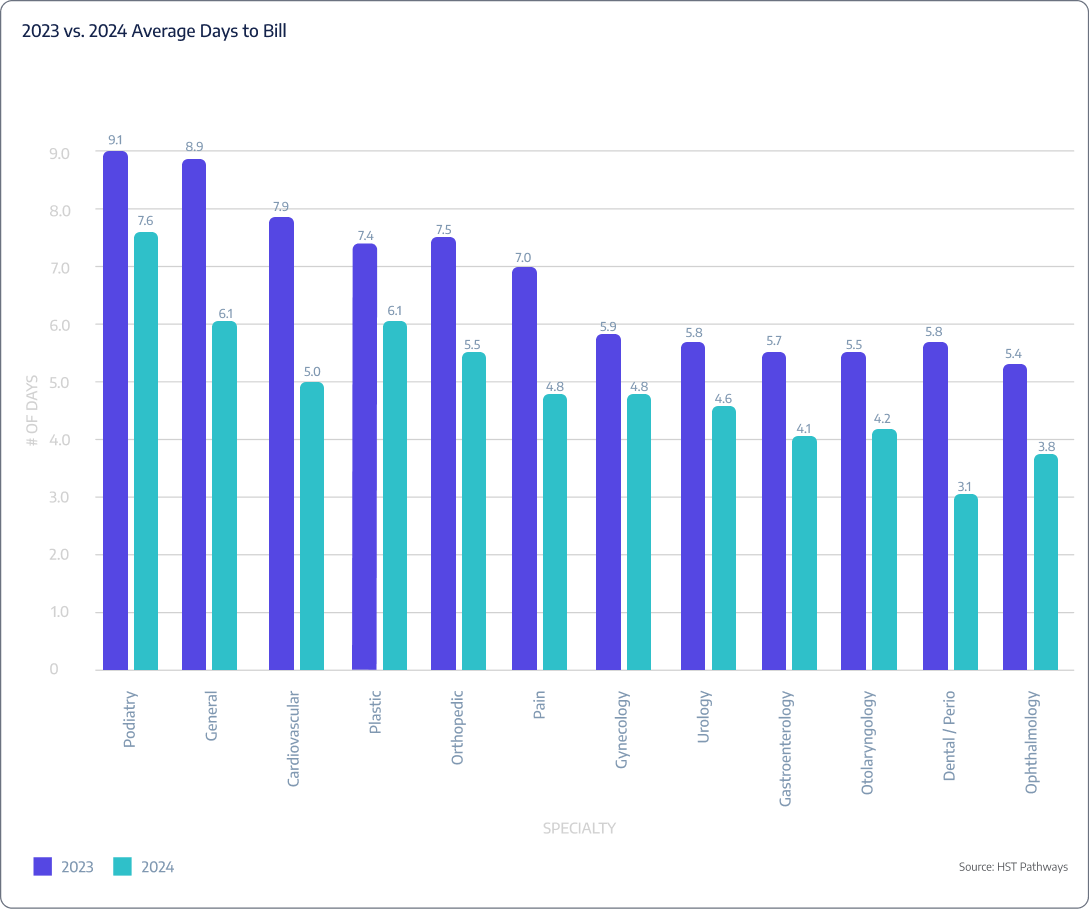


Patient Journey: Post-Day of Service
5. Perform Claim Management
Best Practices
The financial sustainability of surgery centers heavily relies on an efficient and effective claim management process. Claim management involves preparing, submitting, tracking, and managing insurance claims for the services provided by the surgery center. Proper claim management ensures timely and accurate reimbursement, which is crucial for maintaining cash flow and operational efficiency. Furthermore, it also plays a critical role in compliance with payer requirements and regulatory guidelines.
Advanced technology, including EHR, practice management, and electronic claims submission systems, will streamline the entire claim management process. You will also need to regularly monitor the status of submitted claims to identify and address any issues, such as denials or requests for additional information, in a timely manner.
Key Process Steps
Prepare the insurance claim by compiling all necessary information, including patient demographics, insurance details, procedure codes, and charges.
Submit the insurance claim to the payer either electronically through a clearinghouse or via direct submission, depending on the payer’s requirements.
Regularly monitor the status of submitted claims to identify and address any issues in a timely manner via your practice management system or the payer’s online portal.
If a claim is denied, identify the reason for the denial, make the necessary corrections, and resubmit the claim as quickly as possible.
Once the payment is received, post the payment to the patient’s account in the practice management system and reconcile the payment with the charges submitted.
Key Performance Indicators
Clean claim rate
Claim rejection rate
Claim denial rate
Days in A/R
Benchmarking Data
ASCs are typically experiencing a 4% denial rate on their claims.


Regularly Recurring Operations
- Order Supplies
- Review Shift Coverage
- Review Collections, Outstanding AR, and Claim Denials
- Follow Up with Patients on Overdue Balances
- Reconcile Discrepancies in Posted Payments
- Review Quality Outcomes
- Perform Audit of Medication Cabinets


Regularly Recurring Operations: Daily/Weekly
Order Supplies
Best Practices
Ordering new supplies to restock the inventory room is a crucial part of operations. An adequate stock of necessary supplies ensures that the center can operate efficiently and provide patients with the highest level of care. On the other hand, inadequate supplies can lead to delays, increased costs, and even compromise patient safety.
Implementing best practices and following key process steps are essential for maximizing the efficiency and accuracy of the ordering process. Regularly checking inventory levels, utilizing an automated inventory management system, establishing minimum and maximum levels, implementing a standardized ordering process, building solid relationships with reliable suppliers, and regularly reviewing supplier performance are all critical steps. Proper attention to each process step will ensure that the surgery center always has an adequate stock of necessary supplies.
Key Process Steps
Regularly check the inventory levels of all supplies to determine what needs to be ordered. This can be done manually or using an automated inventory management system.
Create a list of items and their quantities. This should be done based on each item’s minimum and maximum inventory levels.
The order should be authorized by a designated person or team before it is placed. This helps in avoiding unnecessary or excessive orders.
Place the order with the selected supplier. This can be done online, by phone, or by fax, depending on the supplier’s requirements.
Verify the order once it is received to ensure that all items are received in the correct quantities, in good condition, and at the negotiated price.
Update the inventory records to reflect the new stock levels. This can be done manually or automatically if using an automated inventory management system.
Store the supplies in their designated areas, ensuring that they are easily accessible and organized.
Key Performance Indicators
Order lead time
Inventory turnover rate
% Expired inventory
Order accuracy
Stockouts


Regularly Recurring Operations: Daily/Weekly
Review Shift Coverage
Best Practices
Confirming adequate staff scheduled each week is essential for the smooth functioning of the center, maintaining high levels of patient safety, and ensuring employee well-being. Overstaffing can lead to increased costs, while understaffing can lead to delays, decreased quality of care, and employee burnout. Utilizing staff scheduling software, considering staff preferences, regularly reviewing staffing needs, and implementing a fair and transparent scheduling process are all elements of success.
With the nationwide staffing shortage, retention and satisfaction are more important than ever. Another strategy to consider is cross-training. Cross-training increases efficiency as tasks can be redistributed based on the workload and staff availability, increases job satisfaction as staff members gain new skills, optimizes staff schedules, and reduces overtime costs.
Lastly, leading surgery centers see success when they implement scheduling software that allows staff to see and manage their schedule, adding a sense of control and autonomy that leads to the work/life balance that works for them.
Key Process Steps
Determine the staffing needs of the center for the upcoming week. This should be based on the scheduled surgeries, historical data, and any other relevant factors.
Create a preliminary schedule for the upcoming week. This should be done using staff scheduling software and should consider staff preferences.
Communicate the preliminary schedule to the staff. This can be done via email, a staff portal, or any other communication method used by the center.
Manage any shift swaps and requests from the staff. This should be done in a fair and transparent manner, with clear criteria for approving or denying requests.
Finalize the schedule after considering all shift swaps and requests. Ensure that the schedule is aligned with the staffing needs of the center.
Communicate the final schedule to the staff. Ensure that all staff are aware of their scheduled shifts for the upcoming week.
Monitor the schedule throughout the week and make any necessary adjustments.


Regularly Recurring Operations: Daily/Weekly
Review Collections, Outstanding AR, and Claim Denials
Best Practices
Regularly reviewing financial metrics is essential for maintaining healthy cash flow, identifying and addressing issues promptly, and ensuring the financial sustainability of your center. Successful financial management includes, but certainly is not limited to, having a strong denial management process, regularly reviewing payer contracts, using a proactive collections approach, and consistently monitoring financial metrics.
Leading surgery centers employ advanced practice management software, such as HST, that can track collections, accounts receivable, and denials in real time, generate reports, and provide insights into the center’s financial health at a moment’s notice. The most seamless revenue cycles utilize as much software and automation as possible.
Key Process Steps
Generate financial reports that provide an overview of the collections, accounts receivable, and denials for the past week. This should be done using financial management software.
Review the collections for the past week to ensure that all amounts received are accurate and aligned with the payer contracts. Identify any discrepancies or issues and address them in a timely manner.
Review the accounts receivable to identify any outstanding amounts that need to be collected. Implement a proactive collections process that includes regular follow-up with payers and patients for outstanding amounts.
Review the denials for the past week to identify any trends or patterns. Implement a robust denial management process to address denials in a timely and efficient manner.
Analyze key financial metrics to identify trends and areas for improvement.
Implement any necessary actions based on the review and analysis. This may involve making changes to the billing or collections process.
Key Performance Indicators
Denial rate
Days in A/R
A/R Aging: 30 days, 60 days, 90+ days
Benchmarking Data


Regularly Recurring Operations: Daily/Weekly
Follow Up with Patients on Overdue Balances
Best Practices
Following up with patients on overdue balances every week is essential for maintaining healthy cash flow and ensuring the financial stability of a surgery center.
It is common knowledge that collecting payment upfront, before the patient’s procedure, is a best practice for a multitude of reasons. But it is also common knowledge that as patient responsibility continues to increase, upfront collections will become more complex, and more and more patients will delay payment and opt-in to payment plans. Your surgery center must be prepared.
Implementing a clear communication strategy, utilizing advanced billing and collections software, such as HST, implementing a structured follow-up process, providing multiple payment options, and training staff on effective communication are all crucial elements for successful follow-up on overdue balances.
Key Process Steps
Identify the overdue balances by generating an aging report. This should be done using practice management software.
Prepare a follow-up list that includes the details of the patients with overdue balances, the amount overdue, and the number of days overdue.
Conduct an initial follow-up with the patients on the list. Your software should automate as much of the outreach via text or email as possible.
Document the details of the follow-up, including the date and time of the follow-up, the mode of communication, and the response of the patient.
Conduct subsequent follow-ups via phone at predetermined intervals if the balance remains unpaid. Escalate the follow-up actions as necessary, which may include sending a final notice or referring the account to a collection agency.
Process any payments received from the patients. Update the patient account accordingly.
Monitor and analyze the follow-up process to identify any trends or areas for improvement.
Key Performance Indicators
% of cases sent to collections
Post-DOS collection rates


Regularly Recurring Operations: Daily/Weekly
Reconcile Discrepancies in Posted Payments
Best Practices
Discrepancies in posted payments can lead to significant financial issues and headaches, including cash flow problems, inaccurate financial reporting, and strained relationships with payers and patients.
To improve the accuracy of your reconciliation process, your billing team should have access to advanced payment processing software, such as HST, that can automatically post payments, identify discrepancies, and generate reconciliation reports. Your billing team should also be knowledgeable enough to identify the root cause of the discrepancy to help avoid the same outcome in the future (such as incorrect procedure codes, insurance denials, internal posting errors, and so on).
Additional tips for successful reconciliation include implementing a standardized reconciliation process, regularly reviewing payer contracts, and maintaining accurate and complete patient payment records.
Key Process Steps
Review the posted payments by generating a reconciliation report. This should be done using payment processing software.
Identify any discrepancies in the posted payments.
Investigate the discrepancies identified to determine the cause.
Resolve the discrepancies identified. This may involve making adjustments to the posted payments or contacting the payer for clarification.
Document the reconciliation process, including the discrepancies identified, the investigation conducted, and the resolution implemented.
Monitor and analyze the reconciliation process to identify any trends or areas for improvement.
Key Performance Indicators
Overpayment/underpayment
Reoccurrence rate of root causes identified


Regularly Recurring Operations: Daily/Weekly
Review Quality Outcomes
Best Practices
Ensuring high-quality outcomes is the #1 priority for any surgery center. Quality outcomes not only lead to better patient satisfaction and improved reputation but also can impact the center’s financial performance through payer reimbursements and avoiding potential penalties and lawsuits.
Every surgery center needs to implement a comprehensive quality measurement system that tracks various quality indicators, such as surgical complications, infection rates, burns, falls, and more. Between your electronic charting software and your practice management software, such as HST, there will be various locations for discharge nurses to input these data points and provide comprehensive analytics and reports for you to pull and review easily.
Achieving high-quality outcomes requires surgeons, nurses, anesthesiologists, administrative staff, and the rest of the care team to be engaged and proactive. To build a culture around improving outcomes, regularly review and update the quality indicators being tracked, share results, crowdsource ideas for improvement, and implement a continuous improvement process.
Key Process Steps
Configure your electronic charting software to collect data on the quality indicators being tracked.
Train your team on the importance of tracking this information and how to accurately and consistently input the data.
Analyze the data collected to identify any trends, areas for improvement, or discrepancies.
Implement any necessary changes based on the review and analysis.
Monitor the impact of the changes implemented.
Key Performance Indicators
SSI (surgical site infection) rates
Adverse drug reaction
Sharps injury
Exposure event
Cardiac or respiratory arrest
Burns
Falls
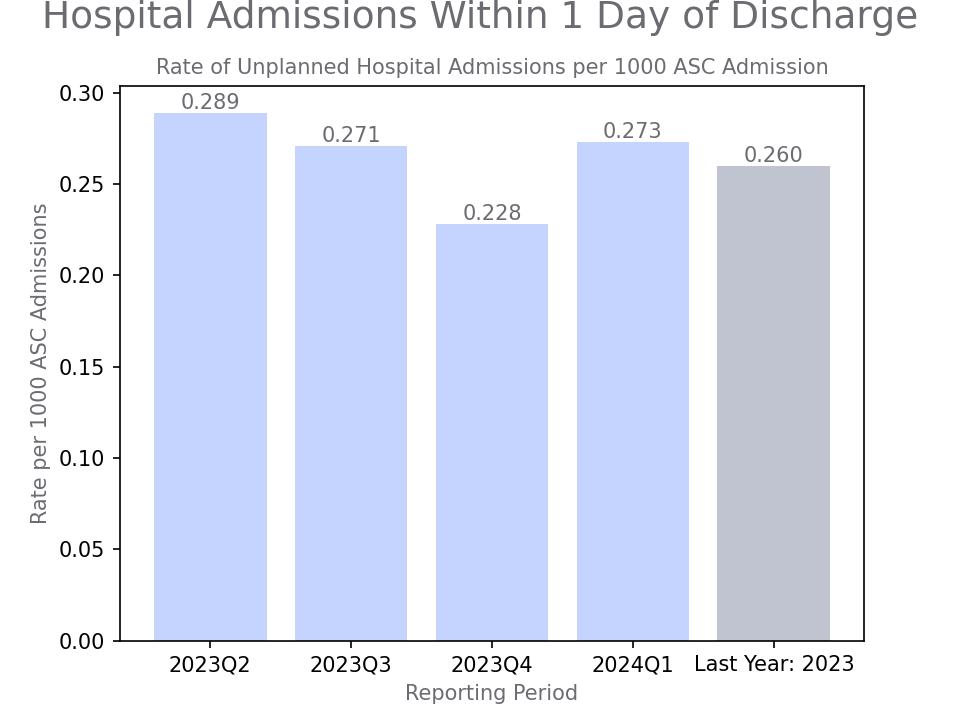
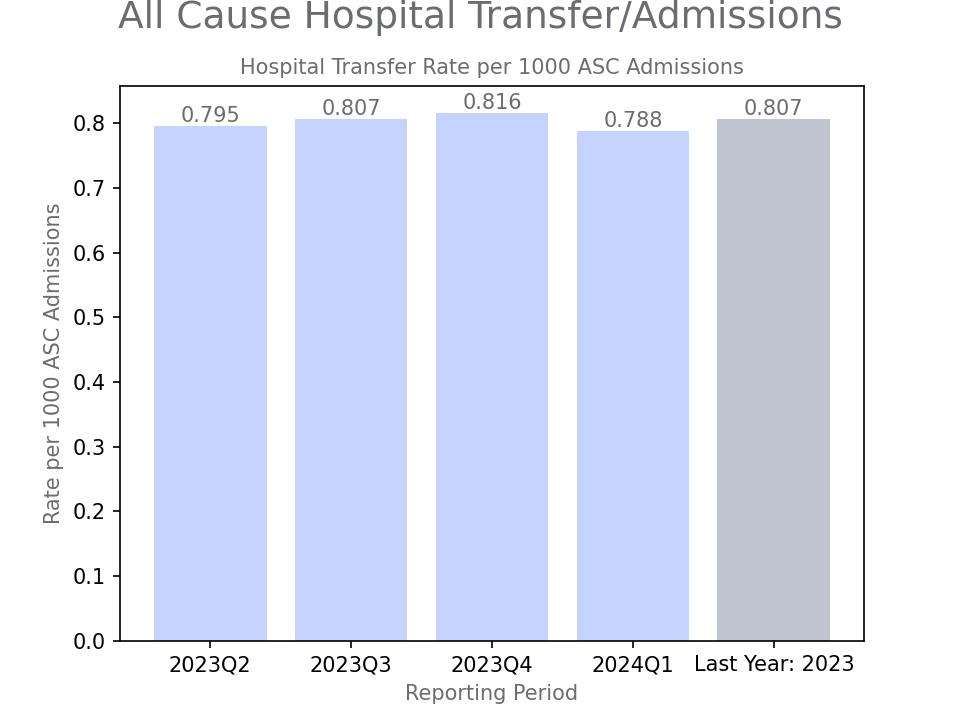
Hospital transfers
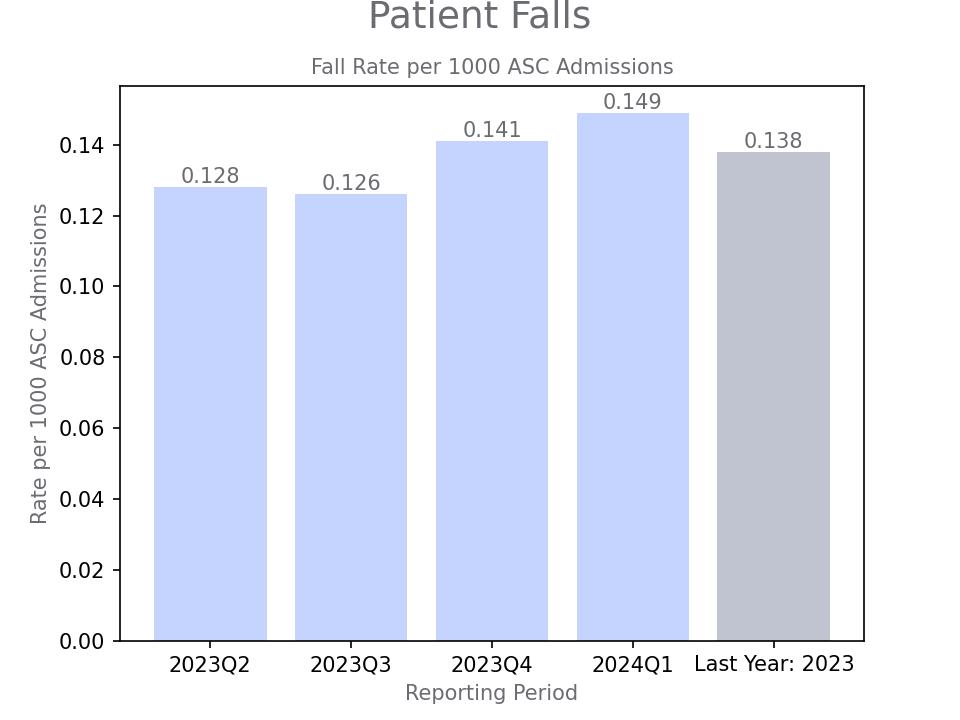
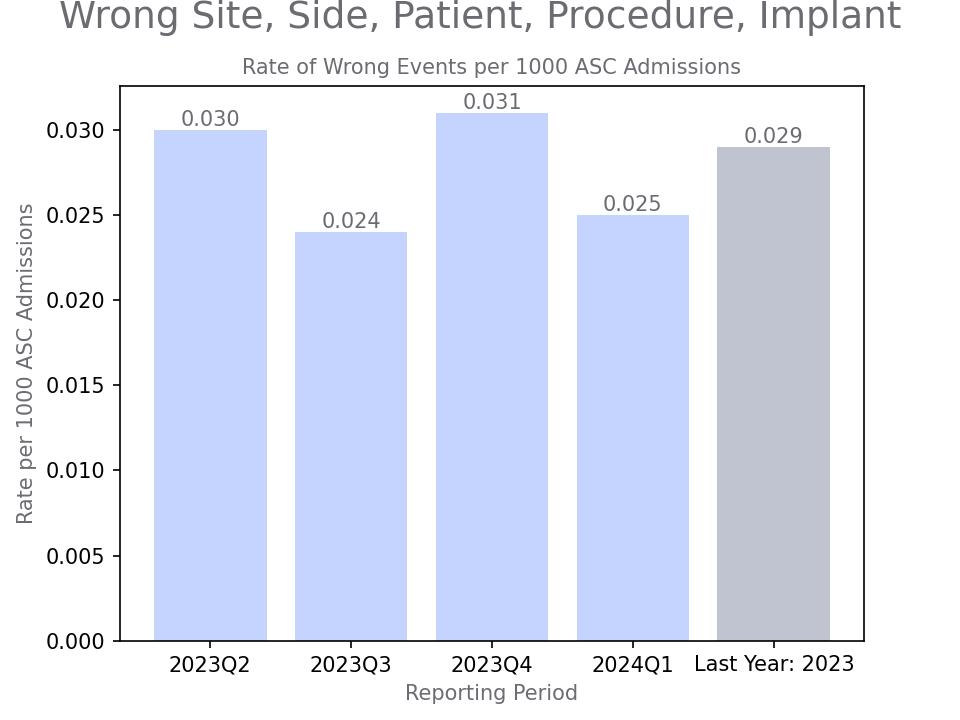
Wrong site, wrong side, wrong patient, wrong procedure, wrong implant
Benchmarking Data


Regularly Recurring Operations: Daily/Weekly
Perform Audit of Medication Cabinets
Best Practices
The current methods used by most surgery centers for managing narcotics (double-locked cabinets and paper logs) present numerous vulnerabilities and create an environment that is highly susceptible to drug diversion. Due to these standard practices, an estimated 95% of drug diversion incidents go undetected [Source: MedServe].
To prevent drug diversion at your surgery center, leadership will need to conduct mock investigations to prepare staff, implement rigorous documentation processes, foster a culture where staff feel safe reporting suspicious activities, and require dual verification every step of the way. Digital narcotic cabinets offer the most secure solution for centers able to afford technology.
Regular auditing of medication cabinets is also essential to prevent drug diversion. Conducting audits at regular intervals, such as weekly or monthly, establishes a routine check that keeps discrepancies in check. Additionally, performing unannounced spot checks helps detect any irregularities between scheduled audits. By following these best practices, surgery centers can significantly reduce the risk of drug diversion and promote a safer environment for patients and staff.
Key Process Steps
Develop a comprehensive audit plan, including frequency and assigned personnel.
Compare current inventory with documented records to identify discrepancies.
Review access logs.
Investigate discrepancies immediately, documenting findings and actions taken.
Compile audit findings into a report for leadership and relevant committees.
Implement corrective actions and re-audit as necessary.
Key Performance Indicators
% of audits with discrepancies
Unauthorized access attempts per month


Regularly Recurring Operations
- Review Profitability Reports
- Review Accreditation, Compliance, and Credentialing Statuses
- Perform Emergency Preparedness Drills
- Perform Marketing Review
- Manage Payroll
- Perform Financial Review
- Hold Quarterly Board Meetings
- Perform Infection Control Audits
- Review Patient Satisfaction Survey Results
- Hold Planning and Business Reviews with Vendors
- Offer Staff Training and Education
- Perform Required QAPI Studies


Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly
Review Profitability Reports
Best Practices
After patient outcomes, profitability is the second highest priority for surgery centers.
Regularly reviewing profitability reports is essential for understanding the center’s financial performance and making informed decisions to enhance profitability. Doing so monthly allows timely detection of any issues and enables the center to implement changes quickly.
As a best practice, your financial and administrative staff should leverage advanced financial analytics tools and practice management software, such as HST, to aggregate and analyze data from various sources, identify trends, and generate actionable insights. In addition, they should also implement a standardized reporting structure that includes key financial indicators, such as revenue, expenses, and net income, as well as detailed breakdowns of these indicators.
Proper attention to each step of the process will ensure that the surgery center can identify and address any areas for improvement, maintain profitability, and provide financial stability.
Key Process Steps
Using technology built into your scheduling and practice management systems, prepare the profitability report for the month.
Review the profitability report with multidisciplinary teams, including the board of directors, to discuss the findings and identify potential root causes of any issues.
Identify areas for improvement based on the review and analysis. This may involve pinpointing areas where expenses can be reduced or flagging certain case attributes to avoid in the future.
Implement any necessary changes based on the review and analysis.
Monitor the impact of the changes implemented on profitability
Key Performance Indicators
Expected profitability per case vs actual profitability
Net revenue by surgeon or specialty
Net revenue by payer
Net revenue
Monthly case volume
Benchmarking Data


Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly
Review Accreditation, Compliance, and Credentialing Statuses
Best Practices
Regularly reviewing accreditation, compliance, and credentialing statuses is essential for ensuring the highest standards of patient care and safety, maintaining operational integrity, and mitigating risk.
First and foremost – it is recommended that you maintain a centralized electronic database of all accreditation, compliance, and credentialing documents and statuses. Without software, such as HST, that utilizes automated tracking and alerts for upcoming deadlines, this process will be burdensome and a major headache with all the moving parts. You should involve key stakeholders, including clinical staff, administrative staff, and leadership, in the review process to ensure comprehensive evaluation and adherence to standards. Lastly, make sure to conduct regular internal audits to assess the center’s adherence to various accreditation, compliance, and credentialing requirements. This includes but is not limited to CMS, JCAHO, AAAHC, The No Surprises Act, state licensing, maintaining physician credentials and privileges, and more.
Key Process Steps
Review the status of accreditation, compliance, and credentialing. This includes checking for any upcoming deadlines, requirements that need to be addressed, or any changes in regulations or standards.
Compare the status with the required standards. Identify any gaps or areas for improvement.
Discuss the findings with key stakeholders, including clinical staff, administrative staff, and leadership. Collaborate to develop action plans to address any identified gaps or areas for improvement.
Implement any necessary changes based on the review and discussion. This may involve updating policies and procedures, conducting additional training, or submitting required documents to accreditation or regulatory bodies.
Update the centralized database with any new documents or changes in status.
Monitor the implementation of changes and follow up on any pending items or deadlines.
Key Performance Indicators
Accreditation renewal rate
Compliance audit pass rate
Incidents of non-compliance
Physician re-credentialing rate


Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly
Perform Emergency Preparedness Drills
Best Practices
Emergency preparedness involves planning, organizing, and training for unexpected events that could disrupt the center’s normal operation or pose a risk to the safety of patients, staff, or visitors. Performing emergency preparedness drills monthly is essential to ensure that all staff are familiar with the emergency procedures, can respond quickly and effectively in an emergency, and can identify and address any areas for improvement in the emergency response plan.
Creating a comprehensive emergency response plan for different scenarios (like fires, power outages, medical emergencies, or active shooters) is key to effective preparedness. Involving all staff, planning for EHR downtime, simulating real-life scenarios, regularly updating the plan, and documenting drills and debriefings are essential steps in ensuring readiness.
Key Process Steps
At the beginning of the year, develop a calendar with your scheduled drills so that you do not miss any that are required by law or accrediting bodies.
Plan the drill in advance. Decide on the type of emergency to be simulated, the date and time of the drill, and the staff members who will participate.
Communicate the plan for the drill to all staff members who will be participating. Make sure they understand the purpose of the drill, what is expected of them, and how the drill will be conducted.
Conduct the drill as planned. Monitor the performance of the staff and the effectiveness of the emergency response plan.
Conduct a debriefing session after the drill. Discuss what went well, what didn’t, and what can be improved.
Update the emergency response plan based on the findings of the drill and the feedback received during the debriefing session.
Document the drill, including the scenario simulated, the staff members who participated, the findings of the drill, and any changes made to the emergency response plan.
Key Performance Indicators
Frequency of drills
Staff completion rate
Drill completion time


Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly
Perform Marketing Review
Best Practices
Surgery centers are often reluctant to lean into marketing because patients are just continuously referred to them, so what does marketing matter? But marketing is about more than just attracting new patients. It’s about building and maintaining relationships with existing patients, the local community, and other potential partners. A good marketing plan includes strategies for keeping patients engaged and satisfied with the services provided, which can lead to repeat business and referrals.
There are plenty of affordable and talented marketing agencies or consultants who could help you develop a simple marketing plan to help build your brand, design your website, establish a solid online presence, create effective messaging, work with local media, drive revenue, and increase case volume.
A well-thought-out marketing plan with clear objectives will help give a competitive advantage, manage reputation, and succeed long-term.
Key Process Steps
Gather current intel about any current marketing efforts, including social media channels, advertisements, letterhead, logo, colors, web analytics, etc., and any results achieved.
Analyze the data to assess the effectiveness of the marketing efforts. This involves comparing the results achieved against the marketing objectives set and the KPIs monitored.
Develop a marketing budget, including website maintenance and updates, online and offline advertising, printed marketing materials, and marketing consultants.
Develop a marketing plan, including clear objectives, the approved budget, a calendar of activities, key stakeholders, and more.
Review objectives on a monthly basis, potentially reallocating the budget, adjusting the marketing channels used, or revising the messaging.
Key Performance Indicators
Website traffic
Social followers
Website conversions
Patient reviews on Google, other sites
Benchmarking Data


Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly
Manage Payroll
Best Practices
Payroll management is a critical function for any organization, including surgery centers. It involves calculating employee salaries, withholding taxes and deductions, paying employee salaries, and filing taxes with government agencies. Completing payroll accurately and on time is essential to maintain employee satisfaction, comply with legal requirements, and maintain the center’s financial stability.
For maximum success, use specialized payroll software to automate the payroll process, reduce manual errors, and guarantee compliance with tax laws and regulations. Use software to maintain accurate and up-to-date employee records, including hours worked, overtime, and vacation days. Lastly, stay up-to-date with the latest legal and tax requirements to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
Key Process Steps
Collect all necessary employee data, including hours worked, overtime, vacation days, and any other relevant information.
Use the payroll software to calculate the payroll. This includes calculating gross pay, deductions, and net pay for each employee.
Process the payroll using software. This includes generating paychecks or direct deposits for employees, withholding taxes, and paying any other deductions.
File the necessary taxes with the relevant government agencies.
Document the entire payroll process, including all data collected, calculations made, and payments processed. This will help in case of any audits or discrepancies in the future.


Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly
Perform Financial Review
Best Practices
Financial management, planning, and budgeting are essential functions for the successful operation of a surgery center. They involve forecasting revenue and expenses, creating a budget, monitoring financial performance, and making necessary adjustments to ensure the financial stability and sustainability of the center. Reviewing these functions monthly allows the center to promptly identify and address any financial issues and make informed decisions supporting its overall objectives.
Using specialized practice management software, such as HST, to streamline the planning, budgeting, and monitoring process will ensure the accuracy and completeness of the financial picture and remove as much manual input and analysis as possible. Involving key stakeholders from the beginning, such as your board of directors, management groups, and administrative staff, will also make sure everyone has alignment and buy-in for the plan/budget. The last thing anyone wants during a board meeting or monthly financial review is for surprises to pop up!
Key Process Steps
Prepare the financial data for the review. This includes gathering data on actual revenue and expenses for the month and comparing it to the budgeted amounts.
Analyze the previous month’s financial performance and cash flow projections for the upcoming month, quarter, and year. This includes identifying any trends or issues that need to be addressed.
Based on the analysis, make any necessary adjustments to the financial plan and budget. This may involve revising revenue or expense forecasts, reallocating resources, or identifying cost-saving opportunities.
Review the financial performance, plan, and budget with key stakeholders.
Document the review, including the analysis conducted, any adjustments made to the plan and budget, and any decisions made during the review with key stakeholders.
Implement any adjustments made to the financial plan and budget. This may involve communicating changes to relevant staff, updating financial management software, or taking other actions as necessary.
Key Performance Indicators
EBITDA
Revenue growth rate
Budget variance
Cash flow
Budget preparation timeline
Benchmarking Data
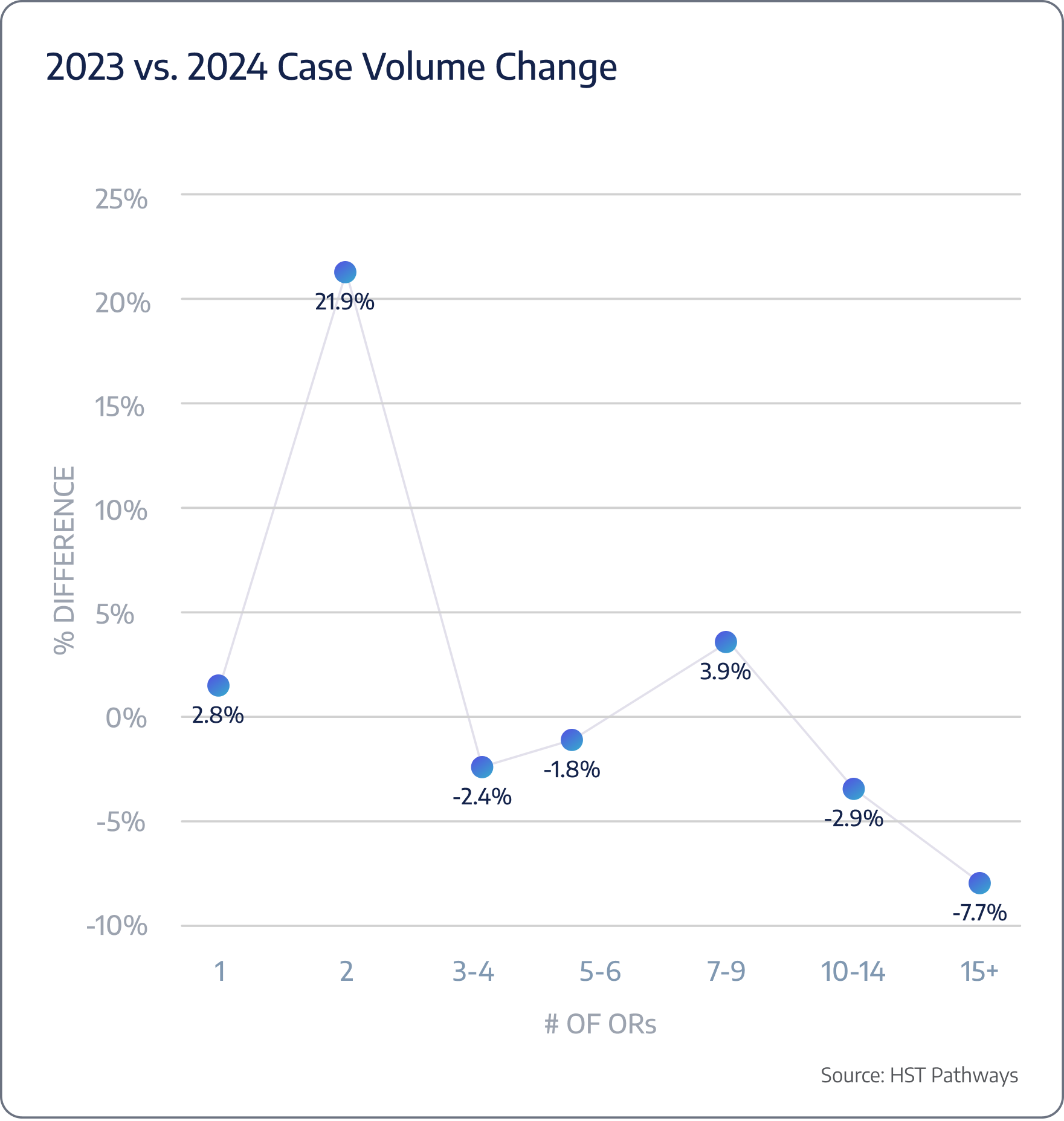
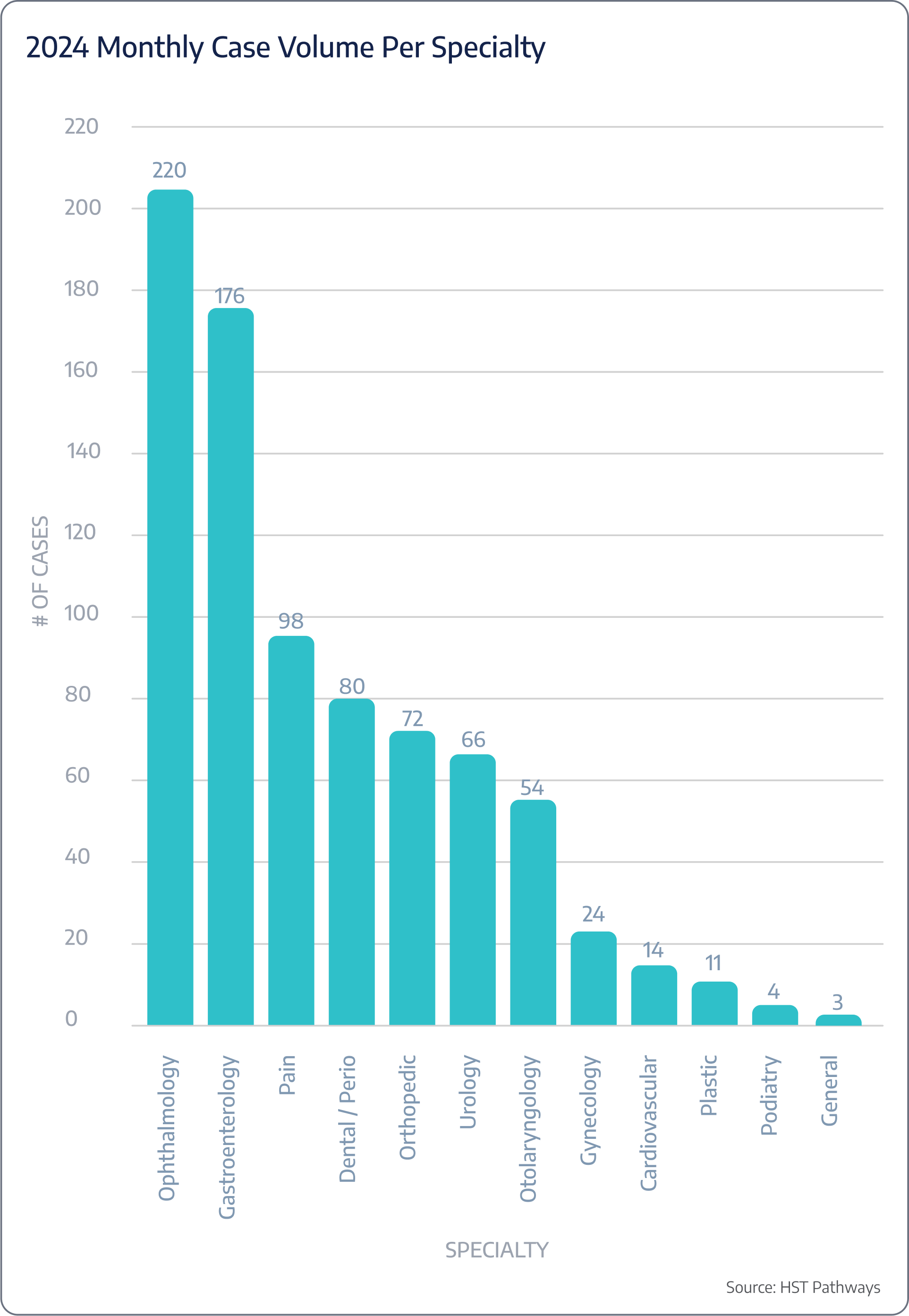
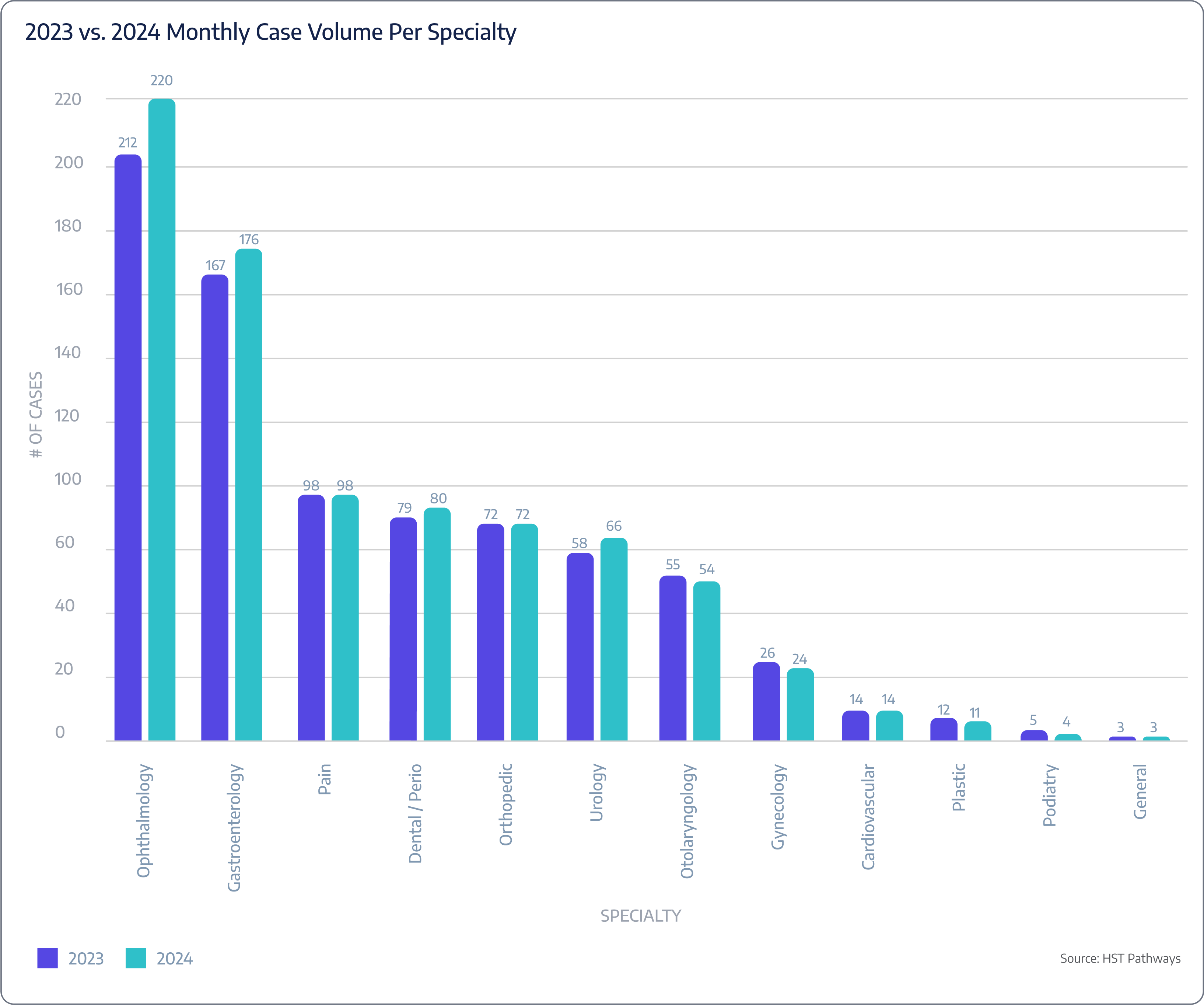


Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly
Hold Quarterly Board Meetings
Best Practices
Board meetings are an essential aspect of the governance of surgery centers. They provide a forum for the board of directors to discuss strategic issues, review financial and operational performance, ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, and make important decisions that will impact the center’s future. Holding board meetings on a quarterly basis allows the board to stay informed about the center’s activities, address any issues promptly, and provide the necessary guidance and support to the center’s management team. It is recommended that you schedule your meetings 2-3 weeks after the quarter ends, do your best to keep them under an hour, and offer the option to join in person or virtually.
While board meetings might not be the most exciting part of running a surgery center, you can make them most effective by preparing a detailed agenda, utilizing consent agenda and action(s) without meetings, and building in engagement. It is also critical that you record detailed minutes of the board meeting, including the discussions, decisions made, and any actions to be taken, as accreditation bodies will be reading these in detail.
Key Process Steps
Prepare a detailed agenda for the board meeting and distribute it, along with any supporting documents, to the board members in advance of the meeting.
Make any necessary logistical arrangements for the meeting, such as securing a meeting location or setting up a video conference.
Conduct the board meeting according to the agenda. Encourage board members to ask questions, express their opinions, and engage in constructive discussions. Record detailed minutes of the meeting.
Distribute the minutes of the board meeting to all board members for their review and approval. Ensure that any action items from the meeting are followed up on in a timely manner and that the board is kept informed of the progress.
Key Performance Indicators
Attendance rates
Board diversity
Your Repeatable Agenda Should Include
Call to Order
Changes in the Agenda
Approval of Previous Minutes
Action(s) Without Meeting
Consent Agenda
Quality/Risk Management
Regulatory Compliance
Managed Care Report
Financial Review
Revenue Cycle Management
Capital Expenditure
Staffing Updates & Human Resources
Other Business / Open Discussion


Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly
Perform Infection Control Audits
Best Practices
Infection control is critical to patient safety and quality of care in surgery centers. Regular audits of infection control practices and procedures are necessary to obtain compliance with established standards and guidelines, identify potential areas of improvement, and prevent avoidable infections. These audits involve a systematic review of the policies, procedures, and practices related to infection prevention and control within the surgery center.
A comprehensive infection control audit typically assesses hand hygiene and personal protective equipment, injection safety and medication handling, equipment reprocessing, environmental cleaning, and handling of blood glucose monitoring equipment. You will need to develop an audit plan, use standardized tools, such as HST, and checklists to guarantee consistency, involve trained auditors, and include a mix of observation, interview, and documentation review to make sure you see a holistic view. To help get started or review your current processes, CMS offers an ASC infection control audit tool on its website, available for download.
Key Process Steps
Develop a comprehensive audit plan that includes the scope of the audit, the criteria to be audited, the methodology to be used, and the schedule for the audit.
Conduct the audit according to the audit plan. Use standardized tools and checklists to ensure a consistent and thorough approach. Include a mix of observation, interview, and document review in the audit methodology.
Analyze the audit findings to identify any areas of non-compliance or areas for improvement.
Follow up on items identified during the audit in a timely manner and make sure the necessary changes are implemented.
Key Performance Indicators
Infection rates


Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly
Review Patient Satisfaction Survey Results
Best Practices
Regularly reviewing patient satisfaction survey results is crucial for understanding the patient’s perspective, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing necessary changes to enhance the patient experience. Conducting these reviews monthly or quarterly allows the surgery center to respond promptly to any issues raised by the patients and to track progress over time.
To turn your satisfaction scores into actionable improvements, you must use software to collect and aggregate patient feedback on your behalf so you can quickly identify trends, areas of strength, and areas for improvement. Your patient satisfaction results can also inspire your next QAPI study, and your software will make it incredibly simple for you to collect and analyze results from one period versus another.
Reminder: The OAS CAHPS survey will be required and linked to reimbursement in CY 2025 for ASCs. If an ASC does not conduct and submit OAS CAHPS as part of the quality reporting requirement, they will receive a reduction of 2.0 percentage points in their annual fee schedule update.
Key Process Steps
Collect survey data from patients on a continuous basis using a standardized survey instrument. Using automated texts or emails will increase your response rates and turnaround time.
Analyze your results using color-coded trend analysis, automated alerts and callouts, graphical dashboards, etc.
Share the results of the survey analysis with staff and stakeholders, including the board of directors.
Develop action plans to address any areas for improvement identified in the survey analysis.
Implement the action plans developed and monitor progress towards the goals set.
Review the effectiveness of the action plans implemented and adjust them as necessary based on feedback and ongoing monitoring.
Key Performance Indicators
Patient response rates
Net promoter score


Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly
Hold Planning and Business Reviews with Vendors
Best Practices
Effective quarterly planning and business reviews with vendors are key to smooth operations, cost efficiency, and no last-minute surprises. Start by maintaining consistent and open communication with all your vendors; this helps build strong relationships and keeps everyone on the same page. Setting clear, mutual goals and expectations for each quarter is also essential. When everyone knows what they’re working towards, collaboration is much smoother.
Another important step is regularly evaluating vendor performance against set benchmarks. Doing so helps ensure that your vendors meet your standards and allows you to address any issues early on. If your supply chain vendor expects disruptions or your anesthesia group expects shortages, being prepared for the unexpected is crucial. Lastly, keeping all contractual terms and obligations transparent and up to date helps avoid misunderstandings and will lead to a smooth working relationship.
Key Process Steps
Identify every vendor and your internal and external primary point of contact for each.
Reach out to each primary point of contact to schedule a standing, quarterly meeting.
Conduct quarterly business review meetings (QBRs) to discuss performance, challenges, and upcoming needs. Prepare relevant performance data and feedback to promote transparency or ask the vendor to do so.
Collaborate with vendors to develop actionable plans to address any issues or improvements.
Document all meeting minutes, agreed actions, and timelines.
Key Performance Indicators
# of contracted vendors (less is usually better)
Budgeted vs. actual costs


Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly
Offer Staff Training and Education
Best Practices
Continuous staff training and education are essential for maintaining high standards of care, staff satisfaction, and staff retention. Start by regularly assessing your staff’s training needs based on performance reviews and industry changes to identify areas where additional training is needed. Consider the requirements for earning AEUs (Accreditation Education Units) or CEs (Continuing Education credits) and encourage your staff to pursue these through accessible options such as the ASCA conference, state association events, or relevant webinars. Implementing cross-training programs is also beneficial, as it not only enhances workforce flexibility and coverage but also helps prevent any single individual from being a critical point of failure by ensuring that multiple team members can competently handle various tasks.
Encouraging staff to obtain relevant certifications and advanced training shows your support for their professional growth. Use interactive and diverse training methods like workshops, simulations, and online modules to keep the learning process engaging and effective. Additionally, cross-training ensures that staff can step into different roles as needed, promoting a more resilient and adaptable team. Finally, establish a system for staff to provide feedback on training programs. Following these best practices can create a robust training and education program that benefits your staff and the surgery center.
Key Process Steps
Identify training needs through performance evaluations, feedback, and trends.
Develop a comprehensive training plan that includes objectives and timelines.
Choose appropriate training programs and certifications.
Conduct training sessions using a mix of instructional methods.
Schedule regular follow-up sessions to reinforce learning and address any gaps.
Key Performance Indicators
Training completion rate
Staff satisfaction
# of staff that are not cross trained


Regularly Recurring Operations: Monthly/Quarterly
Perform Required QAPI Studies
Best Practices
Quality Assurance and Performance Improvement (QAPI) studies are essential for continuous improvement. To be effective, these studies should have a comprehensive scope covering all aspects of care and operations, including clinical outcomes, patient safety, and administrative efficiency. Using a data-driven approach is crucial.
Engaging a multidisciplinary team that includes clinical, administrative, and support staff will help offer diverse perspectives and more thorough analysis. Conduct regular monitoring through quarterly reviews to stay on top of compliance and identify areas for improvement. Finally, transparent communication is key. Share your findings and improvement plans with all staff to foster a culture of transparency and accountability.
Key Process Steps
Define the scope, objectives, and methodology of the QAPI study.
Gather data from relevant sources, focusing on accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Analyze the collected data to identify trends, gaps, and areas for improvement.
Develop action plans to address identified issues.
Execute the action plans, keeping all stakeholders informed and involved.
Review the effectiveness of implemented actions and document outcomes.
Compile a comprehensive report with the study’s findings, actions, and results.
10 QAPI Ideas
Surgical Site Infections
Hospital Transfer Times
Hand Hygiene Compliance
On-Time Starts
Falls Prevention
Same Day Cancellations by Surgeons or Anesthesia
Policy Adherence for Chart Access
No Surprises Act Compliance
OR Turnover Times
Interpreter Utilization and Effectiveness


Regularly Recurring Operations
- Chargemaster Analysis
- Inventory Check
- Payor Contract Review
- Performance Management Reviews
- Prepare Annual Budget
- Vendor Contract Review
- Renew Licenses and Certifications
- Review Policies and Procedures
- Review Legal Compliance


Regularly Recurring Operations: Annual
Chargemaster Analysis
Best Practices
The chargemaster serves as a comprehensive listing of all billable services and items the surgery center provides. It plays a pivotal role in revenue cycle management, serving as the foundation for billing and coding processes. Annual updates ensure that billing remains compliant with current regulations, that all charges reflect the most recent costs and negotiated payer rates, and that the facility remains competitive and financially sustainable. Proper oversight and diligence in this process are paramount to ensuring the surgery center captures all revenue rightfully owed while avoiding potential compliance pitfalls.
When reviewing your chargemaster, most will build it based on a percentage of Medicare’s reimbursement. You can perform the analysis yourself using a tool that is as simple (and free!) as Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets. However, leveraging technology solutions, like automated chargemaster management systems, such as HST, can help save time and reduce errors.
Key Process Steps
Start with a thorough review of the current charge master, noting any items that seem outdated, incorrect, or missing.
Review updates from CMS and other regulatory bodies to identify any required changes to coding, pricing, or billing practices.
Learn your contracts inside and out, as there might be increase limitations and other requirements.
Analyze the current market rates, payer contract terms, and the center’s own cost structures to adjust pricing as necessary.
Before finalizing changes, test the updated charge master in your billing system to validate that all codes and charges are processed correctly.
Conduct training sessions to inform and educate relevant staff about changes to the charge master and its implications.
Key Performance Indicators
% of the cases you capture 100% reimbursement for (hint: if it’s all of them, you are likely undercharging!)
Time it takes to perform an audit
Accuracy of audit


Regularly Recurring Operations: Annual
Inventory Check
Best Practices
By conducting an annual inventory check, centers ensure they can maintain consistent patient care, optimize financial management, and streamline daily operations. A thorough inventory evaluation reduces the risk of overstocking or stockouts, enables accurate budgeting, and helps centers stay prepared for routine and unexpected scenarios. Furthermore, understanding inventory levels and usage trends can lead to better decision-making, reduced waste, and enhanced patient care.
Inventory management software, such as HST, can provide historical data to help you make informed decisions. The software can also track current inventory against your minimum and maximum stock levels to guide reorder points and prevent stockouts or over-purchases. While supply chain issues are certainly better than they were immediately following COVID-19 disruptions, fostering good relationships with suppliers and having various supplies to choose from will help with better purchase deals and timely delivery.
Key Process Steps
Gather previous records, decide on a date, and inform relevant staff. Ensure that operations can either be paused or managed around the inventory process.
Prepare tools and resources, such as inventory sheets, scanners, or dedicated software.
Assign teams or individuals to specific areas or categories.
Count every item on shelves, in storage areas, and in active-use zones. Document quantities and, where applicable, expiration dates.
Enter the physical count results into the inventory management system or database.
Match physical counts against recorded levels. Investigate discrepancies to determine if they are due to theft, loss, or clerical errors.
Examine inventory trends, consumption rates, and wastage. Adjust par levels and ordering practices as needed.
Share the results with management or leadership for insights, feedback, and future planning.
Based on the findings, refine or create inventory management guidelines.
Key Performance Indicators
# expired/unusable items
# of discrepancies between expected vs actual


Regularly Recurring Operations: Annual
Payor Contract Review
Best Practices
Payor contracts are arguably at the center of the revenue cycle process. These contracts, which determine reimbursement rates and terms for services rendered, significantly influence a surgery center’s financial health and viability. An annual review and potential renegotiation of these contracts enable centers to ensure that they receive fair compensation for their services, adapt to changing market conditions, and continue to offer top-tier care to patients. Beyond financial implications, these contracts also impact operational protocols, patient access, and the center’s relationship with insurance providers.
To get the best possible rates, your financial team must analyze and track the performance of your current contracts in real-world scenarios to determine if they are meeting expectations. Gathering external intel, such as industry standards, reimbursement trends, and regional benchmarks, will help to understand where your contracts stand in the larger market. Lastly, there is still a benefit to cultivating a rapport with payor representatives, which can lead to more collaborative and transparent negotiations, so make sure to put a little extra time into building those relationships!
Key Process Steps
Begin by collecting all current payor contracts and organizing them for review.
Evaluate the performance of each contract by looking at reimbursements, denials, delays, etc.
Investigate current industry standards and reimbursement rates, especially for similar procedures and in comparable regions.
Determine what you aim to achieve with the renegotiation, whether it’s higher reimbursement rates, better terms, or other specific goals.
Reach out to payor representatives to initiate the renegotiation process. Express your concerns, present your data, and share your objectives.
Before finalizing, have the renegotiated contract reviewed by legal counsel to ensure its terms are clear, enforceable, and in the center’s best interests.
Once both parties agree and the contract is signed, communicate the new terms to all relevant staff members and update any systems or processes as necessary.


Regularly Recurring Operations: Annual
Performance Management Reviews
Best Practices
Performance Management Reviews (PMRs) help recognize and reward good performance, identify and address performance issues or areas of improvement, support professional growth and development, and enhance communication between managers and employees. When done correctly, PMRs can be a powerful tool to motivate employees, drive productivity, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. To be effective, all parties must perceive the process as fair, transparent, and constructive.
The most successful PMRs set clear objectives, maintain consistency, provide constructive feedback, and encourage open dialogue. Making the review process a two-way conversation where employees can share insights, concerns, and aspirations is key. PMRs can help with staff satisfaction, retention, and recruitment.
Key Process Steps
Gather data related to the employee’s performance, including previous reviews, patient feedback, peer reviews, and any relevant metrics or KPIs.
Set a specific date and time for the review, ensuring both the reviewer and employee can attend without distractions.
Go over the employee’s achievements, areas of improvement, and any discrepancies between expected and actual performance.
Ask employees for their views on their performance, their role, and any challenges they face.
Based on the discussion, set targets and objectives for the upcoming year and suggest any training or skill development programs.
Record the details of the review, including observations, feedback, and goals.
Key Performance Indicators
Staff net promoter score
Retention rates
Promotion rates


Regularly Recurring Operations: Annual
Prepare Annual Budget
Best Practices
A well-prepared budget is more than just numbers on a page – it’s a roadmap, guiding centers in their financial decisions and providing a tool to measure financial health. It forecasts potential challenges, optimizes resource allocation, and establishes a clear financial trajectory that aligns with the center’s goals. In essence, the annual budget ensures that surgery centers can continue providing premier care without compromising operational viability.
The annual budget is typically presented to the board in October for the following year. While preparing, administrators should engage key stakeholders from various departments, review past budgets and financial outcomes, identify essential expenses, and account for upcoming projects, expansions, or other initiatives that may impact the budget. Remember to allocate funds for unforeseen expenses or emergencies.
Key Process Steps
Compile data from the previous year, including revenue, expenses, patient volumes, and any other relevant financial metrics.
Organize discussions with department heads and key personnel to gather input on anticipated needs, challenges, and growth opportunities.
Create a preliminary budget detailing projected revenues and expenses.
Subject the draft budget to rigorous scrutiny, identifying potential inefficiencies or areas that may have been overlooked.
Present the budget to the governing board and physician owners for review and approval.
Once approved, distribute the budget to all relevant departments, ensuring they understand their financial parameters.
Track actual revenues and expenses against the budgeted amounts, identifying any discrepancies.
Key Performance Indicators
Budget variance
Year-over-year growth
Net profit margin
EBITDA


Regularly Recurring Operations: Annual
Vendor Contract Review
Best Practices
Vendor contracts form the backbone of many essential services and supplies that surgery centers rely on daily. Regularly revisiting your vendor agreements ensures that you receive the best value and competitive pricing, make sure you’re not spending unnecessary budget, maintain compliance with regulatory standards, and align vendor relationships with the center’s strategic goals.
Leading surgery centers use vendor management software, such as HST, typically built into your practice management software, to have a centralized repository for all vendor-related information, ensuring easy access and management of contracts, contact details, pricing, and historical data. The software will also help you mitigate risk, identify opportunities for bulk purchases, automate manual processes, and provide real-time analytics and reporting.
Key Process Steps
Create a comprehensive list of all active vendor contracts within the center (ideally within your vendor management software).
Rank contracts based on their value, impact on operations, and upcoming expiration dates.
Assess the performance of each vendor against the contract’s stipulations and any additional criteria that are important to you.
Gather input from staff and departments that frequently interact with the vendor or use their services/products.
Evaluate current contract terms against market standards to identify potential areas of renegotiation.
Approach vendors with findings and open discussions for potential renegotiations, aiming for improved terms or pricing.
Revise contract terms as needed, ensuring all changes are documented.
Submit the revised contracts for appropriate approvals within the center and renew agreements as needed.
Key Performance Indicators
% renewed vs canceled
% change in cost


Regularly Recurring Operations: Annual
Renew Licenses and Certifications
Best Practices
It’s essential for surgery center administrators to be familiar with local, state, and national regulations and to maintain a calendar or tracking system for all required renewals to ensure continuous compliance. Regular renewals of these licenses and certifications affirm the center’s commitment to excellence, protect against legal repercussions, and provide uninterrupted service to patients.
Requirements will vary depending on your exact location. Still, a few examples of licenses and certifications to maintain would be your Certificate of Occupancy, State Department of Health license, accrediting body (JCAHO, AAAHC, AAAASF), CLIA Certificate of Waiver, or DEA license. It’s also important that your administration obtains enough Continuing Education and AEU credits to maintain CASC certifications, if applicable.
This annual process will be much smoother if you use specialized software, such as HST, to notify you of approaching renewal dates or changes in requirements.
Key Process Steps
List all existing licenses and certifications, noting expiration dates and any specific renewal requirements.
Regularly review state and local websites for changes in licensing and certification requirements. Join your state ASC association for updates.
Implement a notification system that alerts the responsible individual or team of upcoming renewal dates well in advance.
Assemble all required documentation, reports, and records necessary for each renewal.
Complete and submit renewal applications, ensuring they are accompanied by any necessary fees and documentation.
Regularly check the status of submitted renewals and respond promptly to any requests for additional information.
Once renewed licenses or certifications are received, store them securely and update digital records.
Key Performance Indicators
Certification renewal rate
% expired


Regularly Recurring Operations: Annual
Review Policies and Procedures
Best Practices
Policies and procedures for a surgery center serve as guiding documents to ensure patient safety, adherence to legal and ethical standards, and standards of operation. Specific policies and procedures can vary based on the type of surgeries performed, the location, and the regulatory environment. Each accrediting body also has its particular standards and requirements, but all strongly emphasize comprehensive, well-documented, and well-implemented policies and procedures.
Your policies and procedures must follow suit as your surgery center evolves and grows. Over the year, you might implement an EHR, adjust pain management protocols, improve your fire safety and evacuation plans, update employee vaccination requirements, or change your family visitation policy. Those are just a few examples of reasons you would need to update your policies and procedures.
Key Process Steps
Begin by collecting all existing P&Ps and creating an index of documents due for review.
Collate recent changes in regulations, industry standards, and within your surgery center that might influence P&Ps.
Engage with different departments and teams to gather feedback on existing P&Ps.
Draft necessary changes or additions to the P&Ps.
Have all necessary parties review (e.g., legal counsel, quality committee, executive committee)
Distribute the updated P&Ps to all relevant staff, ensuring old versions are archived.
Organize sessions to train staff on new or modified P&Ps, ensuring everyone is aware of and understands the changes.
Store the updated P&Ps securely, both digitally and in physical form, ensuring proper version control.
Key Performance Indicators
# of policies/procedures that need to be updated
Staff policy acknowledgement rate


Regularly Recurring Operations: Annual
Review Legal Compliance
Best Practices
Between CMS, OSHA, and all the other state and federal governing bodies, a surgery center must adhere to a growing number of regulations. One of the best practices for achieving legal compliance and staying on top of changes is conducting regular audits. These audits help ensure that the center complies with all relevant laws and regulations.
Another crucial step is regularly reviewing and updating policies to reflect current laws and best practices. It’s also wise to maintain a relationship with legal experts, your state ASC association, and ASCA to stay informed about changes in regulations. Finally, keeping thorough records of compliance activities, audits, and corrective actions guarantees that everything is documented and easily accessible for review.
Key Process Steps
Determine the specific legal requirements applicable to the surgery center, including CMS’ Final Rule, OSHA standards, employment laws, Stark Law, state regulations, etc.
Create a comprehensive compliance plan that outlines policies, procedures, and responsibilities.
Educate staff on relevant laws and compliance procedures.
Schedule and conduct an annual compliance audit to identify any issues.
Develop and implement corrective action plans for any identified compliance issues.
Continuously monitor compliance activities and report findings to leadership.
Key Performance Indicators
Audit completion rate
Staff training completion rate
Incidence rate
Closing Message
Thank you for taking the time to read through our report. We hope you walk away with many insightful and actionable tips to continue providing excellent patient care in a way that is efficient and profitable.
Operating a successful ASC is not the same as it was a decade ago or even five years ago. The industry is undergoing transformative changes, shaped by factors such as regulatory changes, technological advancements, evolving patient expectations, and economic pressures.
Leading surgery centers, with their finger on the pulse of these changes, recognize the emerging challenges. They understand traditional methods will no longer cut it, and a proactive approach is essential. HST Pathways is committed to riding this wave alongside our clients and partners, and we will navigate whatever the future holds together.
About HST Pathways
HST Pathways is the leading provider of a suite of products that have been thoughtfully and clinically designed for the surgery center industry. Our many software offerings provide ASCs with intuitive solutions that cover the entire patient journey and help to unlock revenue, fuel growth, and deliver better care. Build, grow, and run your facility with solutions your entire team will love. See why more than 1,600 clients are choosing HST Pathways by visiting https://www.hstpathways.com/success-stories/.
Data Summary













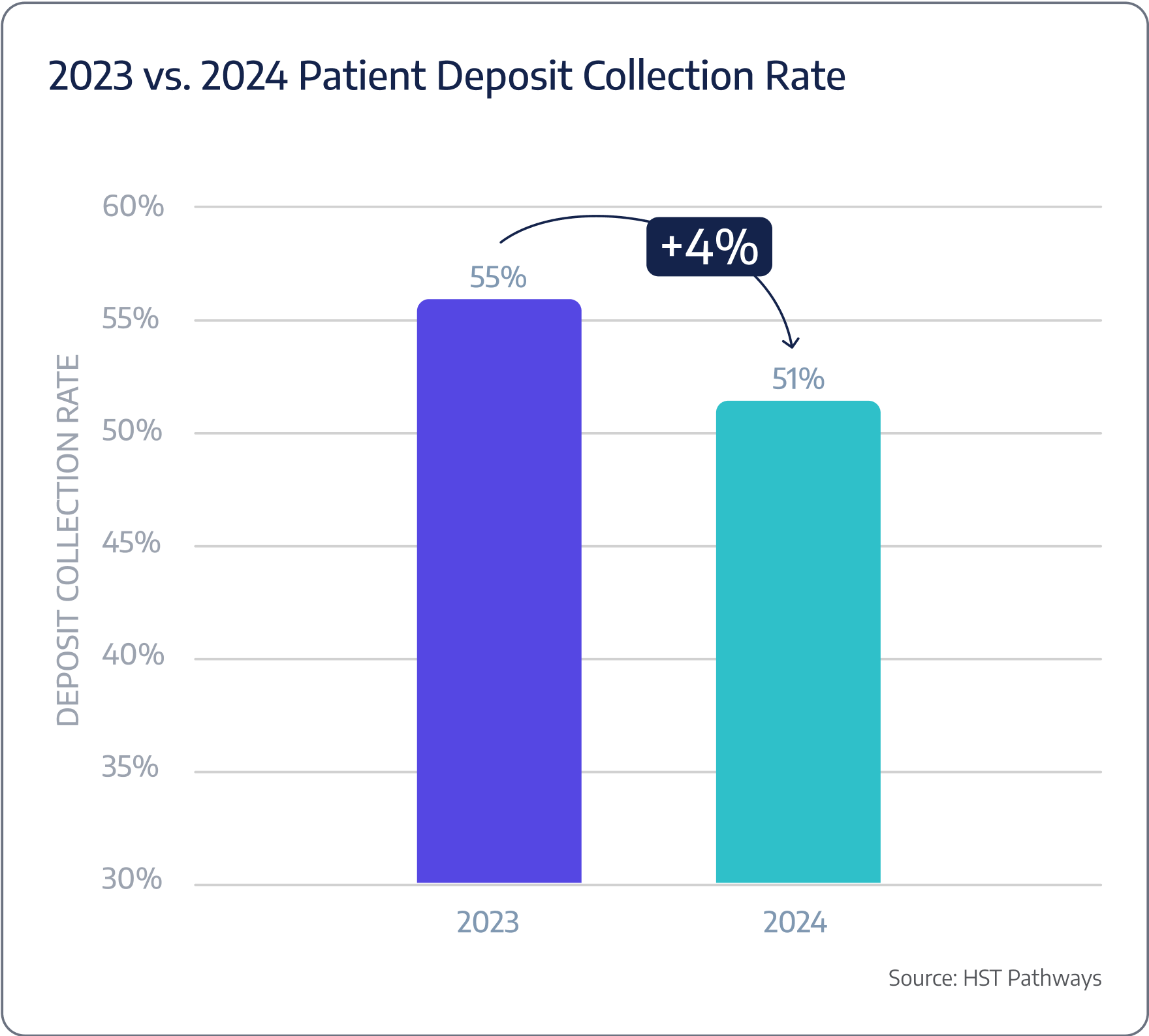















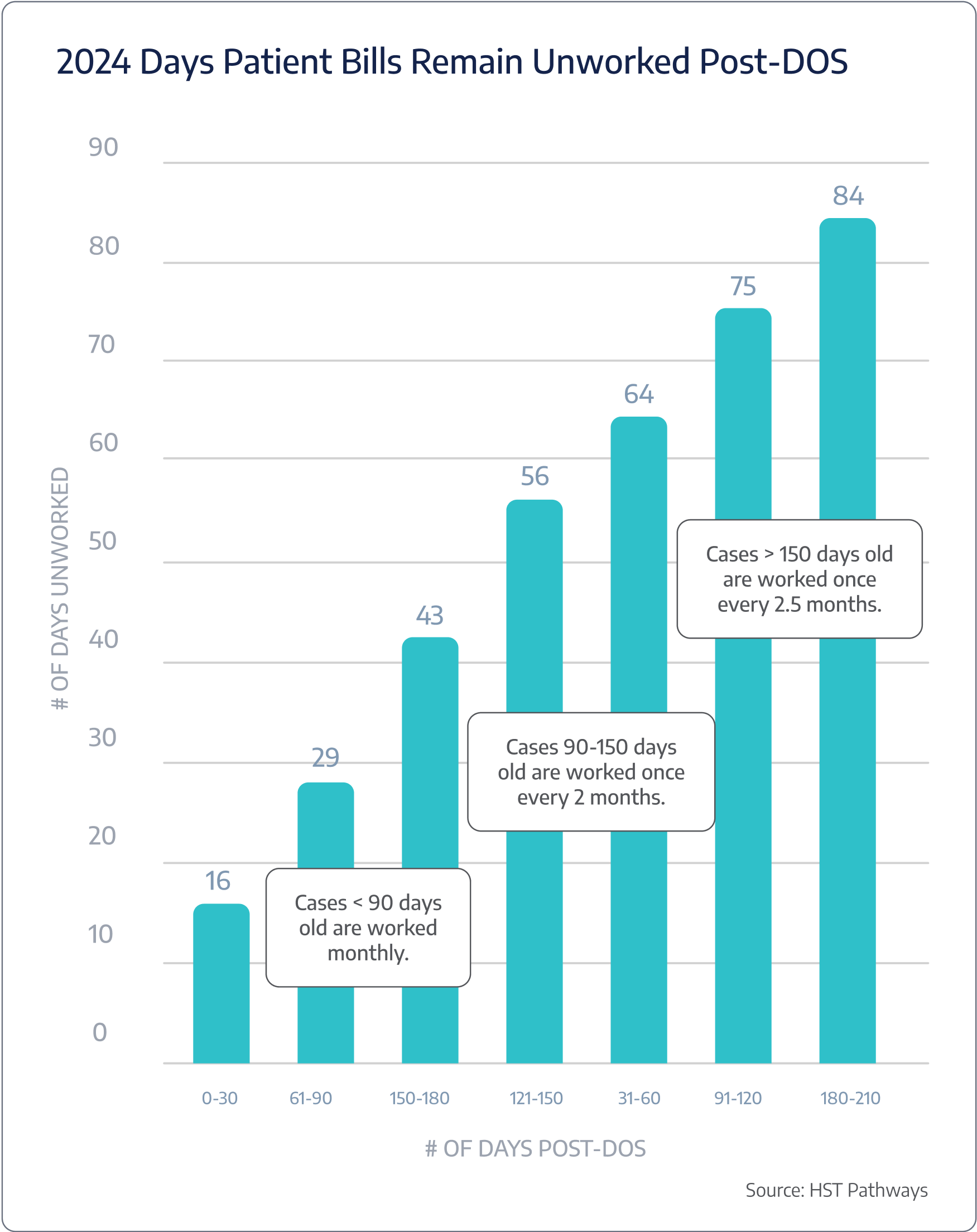


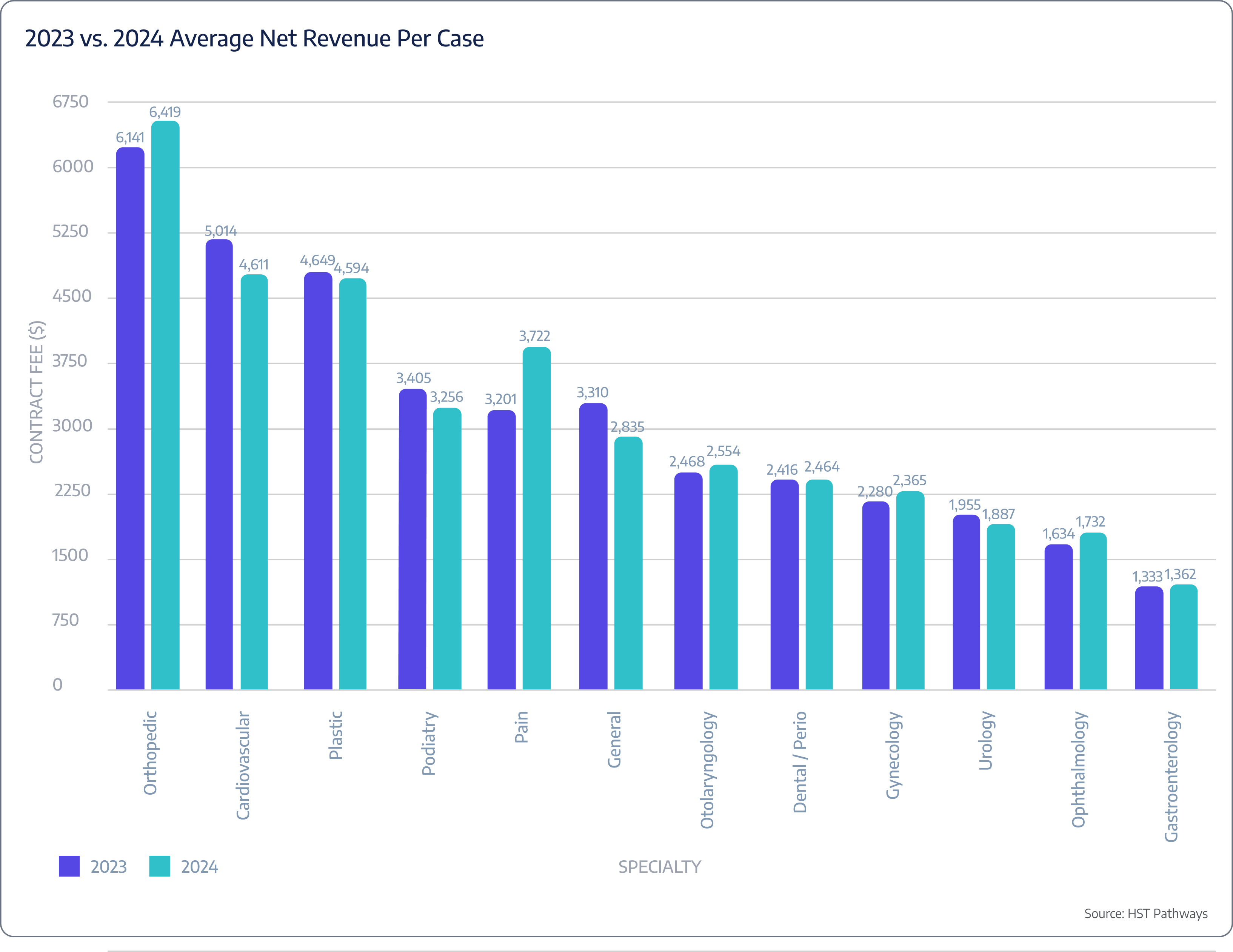



Methodology
This report was developed using a comprehensive approach that included industry research, consultations with clinical experts, data from reputable industry publications, and insights from HST Pathways’ own products.
When benchmarking data was sourced from HST Pathways’ data warehouse, the conclusions for 2024 were based on data from Q1 and Q2 of the year. Year-over-year comparisons included data from Q1-Q4 of 2023 and Q1-Q2 of 2024.
You may notice variations between the 2023 data in the 2023 report and the same data shared in this 2024 report. These differences are due to an extended timeframe and the inclusion of additional client data.
In cases where data was incomplete, missing, or identified as an outlier, those cases and centers were excluded from the analysis. Additionally, to accurately assign a specialty to each case, primary CPT codes were mapped accordingly.